-
摘要:
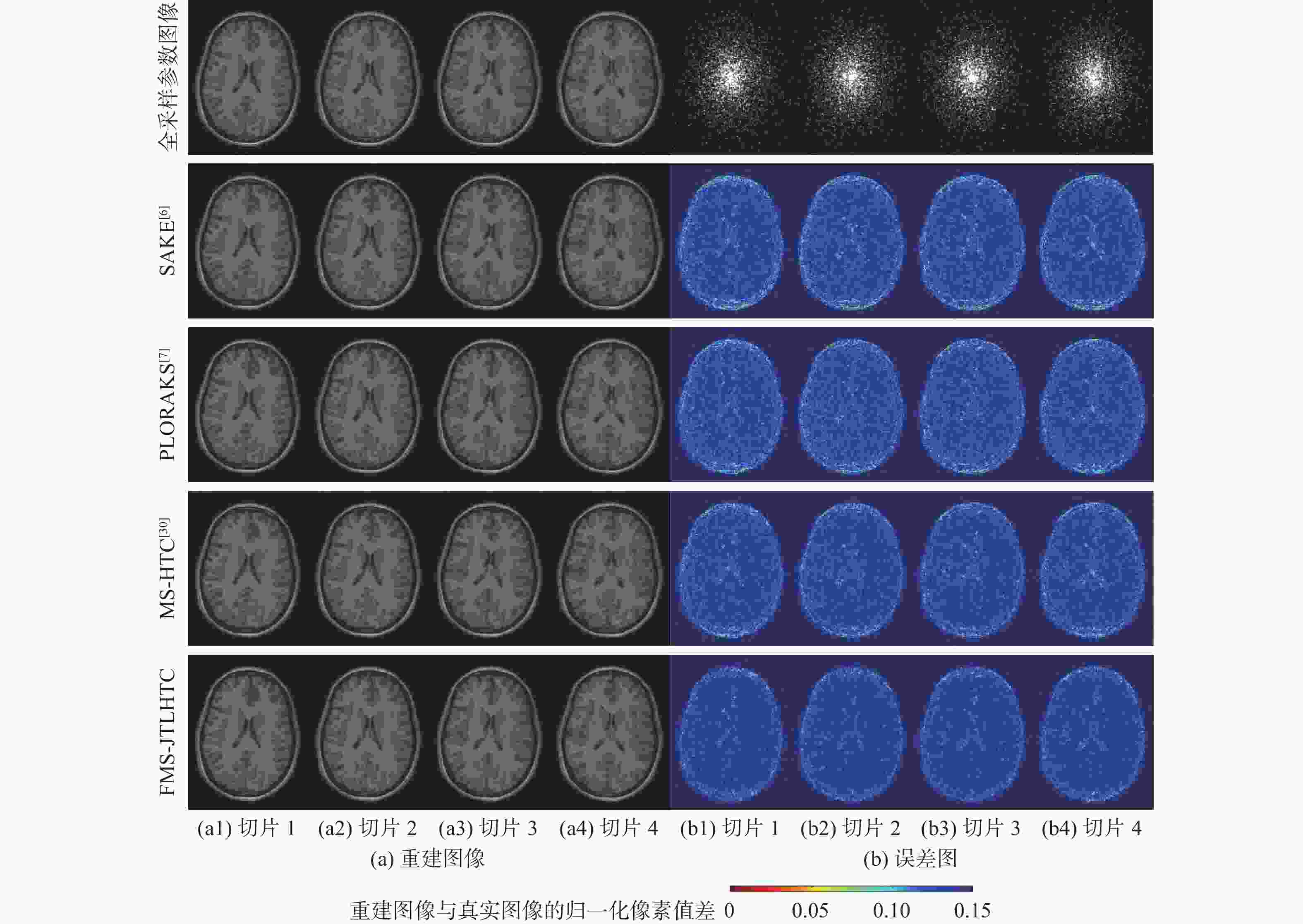
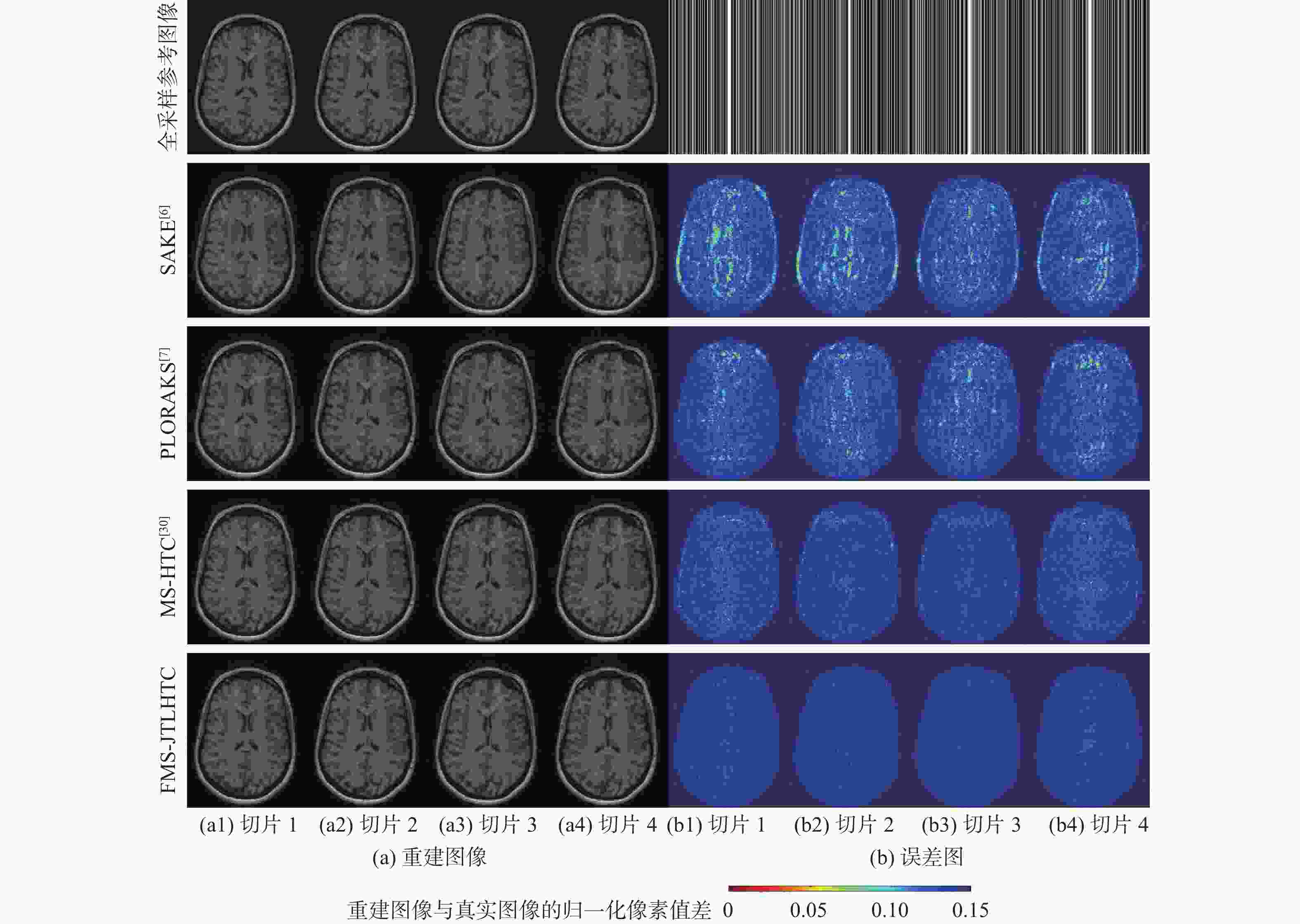
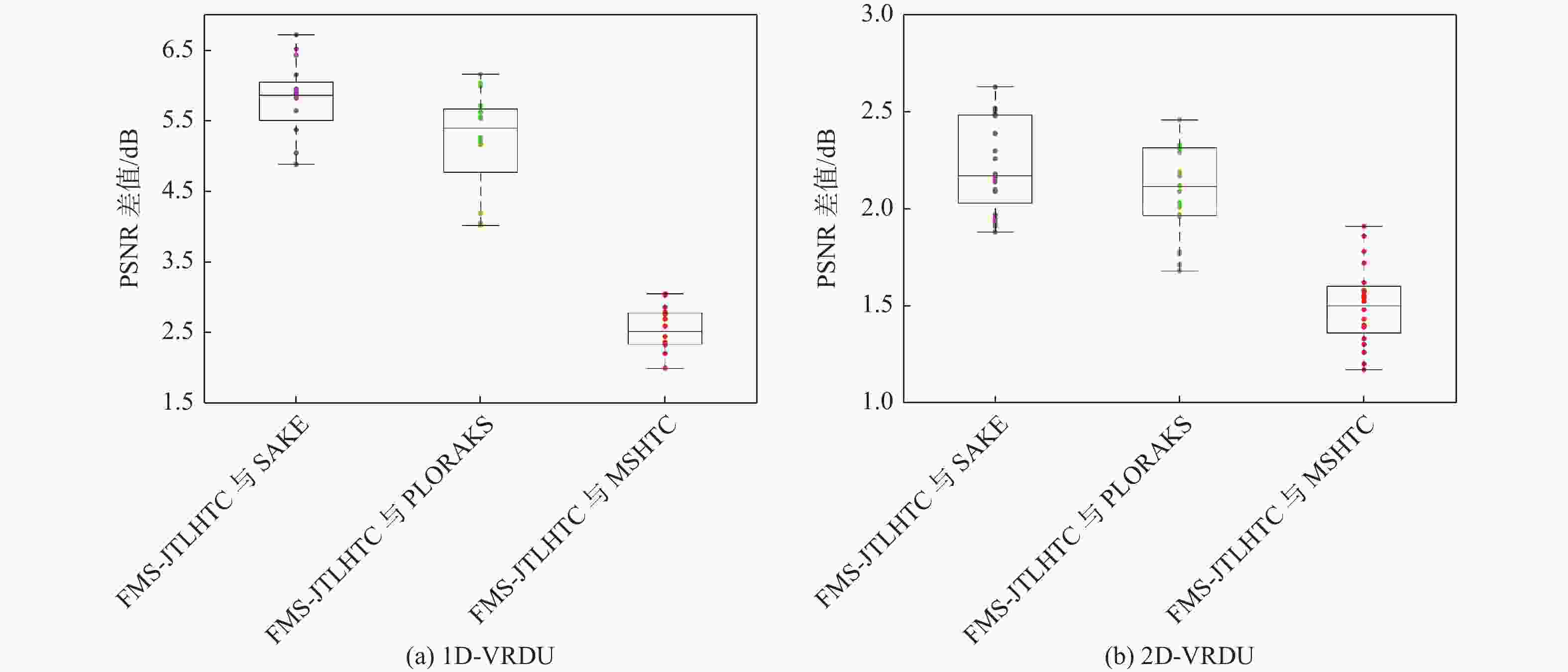
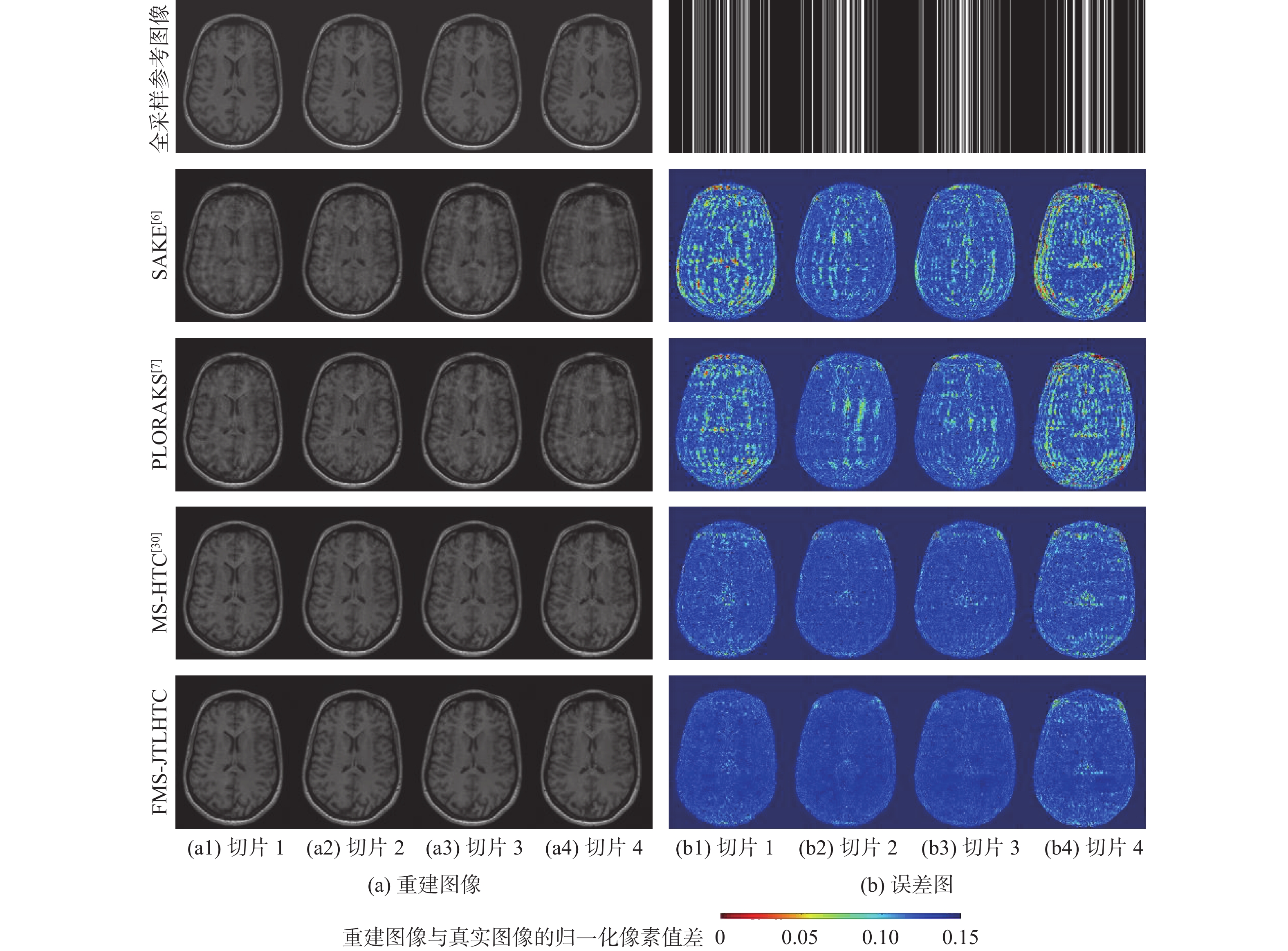
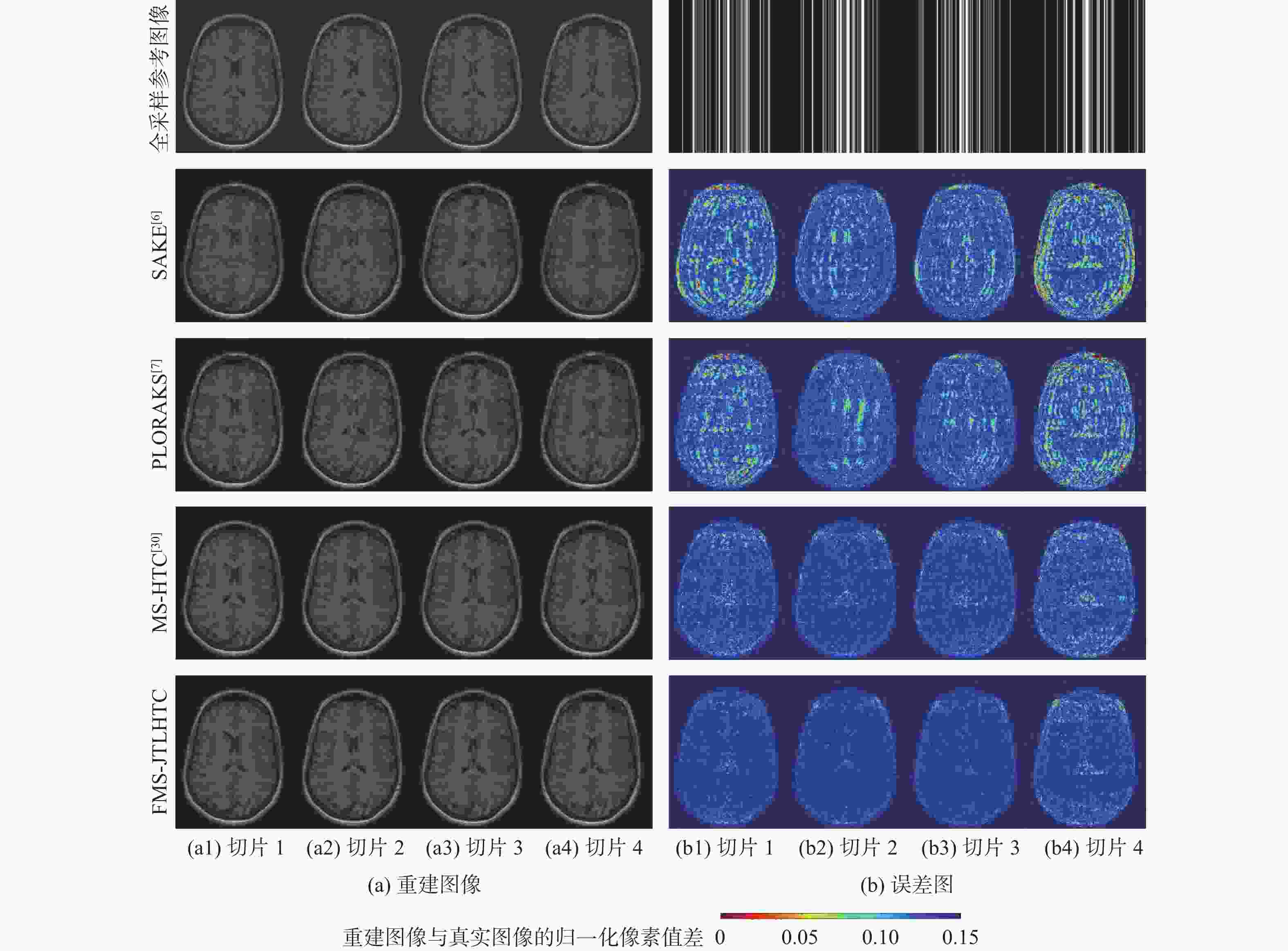
二维(2D)多切片磁共振数据在相邻切片之间具有高度的相关性,通过利用切片间的冗余性能够重建出更高质量的切片图像,但由于硬件条件的限制,2D多切片磁共振成像(MRI)需要耗费大量时间。为提高2D多切片磁共振图像的重建质量和重建速度,将联合稀疏变换学习正则项引入到多切片Hankel张量完成(MS-HTC)模型中,提出一种快速2D多切片磁共振成像重建(FMS-JTLHTC)算法。该算法使用交替方向乘子法对目标问题进行求解;引入快速迭代收缩阈值法加快收敛,并使用图形处理器对算法进行加速。使用4组脑部数据集在2种不同采样模式下进行实验,结果表明:FMS-JTLHTC算法的峰值信噪比(PSNR)相较于同时自动校准和K空间估计(SAKE)算法、并行成像数据的局部K空间领域的低秩建模(PLORAKS)算法和MS-HTC算法分别平均提高了4.04 dB、3.67 dB和2.07 dB,而且重建速度相比MS-HTC算法提高了14倍。
-
关键词:
- 多切片磁共振成像 /
- Hankel张量完成 /
- 联合稀疏变换学习 /
- 交替方向乘子法 /
- 快速迭代收缩阈值法
Abstract:Due to the significant correlation between neighboring slices in two-dimensional (2D) multi-slice magnetic resonance data, higher quality slice pictures can be reconstructed by taking use of the redundancy between slices. However, 2D multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging requires an amount of time. To improve the reconstruction quality and speed of 2D multi-slice (MRI) images, proposes a fast 2D multi-slice MRI reconstruction (FMS-JTLHTC) algorithm, which introduces the joint transform learning regular term into the multi-slice hankel tensor completion (MS-HTC) model. Prior to introducing the fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding procedure to accelerate convergence and utilize the graphics processing unit to speed up the procedure, the alternating direction method of multipliers is used to solve the objective issue. Experiments using four brain datasets in two different sampling modes show that the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of the FMS-JTLHTC algorithm is improved by an average of 4.04 dB, 3.67 dB, and 2.07 dB compared to the simultaneous atuo-calibrating and K-space estimation (SAKE), low-rank modeling of local K-space neighborhoods with parallel imaging data (PLORAKS) and MS-HTC algorithms, respectively, the reconstruction speed is improved by a factor of 14 compared to the MS-HTC algorithm.
-
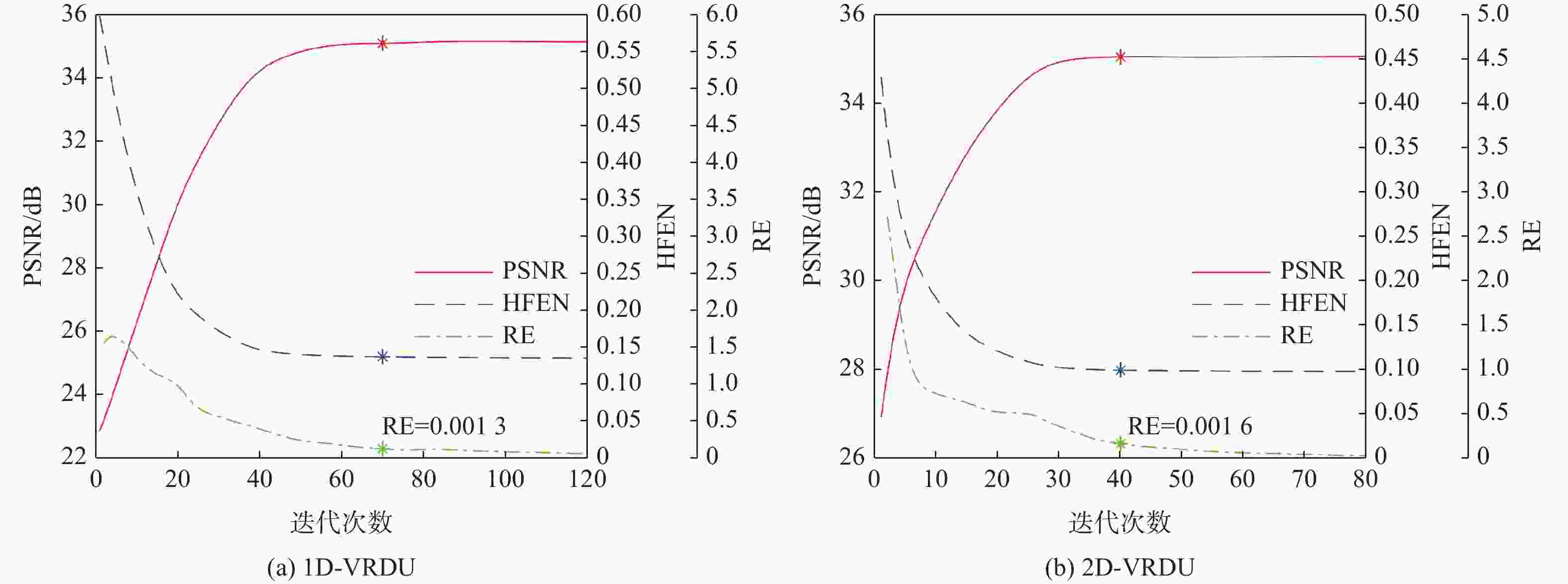
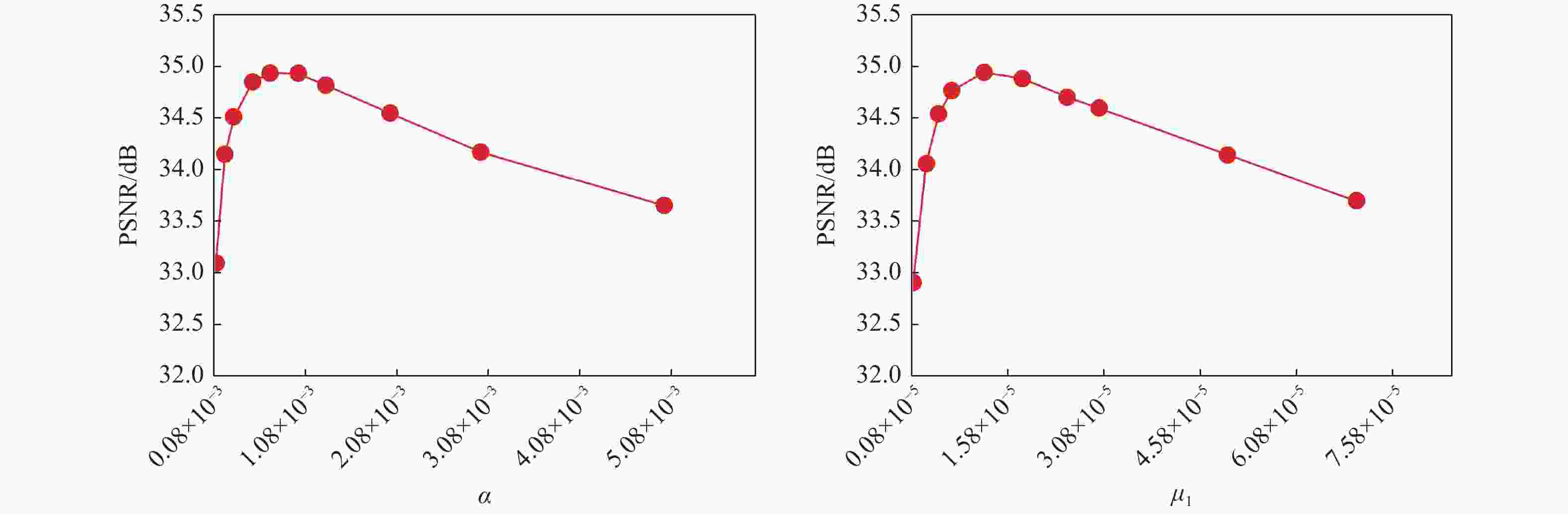
图 7 FMS-JTLHTC算法对5倍加速的1D-VRDU采样模式下dataset 1重建时参数$\alpha $和$ {\mu _1} $的变化对重构图像PSNR值的影响
Figure 7. Effect of variation of parameters $\alpha $ and $ {\mu _1} $ on PSNR values of reconstructed images during dataset 1 reconstruction by FMS-JTLHTC algorithm for 1D-VRDU sampling mode with 5-fold acceleration
表 1 4种算法对不同加速因子的1D-VRDU采样模式下4个数据集重建的评价指标平均值
Table 1. Mean values of evalution indicators reconstructed by four algorithms for four datasets in 1D-VRDU sampling pattern with different acceleration factors
算法 AF PSNR/dB MSSIM FSIM HFEN SAKE[6] 3 32.86 0.9070 0.9961 0.2070 5 28.55 0.8370 0.9912 0.3126 6 27.66 0.8238 0.9889 0.3437 7 27.29 0.8062 0.9875 0.3680 PLORAKS[7] 3 33.85 0.9151 0.9973 0.1814 5 29.27 0.8489 0.9929 0.2892 6 28.11 0.8304 0.9906 0.3282 7 27.53 0.8154 0.9883 0.3659 MS-HTC[30] 3 35.19 0.9317 0.9981 0.1365 5 31.82 0.8844 0.9954 0.2083 6 31.32 0.8805 0.9949 0.2265 7 30.98 0.8711 0.9937 0.2416 FMS-JTLHTC 3 38.01 0.9646 0.9990 0.0997 5 34.59 0.9401 0.9981 0.1504 6 33.71 0.9318 0.9976 0.1698 7 33.39 0.9267 0.9973 0.1830 表 2 4种算法对不同加速因子的2D-VRDU采样模式下4个数据集重建的评价指标平均值
Table 2. Mean values of evalution indicators reconstructed by four algorithms for four datasets in 2D-VRDU sampling pattern with different acceleration factors
算法 AF PSNR /dB MSSIM FSIM HFEN SAKE[6] 3 37.89 0.9571 0.9996 0.0664 5 35.36 0.9326 0.9990 0.0980 8 33.48 0.9148 0.9984 0.1361 10 32.67 0.9068 0.9979 0.1609 12 32.09 0.8977 0.9974 0.1797 PLORAKS[7] 3 37.86 0.9537 0.9996 0.0657 5 35.55 0.9354 0.9991 0.0966 8 33.65 0.9168 0.9984 0.1354 10 32.83 0.9059 0.9979 0.1549 12 32.24 0.8987 0.9975 0.1730 MS-HTC[30] 3 38.55 0.9626 0.9997 0.0591 5 35.98 0.9435 0.9992 0.0850 8 34.21 0.9263 0.9987 0.1144 10 33.26 0.9136 0.9981 0.1343 12 32.92 0.9115 0.9979 0.1458 FMS-JTLHTC 3 39.99 0.9738 0.9997 0.0529 5 37.58 0.9619 0.9995 0.0722 8 35.76 0.9497 0.9992 0.0951 10 34.94 0.9435 0.9989 0.1094 12 34.34 0.9383 0.9988 0.1203 表 3 4种算法对AF=3的1D-Possion欠采样模式下数据集dataset 1重建的评价指标值
Table 3. Values of evalution indicators for four algorithms for reconstruction of dataset dataset 1 in 1D-Possion undersampling pattern with AF=3
表 4 5种算法对AF=5的1D-VRDU采样模式下4个数据集的重建时间与速度
Table 4. Reconstruction times and velocities of five algorithms for four datasets in 1D-VRDU sampling mode with AF=5
算法 t/s 速度提升倍数 Dataset 1 Dataset 2 Dataset 3 Dataset 4 Dataset 1 Dataset 2 Dataset 3 Dataset 4 SAKE[6] 779.35 779.50 779.39 779.17 44.82 36.79 32.14 23.62 PLORAKS[7] 570.30 517.17 578.35 777.84 32.79 24.41 23.85 23.58 MS-HTC[30] 272.46 271.92 271.43 275.41 15.67 12.83 11.19 8.35 rawFMS-JTLHTC 456.81 550.35 624.76 860.09 26.27 25.97 25.76 26.07 FMS-JTLHTC 17.39 21.19 24.25 32.99 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 表 5 5种算法对AF=10的2D-VRDU采样模式下四个数据集的重建时间与速度
Table 5. Reconstruction times and velocities of the five algorithms for four datasets in 2D-VRDU sampling mode with AF=10
算法 t/s 速度提升倍数 Dataset 1 Dataset 2 Dataset 3 Dataset 4 Dataset 1 Dataset 2 Dataset 3 Dataset 4 SAKE[6] 311.95 207.80 259.67 207.94 29.10 19.37 18.15 14.21 PLORAKS[7] 99.62 96.39 98.85 398.66 9.29 8.98 6.91 27.25 MS-HTC[30] 222.17 168.68 193.70 165.82 20.72 15.72 13.54 11.33 rawFMS-JTLHTC 282.55 281.26 376.39 374.50 26.32 26.21 26.30 25.60 FMS-JTLHTC 10.72 10.73 14.31 14.63 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 -
[1] PRUESSMANN K P, WEIGER M, SCHEIDEGGER M B, et al. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 1999, 42(5): 952-962. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199911)42:5<952::AID-MRM16>3.0.CO;2-S [2] SODICKSON D K, MANNING W J. Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 1997, 38(4): 591-603. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910380414 [3] UECKER M, LAI P, MURPHY M J, et al. ESPIRiT: an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: where SENSE meets GRAPPA[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2014, 71(3): 990-1001. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24751 [4] GRISWOLD M A, JAKOB P M, HEIDEMANN R M, et al. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA)[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2002, 47(6): 1202-1210. doi: 10.1002/mrm.10171 [5] LUSTIG M, PAULY J M. SPIRiT: iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2010, 64(2): 457-471. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22428 [6] SHIN P J, LARSON P E Z, OHLIGER M A, et al. Calibrationless parallel imaging reconstruction based on structured low-rank matrix completion[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2014, 72(4): 959-970. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24997 [7] HALDAR J P, ZHUO J W. P-LORAKS: low-rank modeling of local K-space neighborhoods with parallel imaging data[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2016, 75(4): 1499-1514. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25717 [8] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [9] LUSTIG M, DONOHO D, PAULY J M. Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2007, 58(6): 1182-1195. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21391 [10] LAI Z Y, QU X B, LIU Y S, et al. Image reconstruction of compressed sensing MRI using graph-based redundant wavelet transform[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2016, 27: 93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.05.012 [11] YANG J F, ZHANG Y, YIN W T. A fast alternating direction method for TVL1-L2 signal reconstruction from partial Fourier data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 288-297. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2042333 [12] RAVISHANKAR S, BRESLER Y. MR image reconstruction from highly undersampled K-space data by dictionary learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2011, 30(5): 1028-1041. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2090538 [13] AHARON M, ELAD M, BRUCKSTEIN A. K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311-4322. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881199 [14] RAVISHANKAR S, BRESLER Y. Learning sparsifying transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(5): 1072-1086. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2226449 [15] RAVISHANKAR S, BRESLER Y. Efficient blind compressed sensing using sparsifying transforms with convergence guarantees and application to magnetic resonance imaging[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2015, 8(4): 2519-2557. doi: 10.1137/141002293 [16] 李玺兰, 段继忠. 基于稀疏变换学习的改进灵敏度编码重建算法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2022, 45(5): 97-102.LI X L, DUAN J Z. An improved sensitivity encoding reconstruction algorithm based on sparse transform learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022, 45(5): 97-102(in Chinese). [17] 段继忠, 钱青青. 基于SIDWT和迭代自一致性的快速并行成像重建方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(5): 582-592.DUAN J Z, QIAN Q Q. Fast parallel imaging reconstruction method based on SIDWT and iterative self-consistency[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(5): 582-592(in Chinese). [18] DUAN J Z, PAN T, LIU Y, et al. Non-local low-rank constraint-based self-consistent PMRI reconstruction using eigenvector maps[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2023, 17(3): e12180. doi: 10.1049/sil2.12180 [19] PAN T, DUAN J Z, WANG J F, et al. Iterative self-consistent parallel magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction based on nonlocal low-rank regularization[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2022, 88: 62-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2022.01.012 [20] DUAN J Z, LIU C, LIU Y, et al. Adaptive transform learning and joint sparsity based PLORAKS parallel magnetic resonance image reconstruction[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 212315-212326. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3039527 [21] LIN C Y, FESSLER J A. Efficient dynamic parallel MRI reconstruction for the low-rank plus sparse model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2019, 5(1): 17-26. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2018.2882089 [22] OTAZO R, CANDÈS E, SODICKSON D K. Low-rank plus sparse matrix decomposition for accelerated dynamic MRI with separation of background and dynamic components[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2015, 73(3): 1125-1136. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25240 [23] PANG Y, ZHANG X L. Interpolated compressed sensing for 2D multiple slice fast MR imaging[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e56098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056098 [24] DATTA S, DEKA B. Magnetic resonance image reconstruction using fast interpolated compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Optics, 2018, 47(2): 154-165. doi: 10.1007/s12596-017-0428-8 [25] MURAD M, BILAL M, JALIL A, et al. Efficient reconstruction technique for multi-slice CS-MRI using novel interpolation and 2D sampling scheme[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 117452-117466. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004731 [26] DATTA S, DEKA B. Efficient interpolated compressed sensing reconstruction scheme for 3D MRI[J]. IET Image Processing, 2018, 12(11): 2119-2127. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.5473 [27] DATTA S, DEKA B, MULLAH H U, et al. An efficient interpolated compressed sensing method for highly correlated 2D multi-slice MRI[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Accessibility to Digital World. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 187-192. [28] MURAD M, JALIL A, BILAL M, et al. Radial undersampling-based interpolation scheme for multislice CSMRI reconstruction techniques[J]. BioMed Research International, 2021, 2021: 6638588. doi: 10.1155/2021/6638588 [29] DEKA B, DATTA S. Calibrationless joint compressed sensing reconstruction for rapid parallel MRI[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 58: 101871. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101871 [30] LIU Y L, YI Z Y, ZHAO Y J, et al. Calibrationless parallel imaging reconstruction for multislice MR data using low-rank tensor completion[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2021, 85(2): 897-911. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28480 [31] BECK A, TEBOULLE M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183-202. doi: 10.1137/080716542 [32] LIU Y P, LIU T T, LIU J N, et al. Smooth robust tensor principal component analysis for compressed sensing of dynamic MRI[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 102: 107252. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107252 [33] LIU D, ZHOU J J, MENG M M, et al. Highly undersampling dynamic cardiac MRI based on low-rank tensor coding[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2022, 89: 12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2022.01.013 [34] HE J F, LIU X T, LUAN N N. Bi-smooth constraints for accelerated dynamic MRI with low-rank plus sparse tensor decomposition[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2023, 82: 104530. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104530 [35] ZHANG Y H, HU Y. Dynamic cardiac MRI reconstruction using combined tensor nuclear norm and casorati matrix nuclear norm regularizations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1-4. [36] WU T L, GAO B, FAN J C, et al. Low-rank tensor completion based on self-adaptive learnable transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(7): 8826-8838. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3215974 [37] BERGQVIST G, LARSSON E G. The higher-order singular value decomposition: theory and an application [lecture notes][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 151-154. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936030 [38] TUCKER L R. Some mathematical notes on three-mode factor analysis[J]. Psychometrika, 1966, 31(3): 279-311. doi: 10.1007/BF02289464 [39] DE LATHAUWER L, DE MOOR B, VANDEWALLE J. A multilinear singular value decomposition[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2000, 21(4): 1253-1278. doi: 10.1137/S0895479896305696 [40] LIU Y P, CHEN L X, ZHU C. Improved robust tensor principal component analysis via low-rank core matrix[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(6): 1378-1389. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2873142 [41] VANNIEUWENHOVEN N, VANDEBRIL R, MEERBERGEN K. A new truncation strategy for the higher-order singular value decomposition[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2012, 34(2): A1027-A1052. doi: 10.1137/110836067 [42] DUAN J Z, LIU Y, WANG J F. Accelerated SPIRiT parallel MR image reconstruction based on joint sparsity and sparsifying transform learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2023, 9: 276-288. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2023.3252260 [43] GILLARD J. Cadzow’s basic algorithm, alternating projections and singular spectrum analysis[J]. Statistics and Its Interface, 2010, 3(3): 335-343. doi: 10.4310/SII.2010.v3.n3.a7 [44] SOUZA R, BENTO M, NOGOVITSYN N, et al. Dual-domain cascade of U-nets for multi-channel magnetic resonance image reconstruction[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2020, 71: 140-153. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2020.06.002 [45] CORRIVEAU P, WEBSTER A. VQEG evaluation of objective methods of video quality assessment[J]. SMPTE Journal, 1999, 108(9): 645-648. doi: 10.5594/J17594 [46] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [47] ZHANG L, ZHANG L, MOU X Q, et al. FSIM: a feature similarity index for image quality assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(8): 2378-2386. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2109730 -






 下载:
下载: