-
摘要:
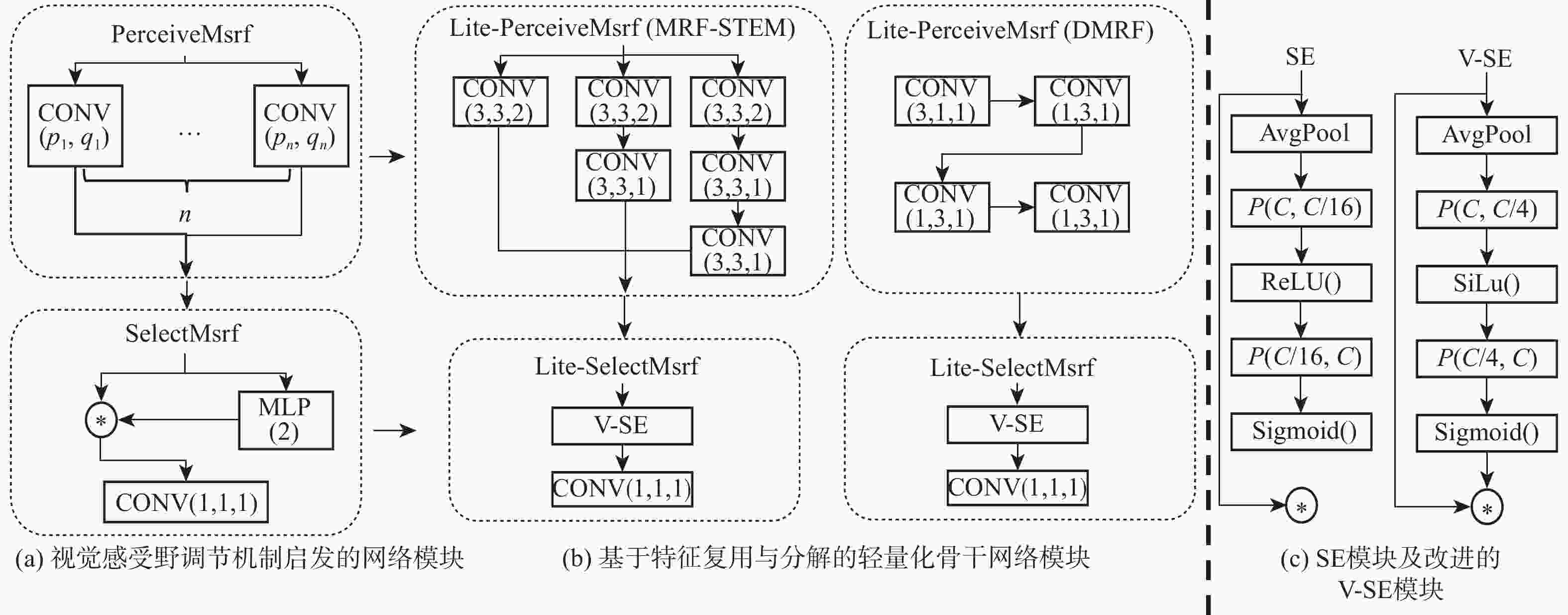
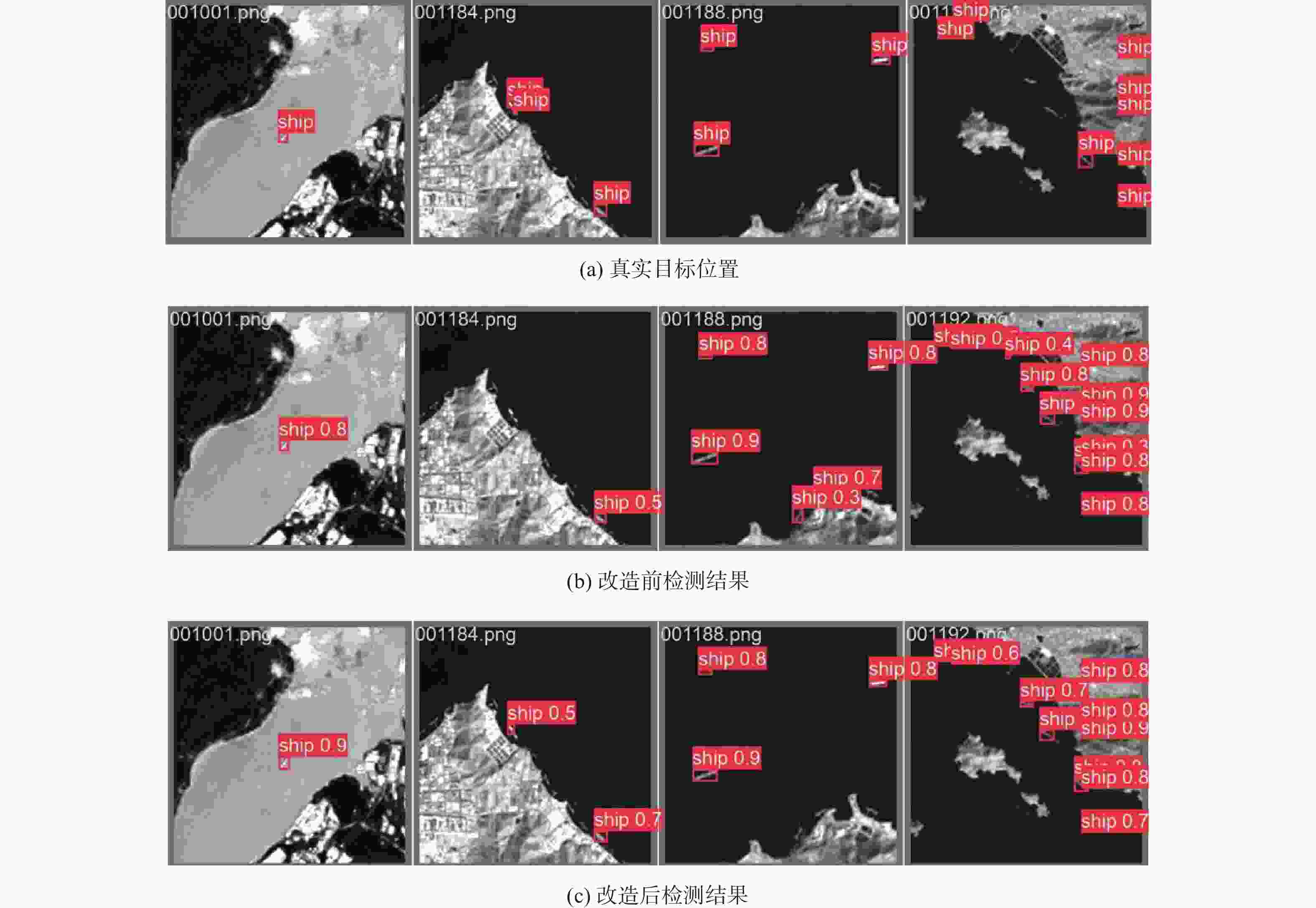
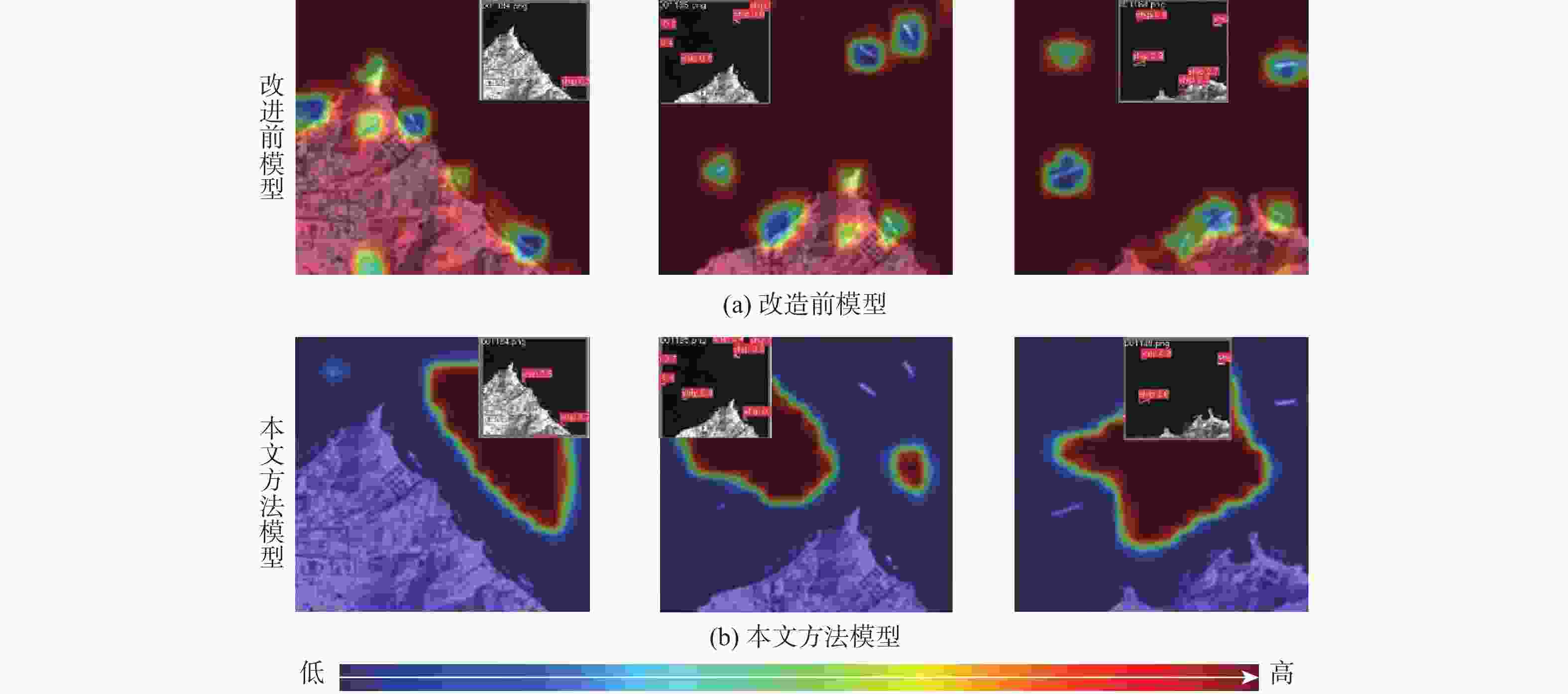
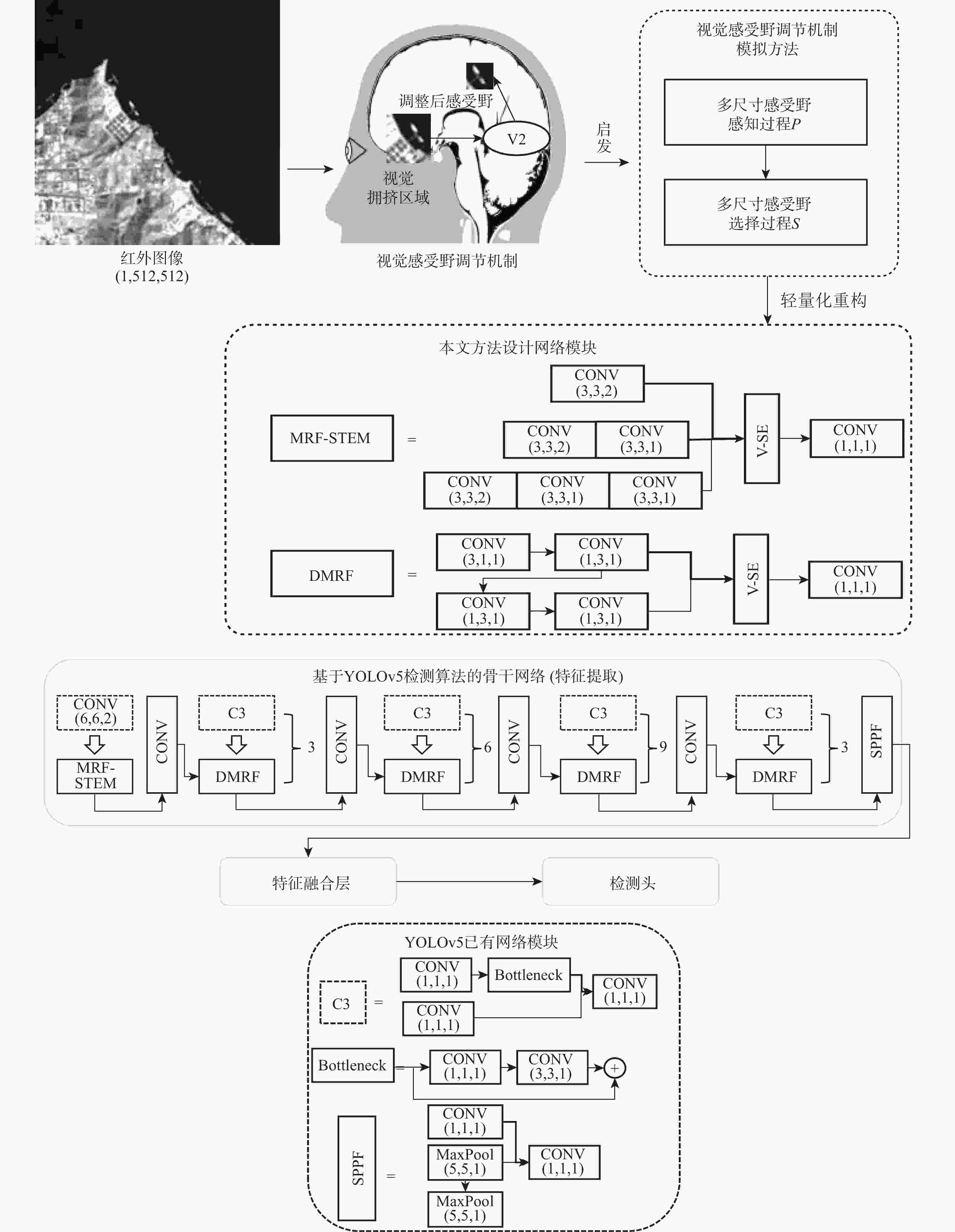
为高效提取红外遥感图像中弱小舰船的深度特征,提出一种轻量化骨干网络设计方法。受视觉注意力驱动的感受野调节机制启发,提出包含多尺寸感受野感知与选择过程的视觉感受野调节机制模拟方法,提高红外弱小舰船目标的表征效果;结合特征复用与卷积核分解的设计思想优化了多尺寸感受野模拟过程,实现轻量特征选择算子模拟多尺寸感受野选择过程,进一步降低网络的运算开销。在红外弱小舰船检测数据集上的实验结果表明:该网络检测精度提高了2%,且相较通用轻量化网络参数量减少2.3×106,计算量降低9.1 GFLOPs次;在存在相似地物干扰的港口及离岸复杂场景下,所提方法有效降低了虚警,并抑制了漏检。
Abstract:A lightweight neural network design method is proposed to efficiently represent small ships in infrared remote sensing images. To improve the representation effect of infrared dim and small targets, a method for simulating the visual receptive field adjustment mechanism that incorporates multi-scale receptive field perception and selection processes is proposed. This method is inspired by the visual attention-driven receptive field adjustment mechanism. A lightweight feature selection operator is devised to enhance the receptive field selection, and feature reuse and convolution kernel decomposition are used to optimize the multi-scale receptive field perception process in order to further increase efficiency. Experimental results on an infrared dim and small ship detection dataset show that the network detection accuracy increased by 2%, with a reduction of 2.3×106 parameters and 9.1×109 computations compared to general lightweight networks. In complex scenarios with similar ground interference, this method effectively reduces false alarms and suppresses missed detections.
-
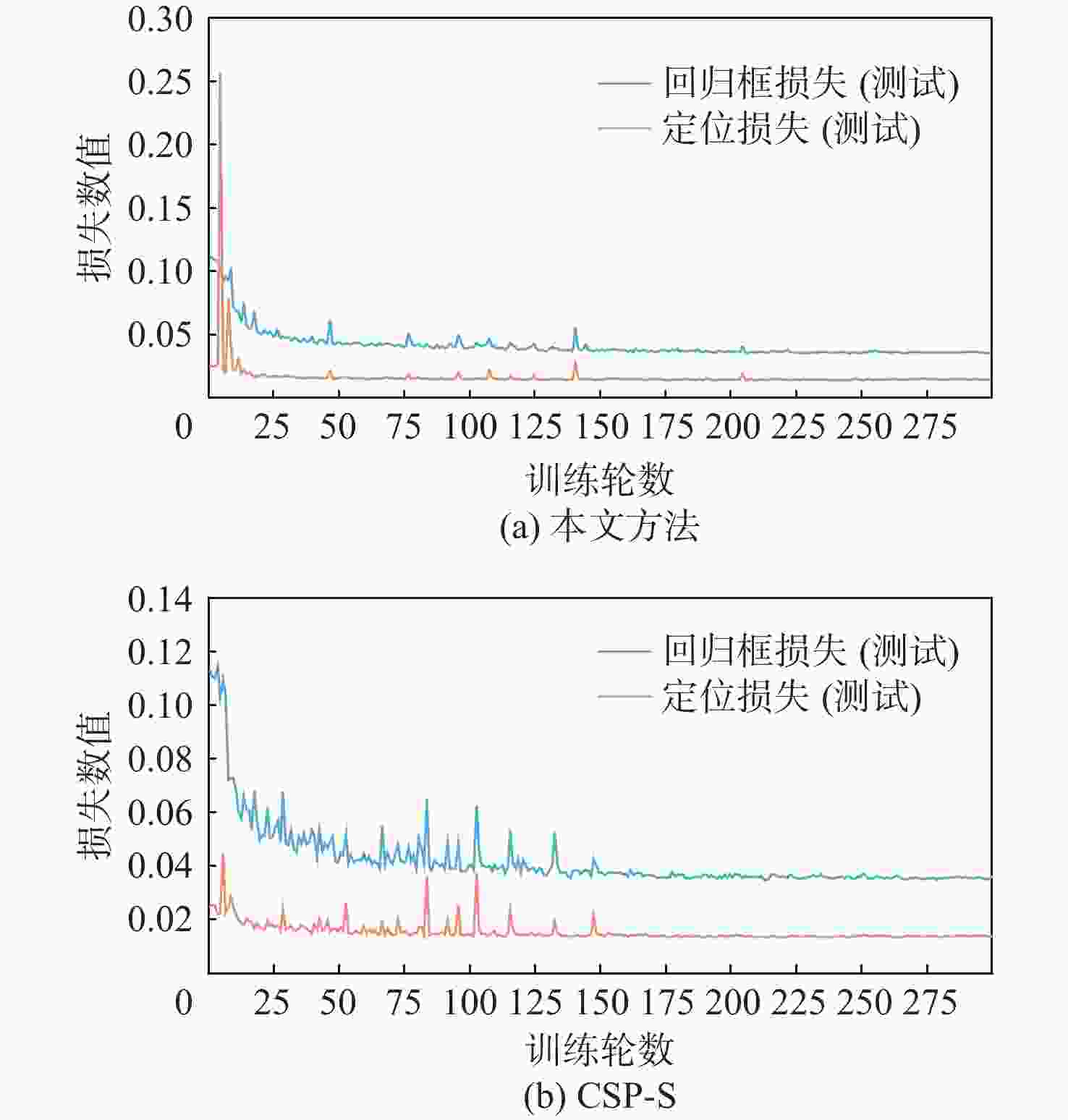
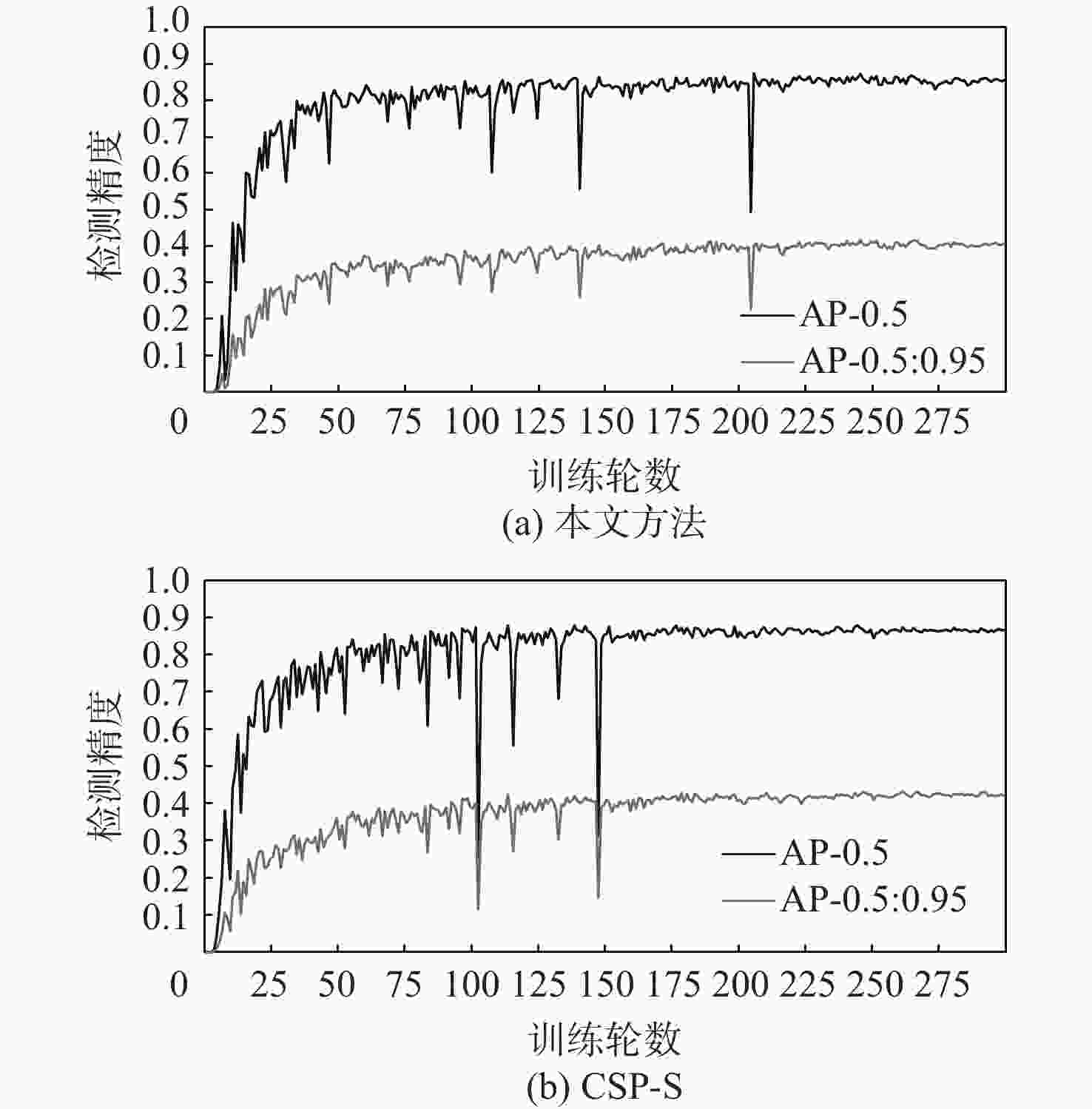
表 1 ISDD[16]数据集上本文方法与先进方法的比较
Table 1. Comparison between the proposed algorithm and advanced algorithms on the ISDD[16] dataset
方法 准确率 召回率 AP-0.5 AP-0.5:0.95 参数量 浮点运算
操作数CSP-N[10] 0.84 0.82 0.86 0.40 1.7×106 4.2 GFLOPs C3X-N[18] 0.88 0.79 0.87 0.42 1.6×106 3.9 GFLOPs Ghost-N[11] 0.87 0.77 0.85 0.40 1.5×106 2.4 GFLOPs SPP-N[15] 0.88 0.77 0.85 0.40 1.6×106 3.1 GFLOPs DMRF-N
(本文方法)0.88 0.78 0.86 0.41 1.3×106 3.6 GFLOPs CSP-S[10] 0.87 0.83 0.87 0.40 7.0×106 16.0 GFLOPs C3X-S[18] 0.88 0.83 0.89 0.45 6.5×106 5.4 GFLOPs Ghost-S[11] 0.91 0.79 0.87 0.43 5.9×106 4.4 GFLOPs SPP-S[15] 0.88 0.84 0.88 0.43 6.4×106 5.3 GFLOPs DMRF-S
(本文方法)0.90 0.79 0.87 0.43 5.1×106 6.9 GFLOPs -
[1] 田祥瑞, 贾茚钧, 罗欣, 等. 基于嵌入式平台的航拍目标智能识别[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2022, 30(11): 153-160.TIAN X R, JIA Y J, LUO X, et al. Target intelligent recognition of aerial photography images based on embedded platform[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2022, 30(11): 153-160(in Chinese). [2] 陈立群, 邹旭, 张磊, 等. 基于国产商用器件的星载智能目标检测技术[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(S2): 728860.CHEN L Q, ZOU X, ZHANG L, et al. Spaceborne intelligent target detection technology based on domestic commercial devices[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(S2): 728860(in Chinese). [3] 韩永赛, 马时平, 何林远, 等. 改进的深度神经网络下遥感机场区域目标检测[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2021, 47(7): 1470-1480.HAN Y S, MA S P, HE L Y, et al. Regional object detection of remote sensing airport based on improved deep neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(7): 1470-1480(in Chinese). [4] 王玺坤, 姜宏旭, 林珂玉. 基于改进型YOLO算法的遥感图像舰船检测[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2020, 46(6): 1184-1191.WANG X K, JIANG H X, LIN K Y. Remote sensing image ship detection based on modified YOLO algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1184-1191(in Chinese). [5] 张冬冬, 王春平, 付强. 基于anchor-free的光学遥感舰船关重部位检测算法[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2024, 50(4): 1365-1374.ZHANG D D, WANG C P, FU Q. Ship’s critical part detection algorithm based on anchor-free in optical remote sensing[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(4): 1365-1374(in Chinese). [6] 王殿伟, 胡里晨, 房杰, 等. 基于改进Double-Head RCNN的无人机航拍图像小目标检测算法[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2024, 50(7): 2141-2149.WANG D W, HU L C, FANG J, et al. Small target detection algorithm based on improved Double-Head RCNN for UAV aerial images[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(7): 2141-2149(in Chinese). [7] 陈金林, 吴一全, 苑玉彬. 无人机视角下目标检测的YOLO系列算法研究进展[J/OL]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2024: 1-33. [2024-05-29]. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=BJHK20240822002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.CHEN J L, WU Y Q, YUAN Y B. Research progress of YOLO series algorithms for target detection from UAV perspective[J/OL]. China Industrial Economics, 2024: 1-33. [2024-05-29]. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=BJHK20240822002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ(in Chinese). [8] 李红光, 王玉峰, 杨丽春. 基于元学习的小样本遥感图像目标检测[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2024, 50(8): 2503-2513.LI H G, WANG Y F, YANG L C. Meta-learning-based few-shot object detection for remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(8): 2503-2513(in Chinese). [9] 吕奕龙, 苟瑶, 李敏, 等. 基于注意力引导和多样本决策的舰船检测方法[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2025, 51(1): 202-213.LYU Y L, GOU Y, LI M, et al. Ship detection method based on attentional guidance and multi-sample decision[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2025, 51(1): 202-213(in Chinese). [10] JOCHER G. YOLOv5 by ultralytics (version 7.0) [EB/OL]. (2022-11-22)[2024-05-29]. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3908559. [11] HAN K, WANG Y H, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1577-1586. [12] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. [13] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [14] HE D J, WANG Y Y, FANG F. The critical role of V2 population receptive fields in visual orientation crowding[J]. Current Biology, 2019, 29(13): 2229-2236. [15] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [16] HAN Y Q, LIAO J W, LU T S, et al. KCPNet: knowledge-driven context perception networks for ship detection in infrared imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 61: 5000219. [17] LUAN S Z, CHEN C, ZHANG B C, et al. Gabor convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4357-4366. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2835143 [18] LIU Y Q, JIA Q, FAN X, et al. Cross-SRN: structure-preserving super-resolution network with cross convolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(8): 4927-4939. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3138431 [19] BANY M M, YEASIN M. Eigen-CAM: visual explanations for deep convolutional neural networks[J]. SN Computer Science, 2021, 2(1): 47. doi: 10.1007/s42979-021-00449-3 [20] LECUN Y, CHOPRA S, HADSELL R, et al. A tutorial on energy-based learning[M]//BAKIR G, HOFMANN T, SCHLKOPF B, et al. Predicting structured data. Cambridage: MIT Press, 2006: 45-49. -






 下载:
下载: