Image super-resolution reconstruction network based on multi-scale spatial attention guidance
-
摘要:
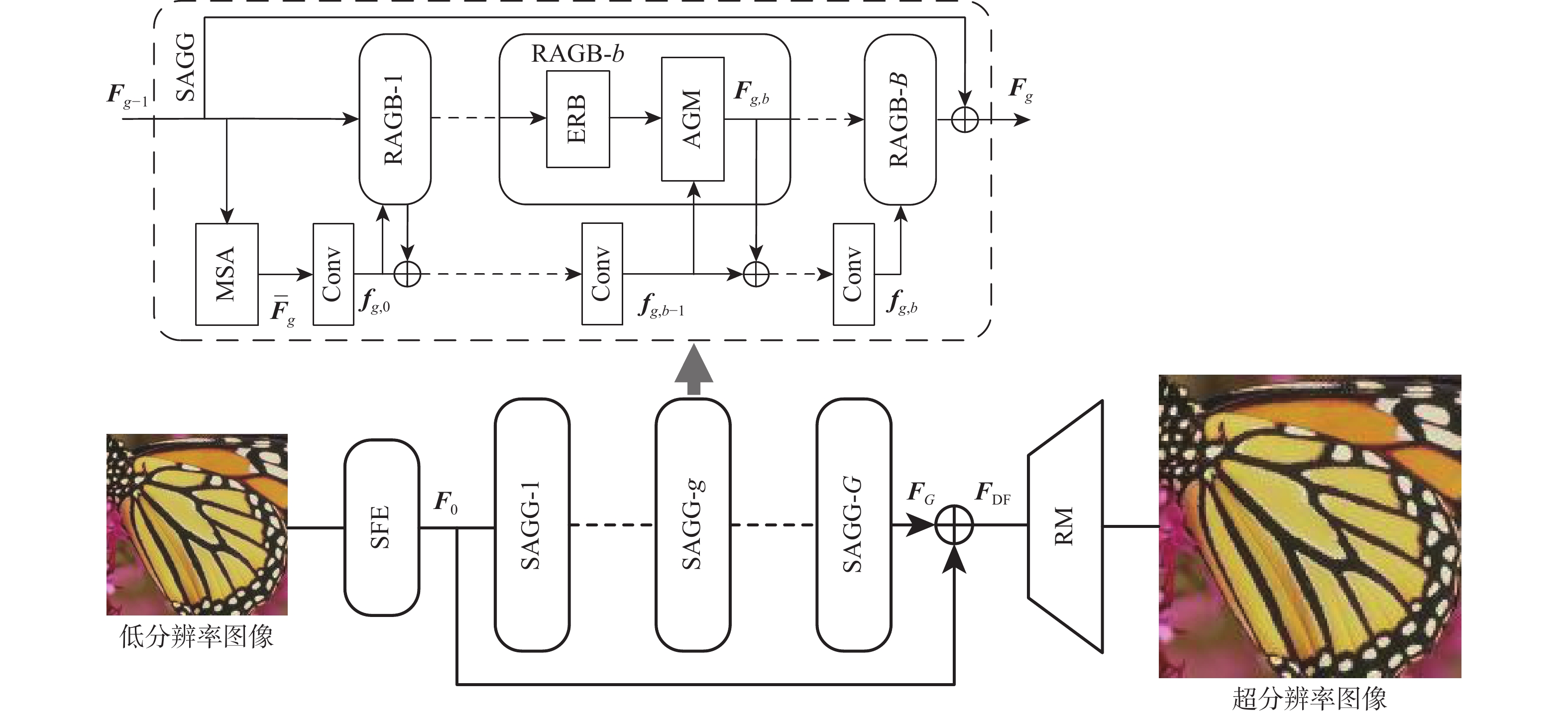
针对基于注意力机制的图像超分辨率重建网络忽视了注意力特征的差异性,仅将注意力机制直接引入到网络模型中,对不同层次特征进行相同处理的问题,设计了一种多尺度空间注意力引导的图像超分辨率重建网络SAGN。提出了增强特征提取残差块(ERB),完善了局部信息的表征能力;集成了多尺度空间注意力(MSA)模块,获取了MSA特征信息;引入了注意力引导模块(AGM),对不同的特征分配个性化的权重,以实现有效的上下文全局特征融合和冗余信息抑制。实验结果表明:量化测试和主观效果上,相比于传统的注意力结构,SAGN在4个基准数据集上都展现出了优越性,其4倍重建结果的峰值信噪比(PSNR)较次优模型平均提高了0.05 dB,进一步证实了SAGN在恢复图像的几何结构和细节方面的优势。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem that the attention-mechanism-based image super-resolution reconstruction network ignores the heterogeneity of attentional features and treats features at different levels uniformly by directly incorporating the attention mechanism into the network model. This study designs a novel multi-scale spatial attention guidance network, namely SAGN, which makes the following key contributions. Firstly, an enhanced feature extraction residual block (ERB) is proposed to enhance the representation capacity of local information. Secondly, to record spatial attention features at various scales, a multi-scale spatial attention (MSA) module is incorporated. Lastly, an attention-guided module (AGM) is introduced to assign individualized weights to different features, facilitating effective fusion of contextual global features and suppression of redundant information. On four benchmark datasets, extensive experimental results show that SAGN outperforms standard attention structures in terms of both subjective visual perception and objective evaluation criteria. Notably, SAGN achieves an average 0.05 dB higher than that of the suboptimal model in peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) for 4 times reconstruction results, further underscoring its efficacy in recovering image geometric structures and fine details.
-
表 1 多尺度空间注意力模块张量尺寸
Table 1. Tensor dimensions of multi-scale spatial attention module
卷积层名称 张量输入尺寸 张量输出尺寸 Conv1×1 $ (C,H,W) $ $ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 2}} \right. } 2},H,W) $ Conv
k=7,s=2,p=0$ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 2}} \right. } 2},H,W) $ $ \begin{gathered} (C / 4, H_1=(H-7) / 2+1, \\ W_1=(W-7) / 2+1 )\end{gathered} $ Conv
k=5,s=2,p=0$ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 4}} \right. } 4},{H_1},{W_1}) $ $ \begin{gathered}({C / 8},{H_2} = ({{{H_1} - 5)} / 2} + 1,\\ {W_2} = ({{{W_1} - 5)} / 2} + 1) \end{gathered} $ Conv
k=3,s=1,p=1$ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 8}} \right. } 8},{H_2},{W_2}) $ $ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 8}} \right. } 8},{H_2},{W_2}) $ DeConv
k=5,s=2,p=0$ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 8}} \right. } 8},{H_2},{W_2}) $ $ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 4}} \right. } 4},{H_1},{W_1}) $ DeConv
k=7,s=2,p=0$ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 4}} \right. } 4},{H_1},{W_1}) $ $ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 2}} \right. } 2},H,W) $ Conv1×1 $ ({C \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {C 2}} \right. } 2},H,W) $ $ (C,H,W) $ 表 2 尺度因子为4时加入不同模块后对模型性能的影响
Table 2. Effect of model performance after adding different modules when scale factor is 4
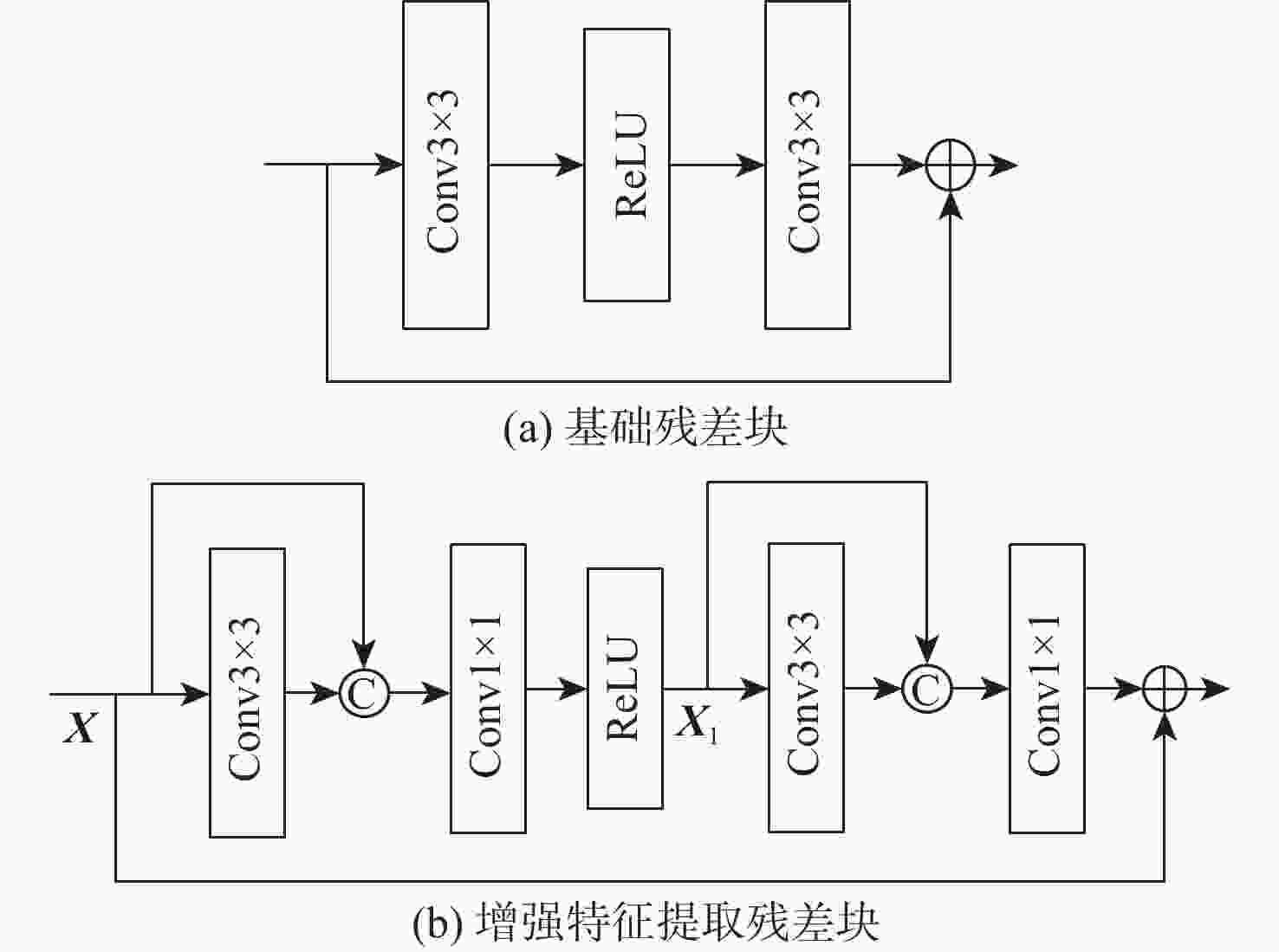
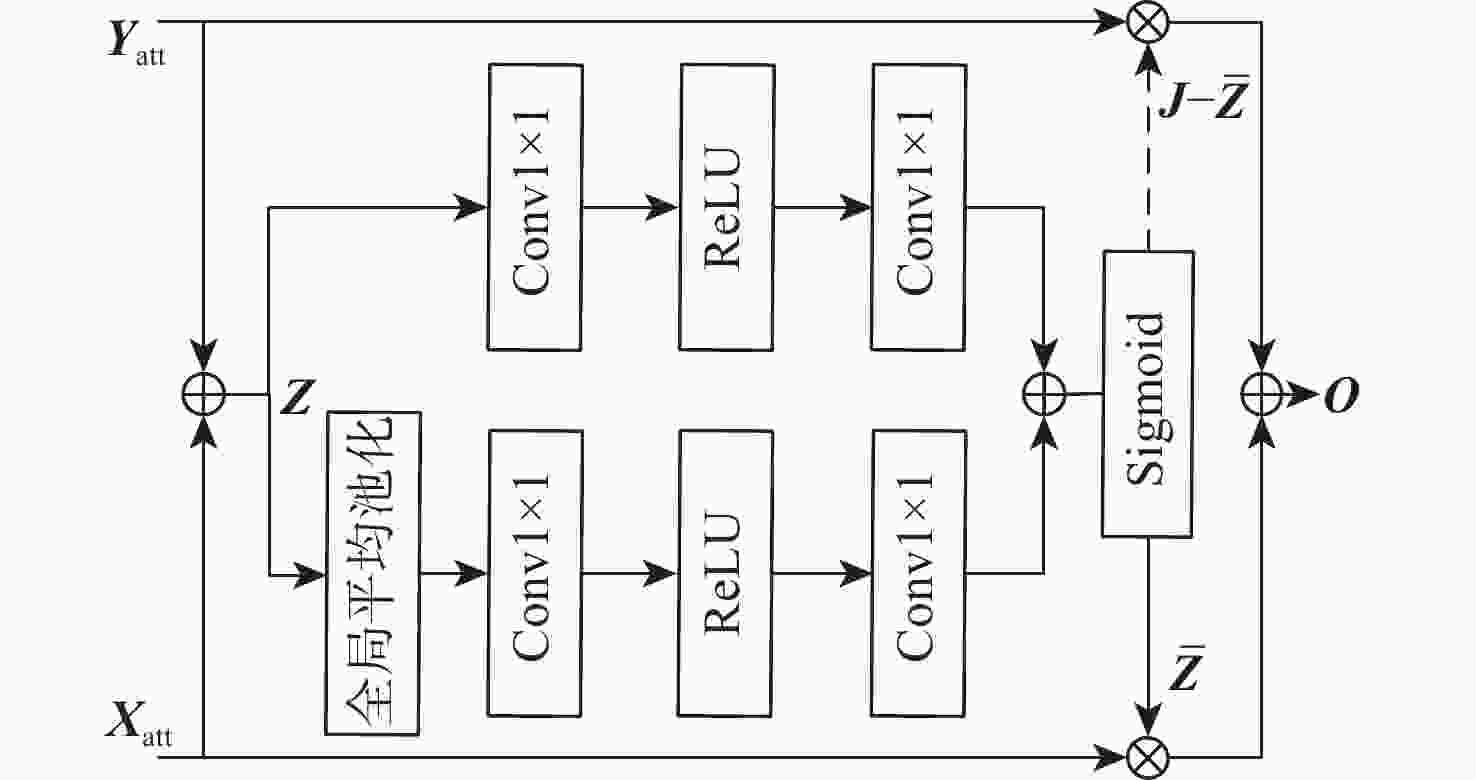
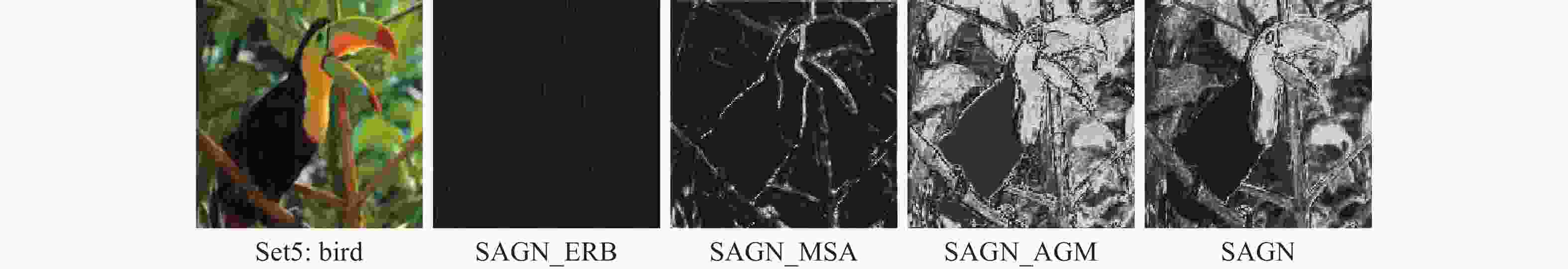
模型 RB ERB ESA MSA AGM 参数量 浮点计算量 PSNR/dB Set5 Set14 B100 Urban100 EDSR_RB √ 3.58×106 223.85 GFLOPs 32.21 28.64 27.59 26.12 SAGN_ERB √ 4.17×106 252.52 GFLOPs 32.28 28.68 27.61 26.16 SAGN_ESA √ √ 4.18×106 266.83 GFLOPs 32.30 28.67 27.61 26.18 SAGN_MSA √ √ 4.32×106 284.58 GFLOPs 32.37 28.71 27.63 26.37 SAGN_AGM √ √ 4.33×106 293.99 GFLOPs 32.35 28.70 27.61 26.26 SAGN √ √ √ 4.48×106 326.05 GFLOPs 32.45 28.73 27.68 26.40 注:性能最优作加粗处理。 表 3 4种注意力引导方式对模型性能的影响
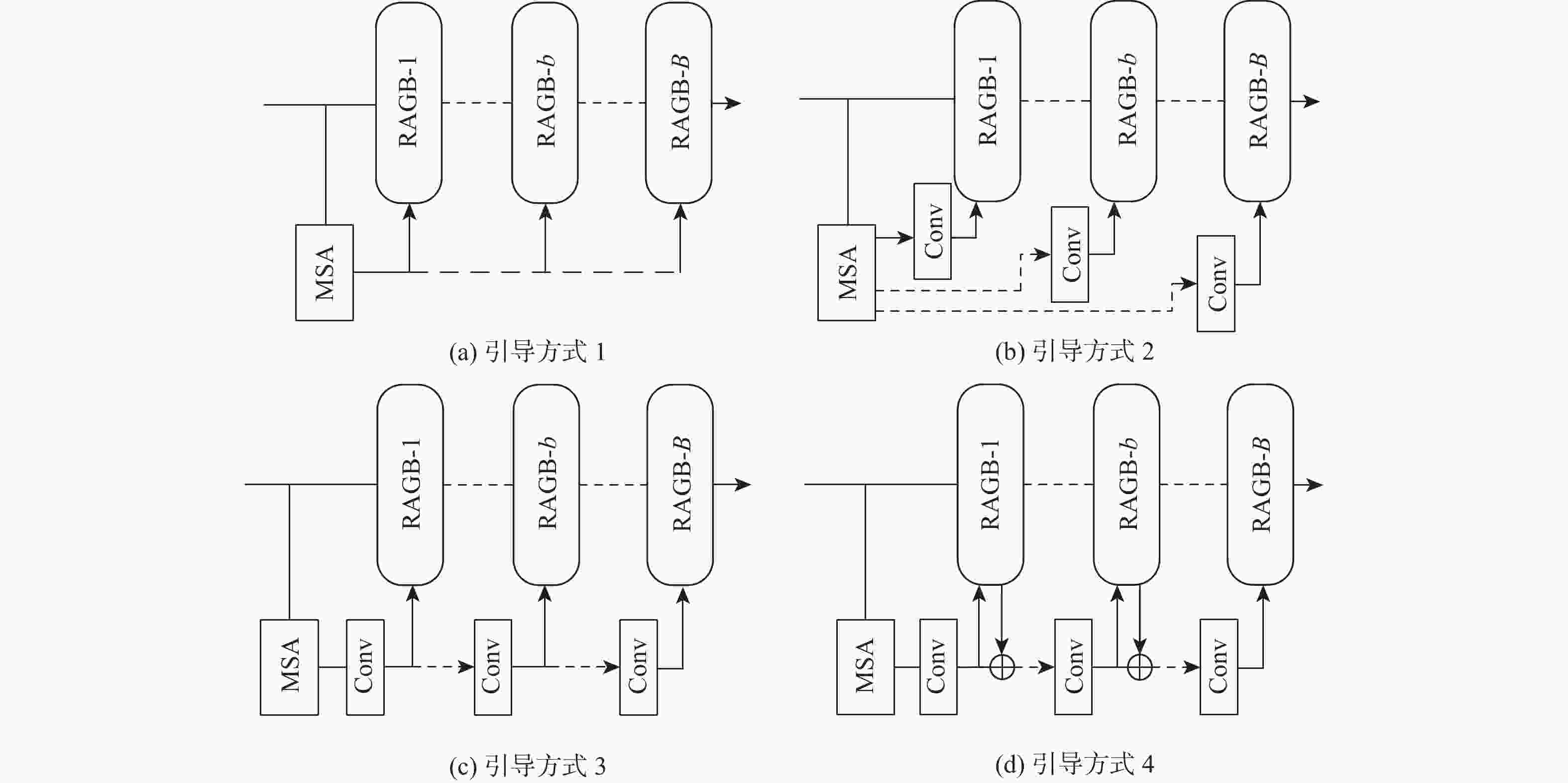
Table 3. Effect of four ways of attention guidance methods on model performance
引导方式 参数量 浮点计算量 PSNR/dB Set5 Set14 B100 Urban100 引导方式1 4.23×106 278.98 GFLOPs 32.38 28.55 27.62 26.25 引导方式2 4.48×106 325.04 GFLOPs 32.45 28.60 27.63 26.23 引导方式3 4.48×106 326.04 GFLOPs 32.41 28.72 27.67 26.38 引导方式4 4.48×106 326.04 GFLOPs 32.45 28.73 27.68 26.40 注:指标最优作加粗处理。 表 4 尺度因子为2、3、4时基准数据集的客观评价指标对比
Table 4. Comparison of objective evaluation indexes with scale factors of 2, 3 and 4 for benchmark datasets
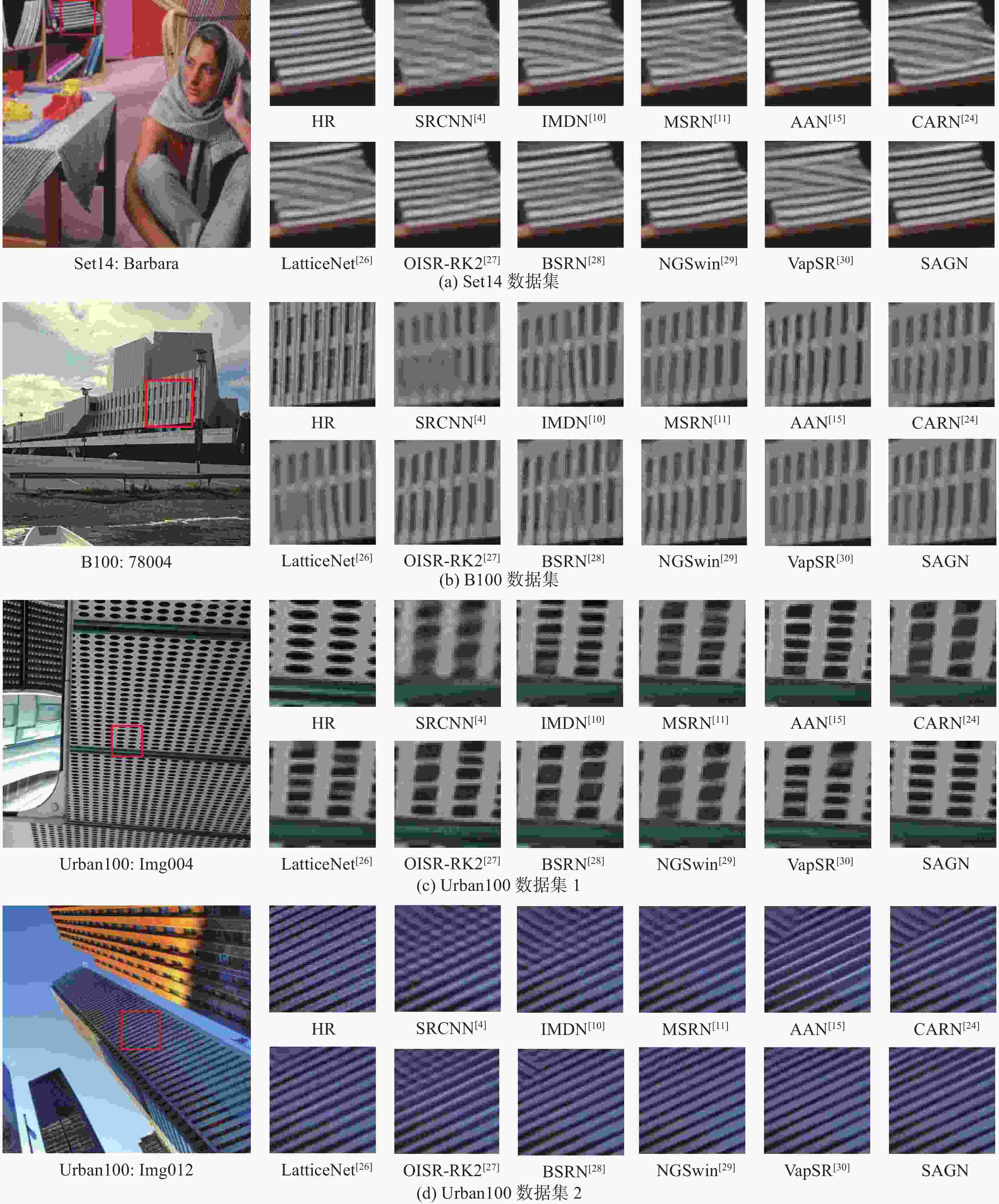
尺度因子 模型 PSNR/dB SSIM Set5 Set14 B100 Urban100 Set5 Set14 B100 Urban100 2 SRCNN[4] 36.66 32.45 31.36 29.50 0.9542 0.9067 0.8879 0.8946 FSRCNN[5] 37.00 32.63 31.53 29.88 0.9558 0.9088 0.8920 0.9020 VDSR[6] 37.53 33.03 31.90 30.76 0.9587 0.9124 0.8960 0.9140 IMDN[10] 38.00 33.63 32.19 32.17 0.9605 0.9177 0.8996 0.9283 MSRN[11] 38.08 33.74 32.23 32.22 0.9605 0.9170 0.9013 0.9326 Cross-SRN[12] 38.03 33.62 32.19 32.28 0.9606 0.9180 0.8997 0.9290 AAF-L[14] 38.09 33.78 32.23 32.46 0.9607 0.9192 0.9002 0.9313 AAN[15] 38.06 33.75 32.22 32.43 0.9608 0.9194 0.9002 0.9311 SwinIR-light[16] 38.14 33.86 32.31 32.76 0.9611 0.9206 0.9012 0.9340 CARN[24] 37.76 33.52 32.09 31.92 0.9590 0.9166 0.8978 0.9256 MRFN[25] 37.98 33.41 32.14 31.45 0.9611 0.9159 0.8997 0.9221 LatticeNet[26] 38.15 33.78 32.25 32.43 0.9610 0.9193 0.9005 0.9302 OISR-RK2[27] 38.12 33.80 32.26 32.48 0.9609 0.9193 0.9006 0.9317 BSRN[28] 38.10 33.74 32.24 32.34 0.9610 0.9193 0.9006 0.9303 NGSwin[29] 38.05 33.79 32.27 32.53 0.9610 0.9199 0.9008 0.9324 VapSR[30] 38.08 33.77 32.27 32.45 0.9612 0.9195 0.9011 0.9316 SAGN 38.18 33.87 32.31 32.76 0.9612 0.9210 0.9012 0.9341 3 SRCNN[4] 32.75 29.28 28.41 26.24 0.9090 0.8209 0.7863 0.7989 FSRCNN[5] 33.16 29.43 28.53 26.43 0.9140 0.8242 0.7910 0.8080 VDSR[6] 33.66 29.77 28.82 27.14 0.9213 0.8314 0.7976 0.8279 IMDN[10] 34.36 30.32 29.09 28.17 0.9270 0.8417 0.8046 0.8519 MSRN[11] 34.38 30.34 29.08 28.08 0.9262 0.8395 0.8041 0.8554 Cross-SRN[12] 34.43 30.33 29.09 28.23 0.9275 0.841 0.8050 0.8535 AAF-L[14] 35.54 30.41 29.14 28.40 0.9283 0.8436 0.8062 0.8574 AAN[15] 34.47 30.44 29.14 28.41 0.9279 0.8437 0.8059 0.8570 SwinIR-light[16] 34.62 30.54 29.20 28.66 0.9289 0.8463 0.8082 0.8624 CARN[24] 34.29 30.29 29.06 28.06 0.9255 0.8407 0.8034 0.8493 MRFN[25] 34.21 30.03 28.99 27.53 0.9267 0.8363 0.8029 0.8589 LatticeNet[26] 34.53 30.39 29.15 28.33 0.9281 0.8424 0.8059 0.8538 OISR-RK2[27] 34.55 30.46 29.18 28.50 0.9282 0.8443 0.8075 0.8597 BSRN[28] 34.46 30.48 29.18 28.39 0.9277 0.8449 0.8068 0.8567 NGSwin[29] 34.52 30.53 29.19 28.52 0.9282 0.8456 0.8078 0.8603 VapSR[30] 34.52 30.53 29.19 28.43 0.9284 0.8452 0.8077 0.8583 SAGN 34.63 30.55 29.23 28.67 0.9290 0.8465 0.8082 0.8625 4 SRCNN[4] 30.48 27.49 26.90 24.52 0.8628 0.7503 0.7101 0.7221 FSRCNN[5] 30.71 27.59 26.98 24.62 0.8657 0.7535 0.7150 0.7280 VDSR[6] 31.35 28.01 27.29 25.18 0.8838 0.7674 0.7251 0.7524 IMDN[10] 32.21 28.58 27.56 26.04 0.8948 0.7811 0.7353 0.7838 MSRN[11] 32.07 28.60 27.52 26.04 0.8903 0.7751 0.7273 0.7896 Cross-SRN[12] 32.24 28.59 27.58 26.16 0.8954 0.7817 0.7364 0.7881 AAF-L[14] 32.32 28.67 27.62 26.32 0.8964 0.7839 0.7379 0.7931 AAN[15] 32.30 28.71 27.61 26.27 0.8966 0.7842 0.7374 0.7920 SwinIR-light[16] 32.44 28.77 27.69 26.47 0.8976 0.7858 0.7406 0.7980 CARN[24] 32.13 28.60 27.58 26.07 0.8937 0.7806 0.7349 0.7837 MRFN[25] 31.90 28.31 27.43 25.46 0.8916 0.7746 0.7309 0.7654 LatticeNet[26] 32.30 28.68 27.62 26.25 0.8962 0.7830 0.7367 0.7873 OISR-RK2[27] 32.32 28.72 27.66 26.37 0.8965 0.7843 0.7390 0.7953 BSRN[28] 32.35 28.73 27.65 26.27 0.8966 0.7848 0.7387 0.7908 NGSwin[29] 32.33 28.78 27.66 26.45 0.8963 0.7859 0.7396 0.7963 VapSR[30] 32.38 28.77 27.68 26.35 0.8978 0.7852 0.7398 0.7941 SAGN 32.52 28.82 27.73 26.51 0.8980 0.7860 0.7399 0.7971 注:最优方法作加粗处理。 表 5 尺度因子为2时 Set5数据集上不同方法复杂度对比
Table 5. Complexity comparison of different methods on Set5 dataset under scale factor is 2
模型 参数量 PSNR/dB SSIM 运行时间/ms EDSR[7] 40.73×106 38.11 0.9602 885 MSRN[11] 5.89×106 38.08 0.9605 685 SwinIR[16] 11.5×106 38.35 0.9620 889 SwinIR-light[16] 0.87×106 38.14 0.9611 355 OISR-RK2[27] 4.97×106 38.12 0.9609 558 BSRN[28] 0.32×106 38.10 0.9610 205 DBPN[31] 5.95×106 38.09 0.9600 775 NGSwin[29] 0.99×106 38.05 0.9610 298 VapSR[30] 0.32×106 38.08 0.9612 223 SAGN 4.15×106 38.18 0.9612 425 注:指标最优和次优分别作加粗和下划线处理。 -
[1] 陈嘉琪, 刘祥梅, 李宁, 等. 一种超分辨SAR图像水域分割算法及其应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 700-707. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200366CHEN J Q, LIU X M, LI N, et al. A high-precision water segmentation algorithm for SAR image and its application[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 700-707(in Chinese). doi: 10.11999/JEIT200366 [2] XIAO Y, YUAN Q Q, JIANG K, et al. From degrade to upgrade: learning a self-supervised degradation guided adaptive network for blind remote sensing image super-resolution[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 96: 297-311. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.03.021 [3] GEORGESCU M I, IONESCU R T, MIRON A I, et al. Multimodal multi-head convolutional attention with various kernel sizes for medical image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023. [4] DONG C, LOY C C, HE K M, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [5] DONG C, LOY C C, TANG X O. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 391-407. [6] KIM J, LEE J K, LEE K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1646-1654. [7] LIM B, SON S, KIM H, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1132-1140. [8] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [9] 程德强, 郭昕, 陈亮亮, 等. 多通道递归残差网络的图像超分辨率重建[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(3): 605-618. doi: 10.11834/jig.200108CHENG D Q, GUO X, CHEN L L, et al. Image super-resolution reconstruction from multi-channel recursive residual network[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(3): 605-618(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.200108 [10] HUI Z, GAO X B, YANG Y C, et al. Lightweight image super-resolution with information multi-distillation network[C]//Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2019: 2024-2032. [11] LI J C, FANG F M, MEI K F, et al. Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 527-542. [12] LIU Y Q, JIA Q, FAN X, et al. Cross-SRN: structure-preserving super-resolution network with cross convolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(8): 4927-4939. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3138431 [13] LIU J, ZHANG W J, TANG Y T, et al. Residual feature aggregation network for image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2356-2365. [14] WANG X H, WANG Q, ZHAO Y Z, et al. Lightweight single image super-resolution network with attentive auxiliary feature learning[C]//Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2021: 268-285. [15] CHEN H, GU J, ZHANG Z, et al. Attention in attention network for image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021. [16] LIANG J Y, CAO J Z, SUN G L, et al. SwinIR: image restoration using swin Transformer[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1833-1844. [17] ZHAO H Y, KONG X T, HE J W, et al. Efficient image super-resolution using pixel attention[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 56-72. [18] SHI W Z, CABALLERO J, HUSZÁR F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1874-1883. [19] BEVILACQUA M, ROUMY A, GUILLEMOT C, et al. Low-complexity single-image super- resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Surrey: BMVA Press, 2012: 135.1-135.10. [20] ZEYDE R, ELAD M, PROTTER M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Curves and Surfaces. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 711-730. [21] MARTIN D, FOWLKES C, TAL D, et al. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics[C]//Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2001: 416-423. [22] HUANG J B, SINGH A, AHUJA N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 5197-5206. [23] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [24] AHN N, KANG B, SOHN K A. Fast, accurate, and lightweight super-resolution with cascading residual network[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 256-272. [25] HE Z W, CAO Y P, DU L, et al. MRFN: multi-receptive-field network for fast and accurate single image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 22(4): 1042-1054. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2937688 [26] LUO X T, XIE Y, ZHANG Y L, et al. LatticeNet: towards lightweight image super-resolution with lattice block[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 272-289. [27] HE X Y, MO Z T, WANG P S, et al. ODE-inspired network design for single image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1732-1741. [28] LI Z Y, LIU Y Q, CHEN X Y, et al. Blueprint separable residual network for efficient image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 832-842. [29] CHOI H, LEE J, YANG J. N-gram in swin Transformers for efficient lightweight image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 2071-2081. [30] ZHOU L, CAI H M, GU J J, et al. Efficient image super-resolution using vast-receptive-field attention[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Berlin: Springer, 2023: 256-272. [31] HARIS M, SHAKHNAROVICH G, UKITA N. Deep back-projection networks for super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1664-1673. -







 下载:
下载: