Grid error modeling aided GNSS/IMU integrated navigation comprehensive quality control algorithm
-
摘要:
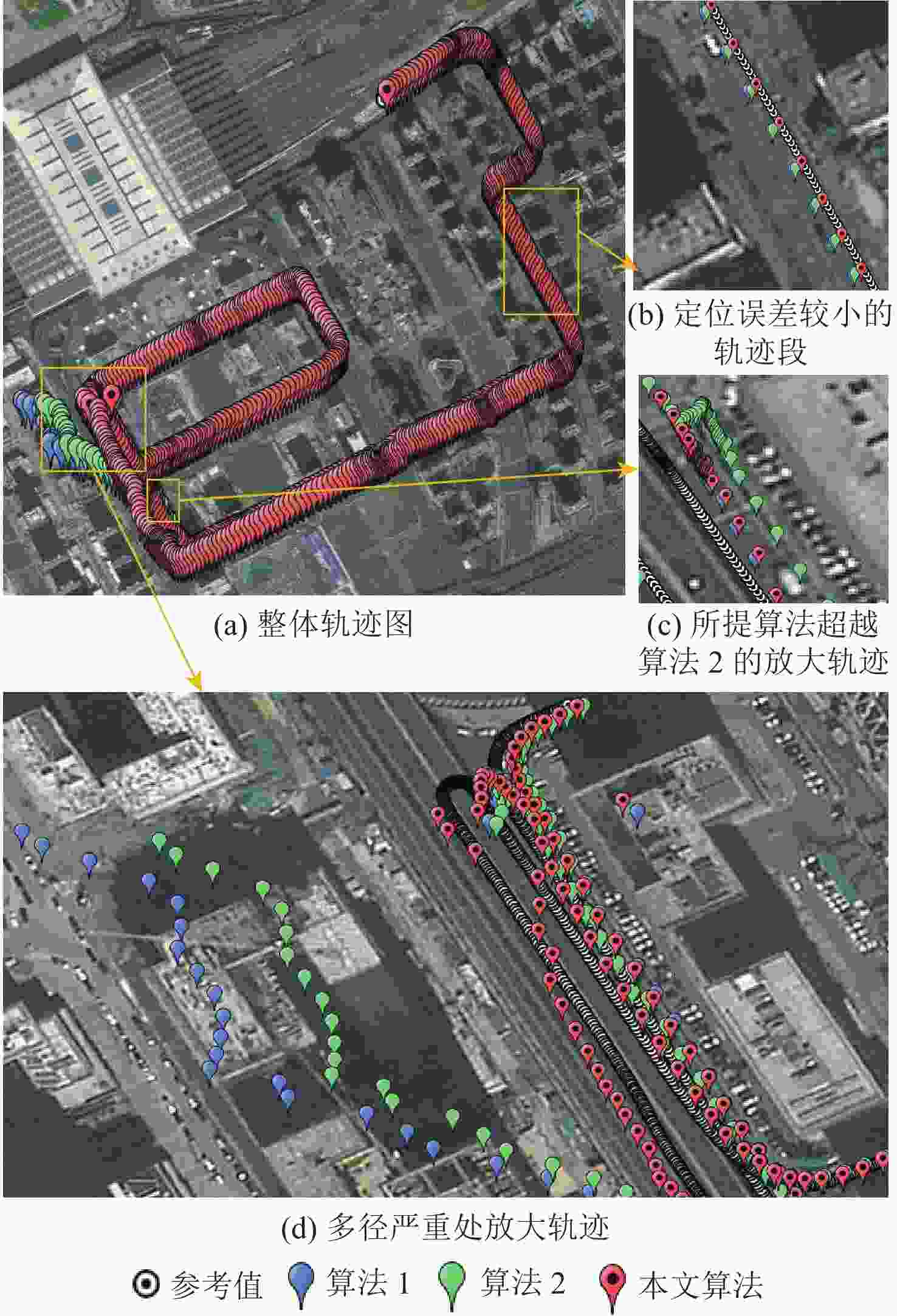
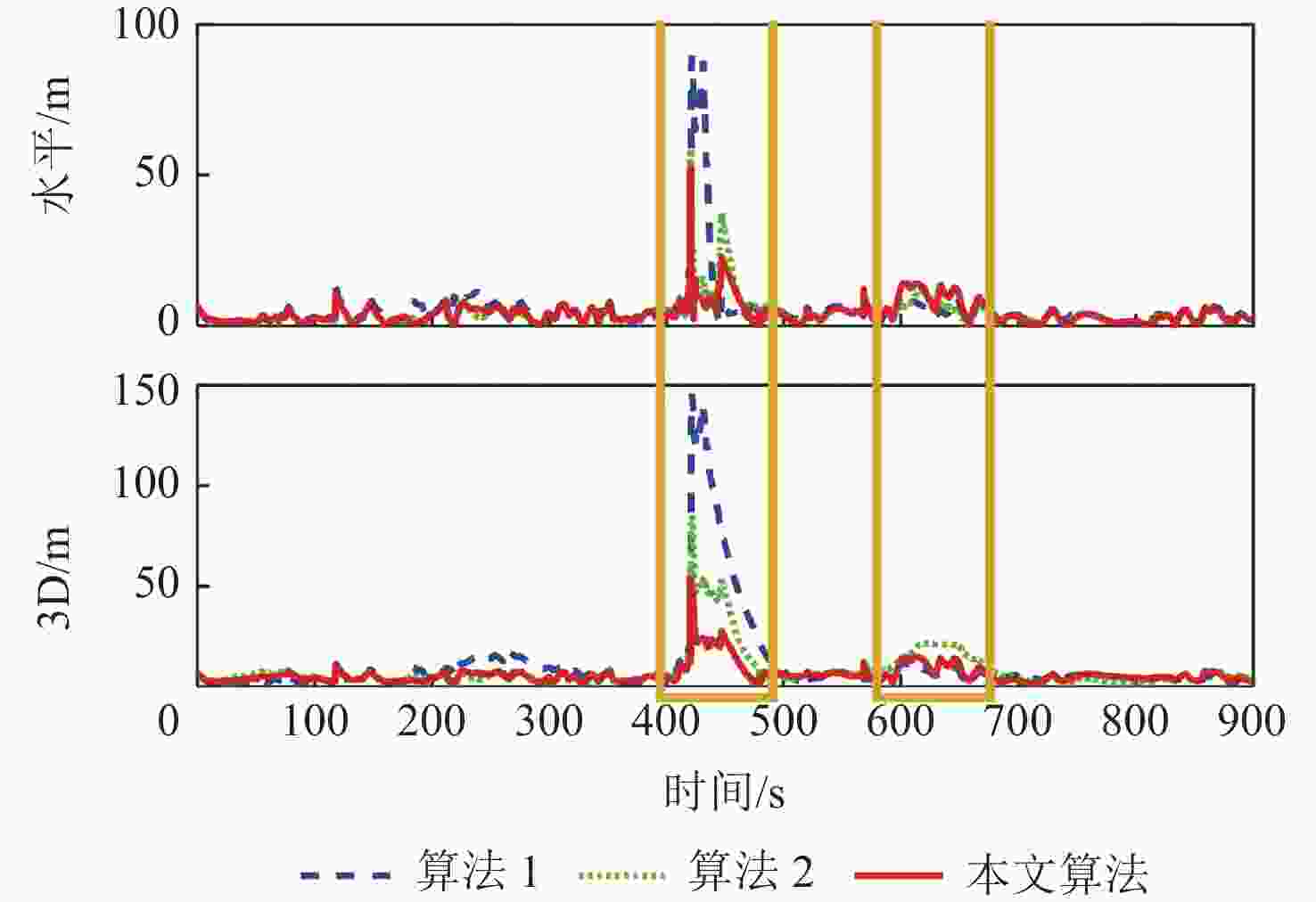
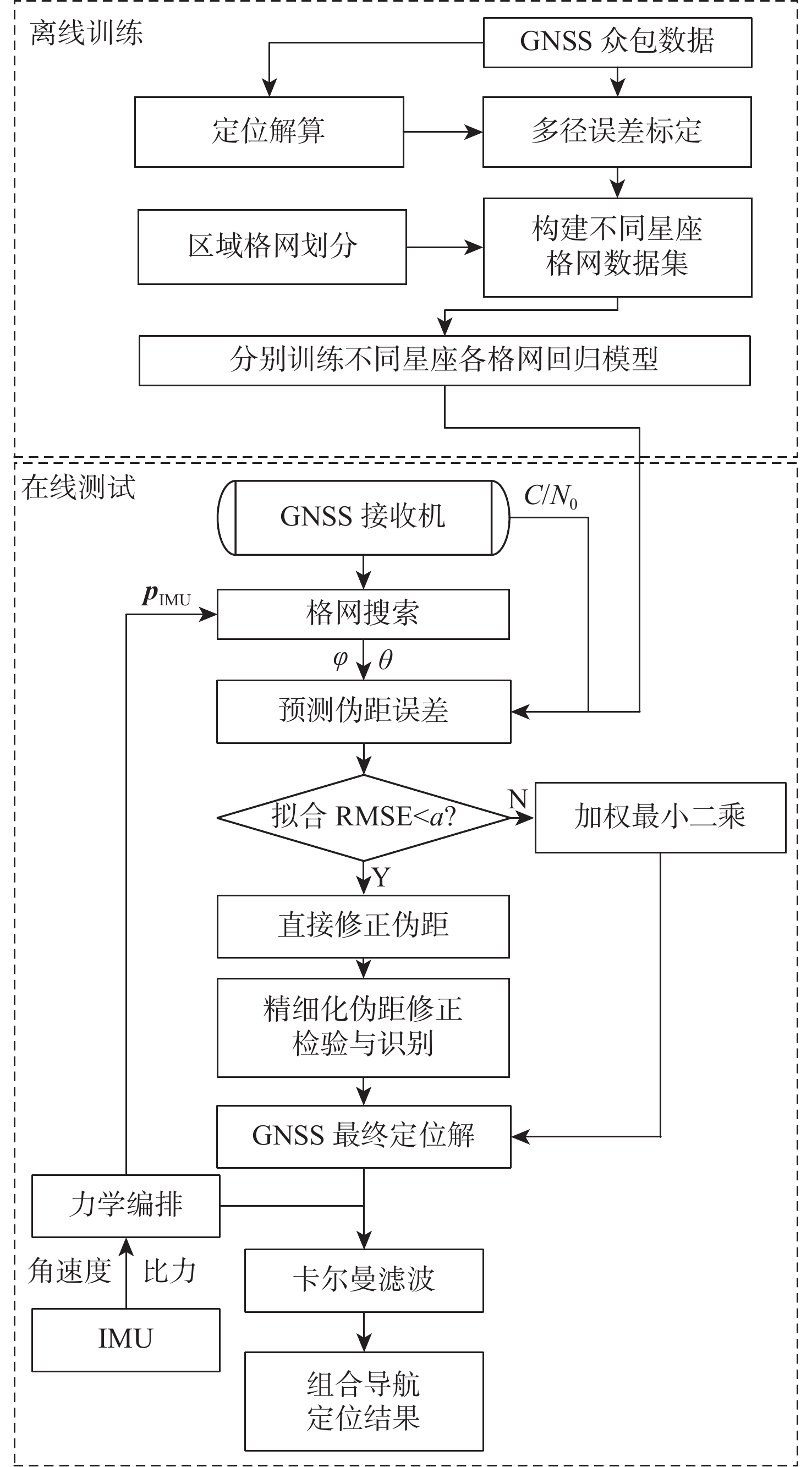
在城市复杂环境中,全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)由于高楼等障碍物的遮挡和反射,易产生非视距接收(NLOS)与多径干扰(MI),定位精度和可靠性严重下降,无法满足用户高精度和高可靠性的定位、导航和授时(PNT)服务需求。基于GNSS原始观测量的信号分类和多径建模方法对于缓解城市环境中GNSS多径效应,提高定位精度有重要意义,但这类模型的精度、效率和检验方法往往存在欠缺。提出了一种格网误差建模辅助的GNSS/IMU组合导航综合质量控制算法,通过对城市区域进行格网伪距误差建模,并且实现基于格网拟合精度和卫星故障检验构建精细化的综合质量控制,有效地优化了城市复杂环境下的GNSS/IMU组合导航定位性能。城市环境车载实验表明,所提算法相较传统GNSS/IMU组合导航算法在水平和3D方向上分别提升了50.23%和66.77%,相较基于格网建模算法提升了11.56%和40.53%。
-
关键词:
- GNSS/IMU组合导航 /
- 伪距误差建模 /
- 质量控制 /
- 加权最小二乘 /
- 故障检验
Abstract:In the complex urban environment, Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals are prone to non-line-of-sight reception (NLOS) and multipath interference (MI) due to the occlusion and reflection of obstacles such as tall buildings. The positioning accuracy and reliability are seriously reduced, which cannot meet the user’s high precision and reliability positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) service requirements. Signal classification and multipath modeling methods based on machine learning and data-driven are of great significance for alleviating GNSS multipath effect and improving positioning accuracy in urban areas. But the accuracy, efficiency and adaptivity of such models still need to be improved. In this paper, a grid error modeling aided GNSS/Inertial measurement unit (IMU) integrated navigation comprehensive quality control algorithm is proposed. Besides the grid pseudorange error modeling, it proposes a refined comprehensive quality control strategy based on grid fitting accuracy and satellite fault detection, thus optimizes the performance of GNSS/IMU integrated navigation in complex urban environments. The field test in urban environment shows that compared with the traditional GNSS/IMU integrated navigation algorithm, the horizontal and 3D positioning accuracy of the proposed algorithm are improved by 50.23% and 66.77%, respectively, and compared with the grid pseudorange error modeling algorithm, they are improved by 11.56% and 40.53%, respectively.
-
表 1 实验算法描述
Table 1. Experiment algorithm description
算法 算法内容及步骤 算法1 基于传统卡尔曼滤波的GNSS/IMU松组合 算法2 1. 基于格网模型预测值对全部卫星进行伪距修正后定位; 2. 与IMU进行松组合 本文算法 1. 根据格网拟合精度选择当前历元进行伪距修正或加权最小二乘; 2. 根据卫星故障检验与识别结果选择每颗卫星是否进行剔除或修正; 3. 与IMU进行松组合 表 2 STIM300参数
Table 2. Parameters of STIM300
参数 数值 加速度计零偏不稳定性/mg 0.05 加速度计随机游走/(m·s−1·h−1/2) 0.06 陀螺仪零偏不稳定性/((°)·h−1) 0.5 陀螺仪随机游走/((°)·h−1/2) 0.15 表 3 HGuideN580参数
Table 3. Parameters of HGuideN580
参数 数值 加速度计零偏不稳定性/mg 0.025 加速度计随机游走/(m·s−1·h−1/2) 0.03 陀螺仪零偏不稳定性/((°)·h−1) 0.25 陀螺仪随机游走/((°)·h−1/2) 0.04 表 4 3种算法定位精度对比
Table 4. Positioning accuracy comparison of the three algorithms
类型 RMSE/m 提升率1/% 提升率2/% 算法1 算法2 本文算法 北 2.93 2.82 2.37 3.75 19.11 东 10.20 5.27 4.72 48.33 53.75 地 20.27 11.30 5.47 44.25 64.92 水平 10.61 5.97 5.28 43.71 50.23 3D 22.88 12.78 7.60 44.16 66.77 注:提升率1是算法2相对算法1的提升比例、提升率2是本文算法相对算法1的提升比例。 -
[1] ZHU N, MARAIS J, BÉTAILLE D, et al. GNSS position integrity in urban environments: a review of literature[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(9): 2762-2778. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2766768 [2] 冯晓超, 程晓滨, 赵珂. GNSS接收机抗多径技术[J]. 电讯技术, 2010, 50(8): 180-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2010.08.038FENG X C, CHENG X B, ZHAO K. Anti-multipath technology for GNSS receivers[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2010, 50(8): 180-184(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2010.08.038 [3] Kumar S, Moore K B. The evolution of global positioning system (GPS) technology[J]. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 2002, 11: 59-80. doi: 10.1023/A:1013999415003 [4] 邵晨, 曾庆化, 邱文旗, 等. GNSS多径抑制基带处理算法综述[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2022, 9(5): 1-14.SHAO C, ZENG Q H, QIU W Q, et al. Overview of GNSS multipath mitigation baseband processing algorithm[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2022, 9(5): 1-14(in Chinese). [5] 李岩, 董玮, 徐鹏程, 等. GNSS抑制多径技术研究进展[J]. 汽车电器, 2022(7): 55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8639.2022.07.021LI Y, DONG W, XU P C, et al. Research status and prospect of GNSS multi-path signal suppression technology[J]. Auto Electric Parts, 2022(7): 55-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8639.2022.07.021 [6] YOZEVITCH R, MOSHE B B, WEISSMAN A. A robust GNSS LOS/NLOS signal classifier[J]. Navigation-Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 2016, 63(4): 429-442. doi: 10.1002/navi.166 [7] QUAN Y M, LAU L, ROBERTS G W, et al. Convolutional neural network based multipath detection method for static and kinematic GPS high precision positioning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(12): 2052. doi: 10.3390/rs10122052 [8] GUERMAH B, EL GHAZI H, SADIKI T, et al. A robust GNSS LOS/multipath signal classifier based on the fusion of information and machine learning for intelligent transportation systems[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Technology Management, Operations and Decisions. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 94-100. [9] SUN R, WANG G Y, ZHANG W Y, et al. A gradient boosting decision tree based GPS signal reception classification algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 86: 105942. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105942 [10] 刘成, 李芳. 不同卫星定位加权方法的比较与分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2018, 43(8): 39-44.LIU C, LI F. Comparison and analysis of different GNSS weighting methods[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2018, 43(8): 39-44(in Chinese). [11] 付红波. 城市复杂环境下不同加权模型对动态SPP定位性能影响分析[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(3): 139-143.FU H B. Analysis of the influence of different weighted models on dynamic SPP positioning performance in urban complex environment[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(3): 139-143(in Chinese). [12] SUN R, WANG G Y, CHENG Q, et al. Improving GPS code phase positioning accuracy in urban environments using machine learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(8): 7065-7078. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3037074 [13] SUN R, ZHANG Z X, CHENG Q, et al. Pseudorange error prediction for adaptive tightly coupled GNSS/IMU navigation in urban areas[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 26(1): 28. [14] SUN R, FU L X, CHENG Q, et al. Resilient pseudorange error prediction and correction for GNSS positioning in urban areas[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(11): 9979-9988. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3235483 [15] SONG B, MA X D, ZHANG S B. Analysis of BDS satellite orbit periodicity[J]. GNSS World of China, 2016, 41(5): 47-50. [16] 程琦, 胡杰, 王均晖, 等. 基于数据驱动的无人机加权最小二乘定位算法[J]. 指挥信息系统与技术, 2020, 11(6): 76-80.CHENG Q, HU J, WANG J H, et al. Weighted least square positioning algorithm of UAV based on data drive[J]. Command Information System and Technology, 2020, 11(6): 76-80(in Chinese). [17] 韩清清. GNSS接收机自主完好性监测算法优化及性能分析[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020.HAN Q Q. Optimization and performance analysis of autonomous integrity monitoring algorithm for GNSS receiver[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2020(in Chinese). [18] 施颖. 面向非高斯噪声条件的列车卫星定位完好性监测方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2019.SHI Y. Research on integrity monitoring method for satellite based train positioning under non-gaussian noise conditions[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: