Railway panoramic segmentation based on recursive gating enhancement and pyramid prediction
-
摘要:
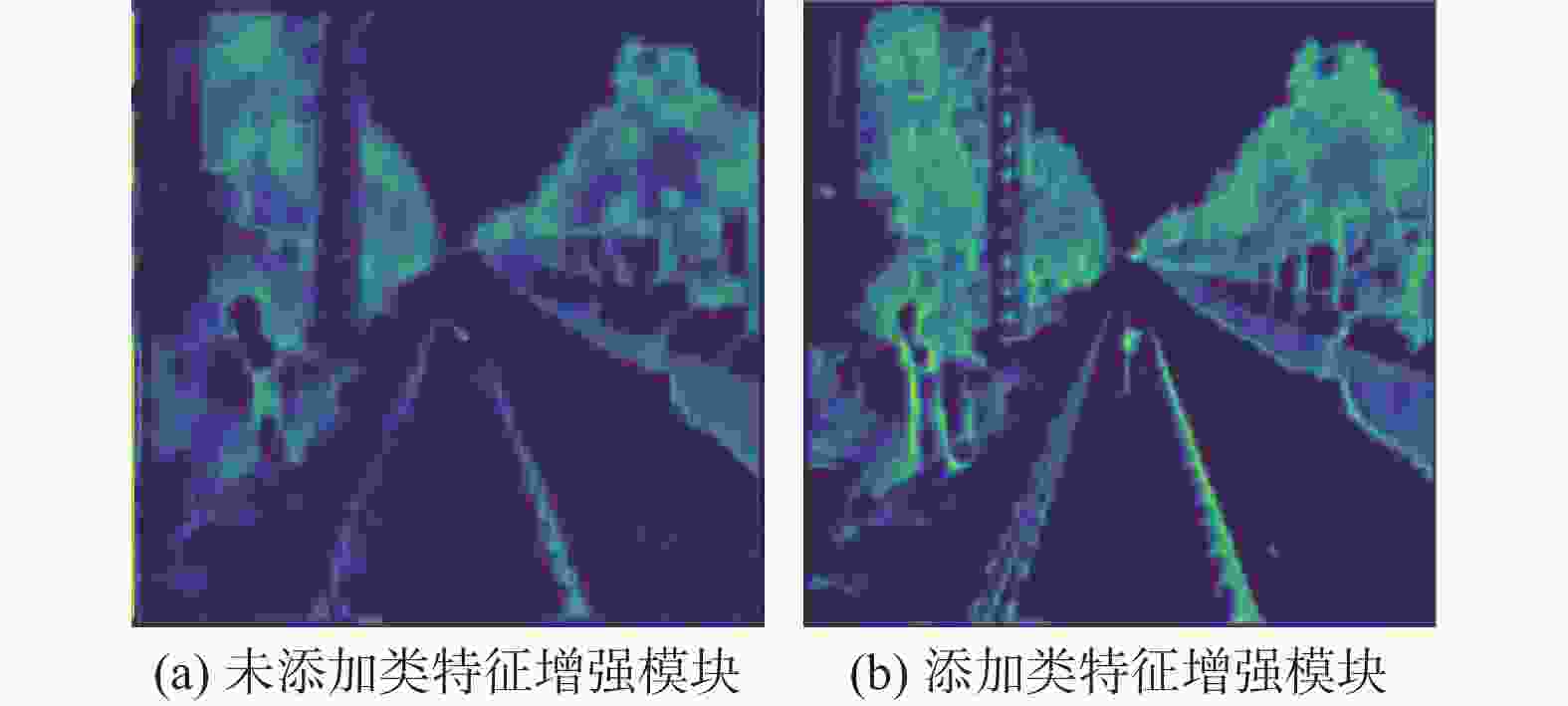
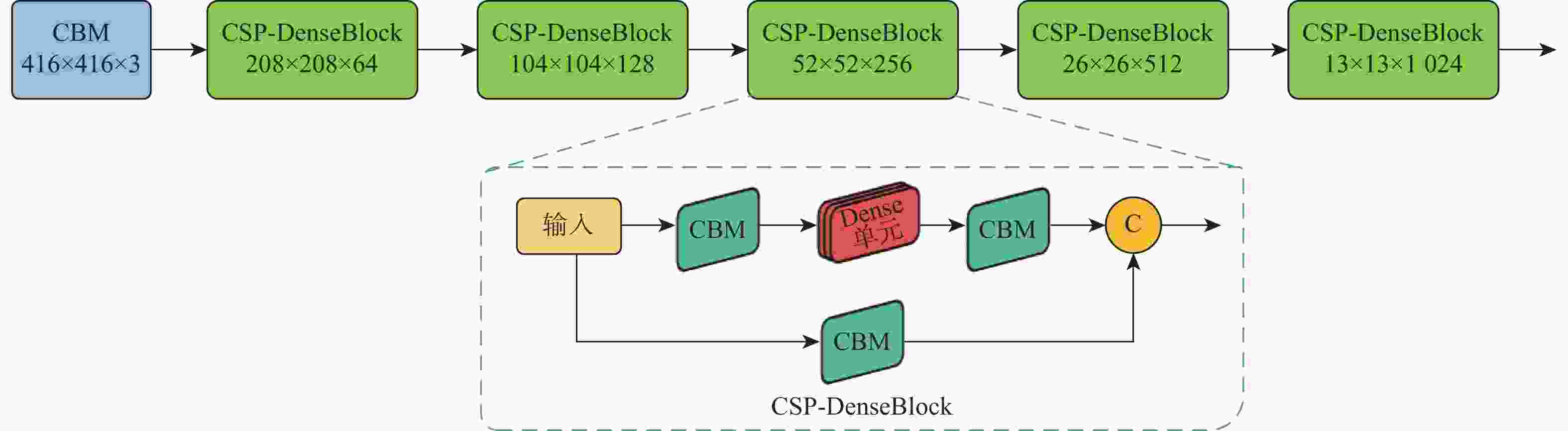
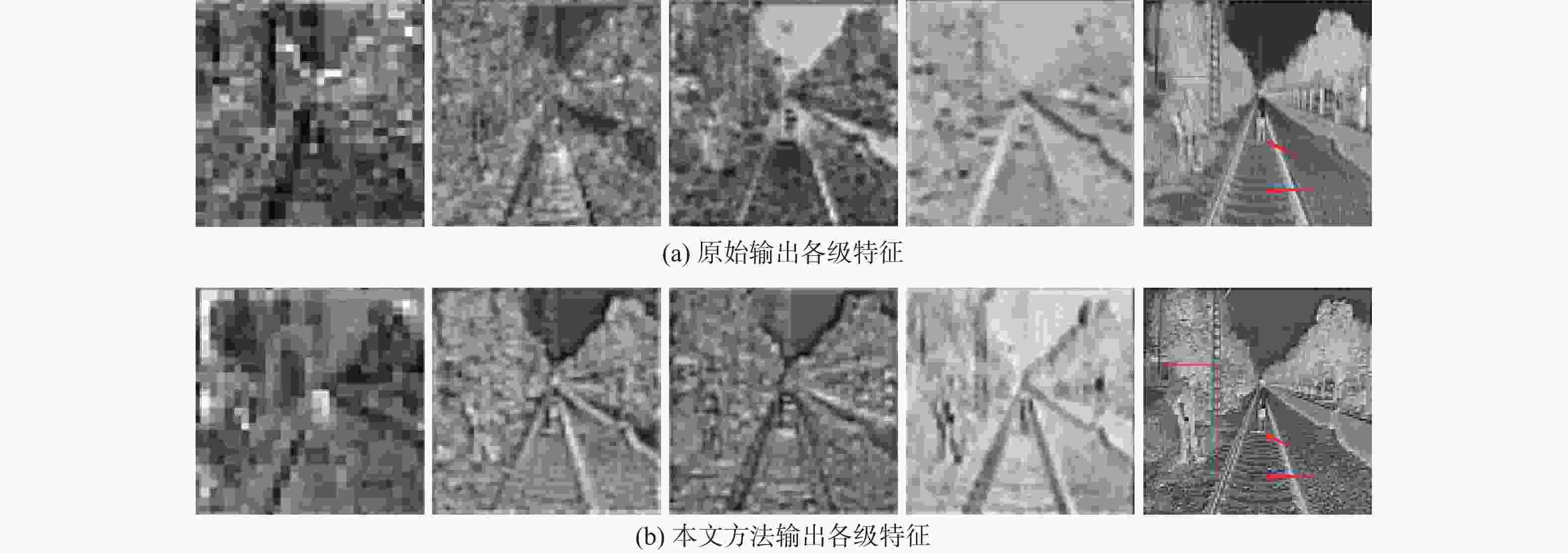
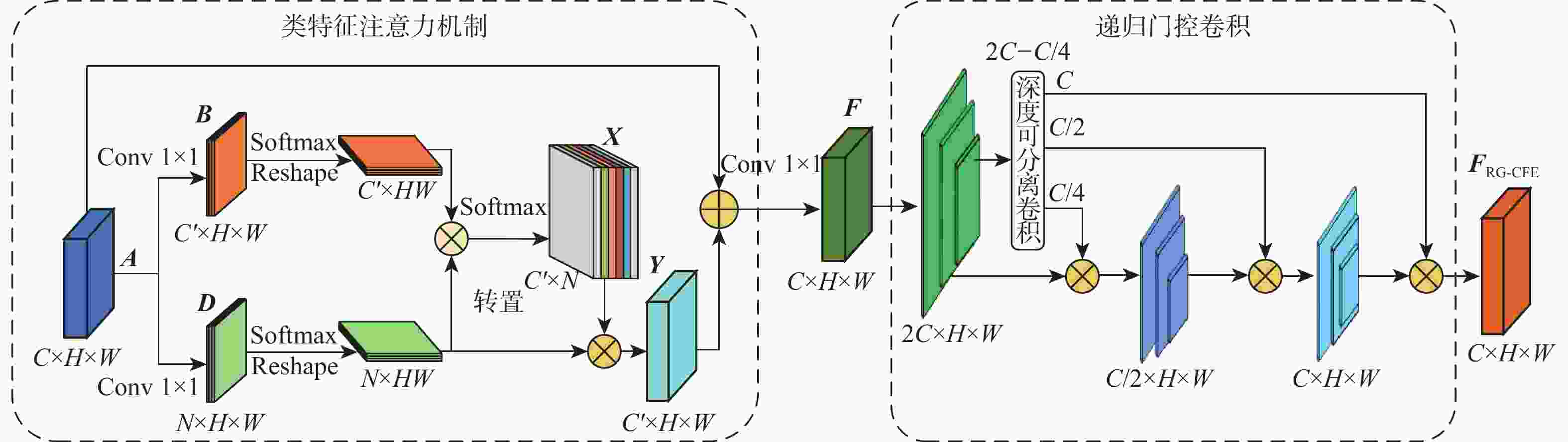
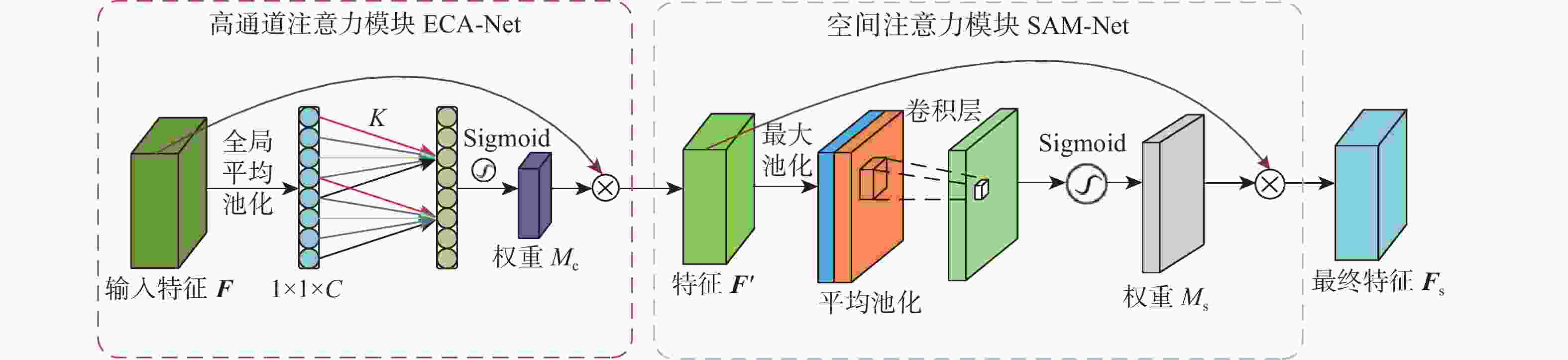
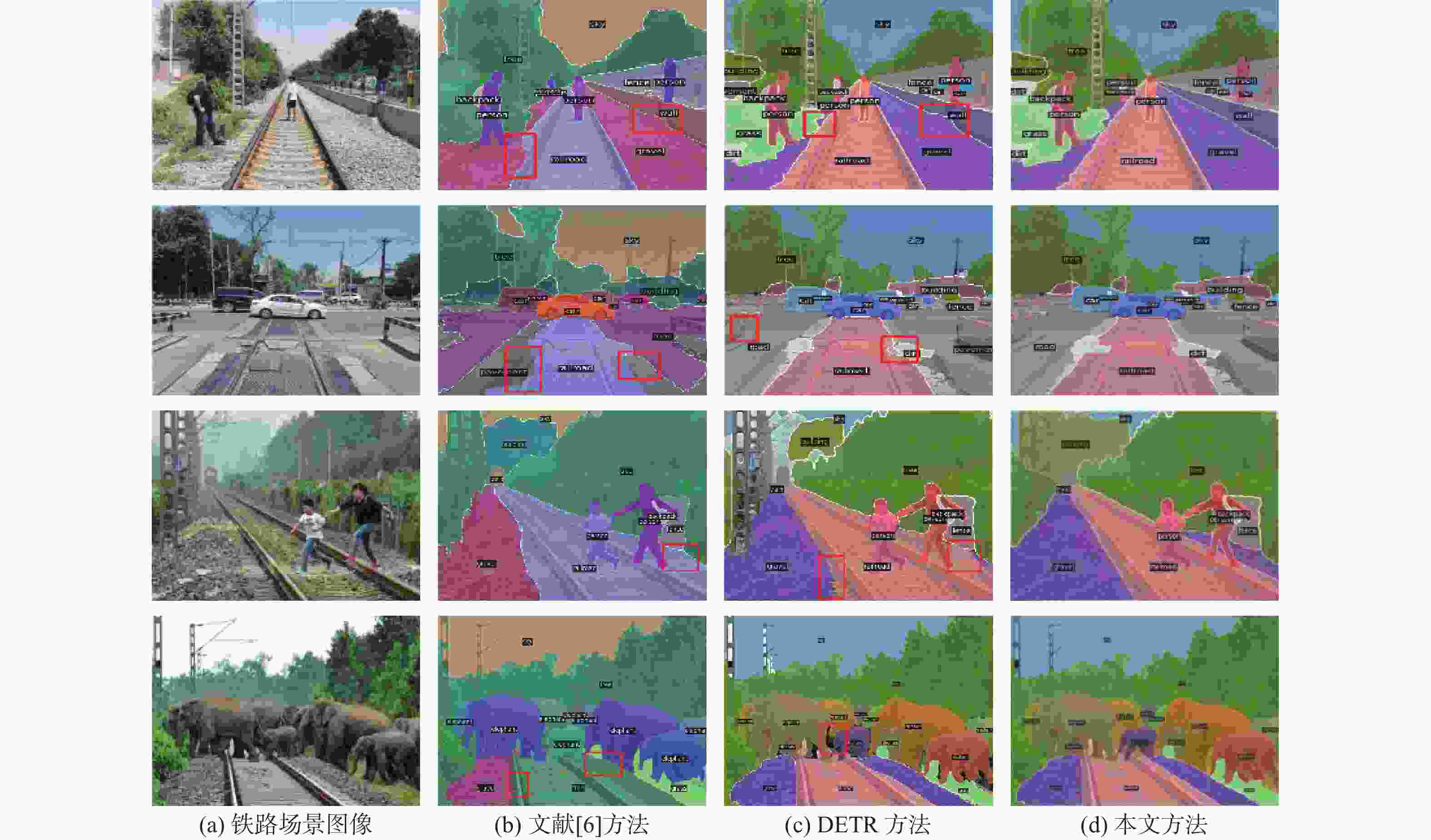
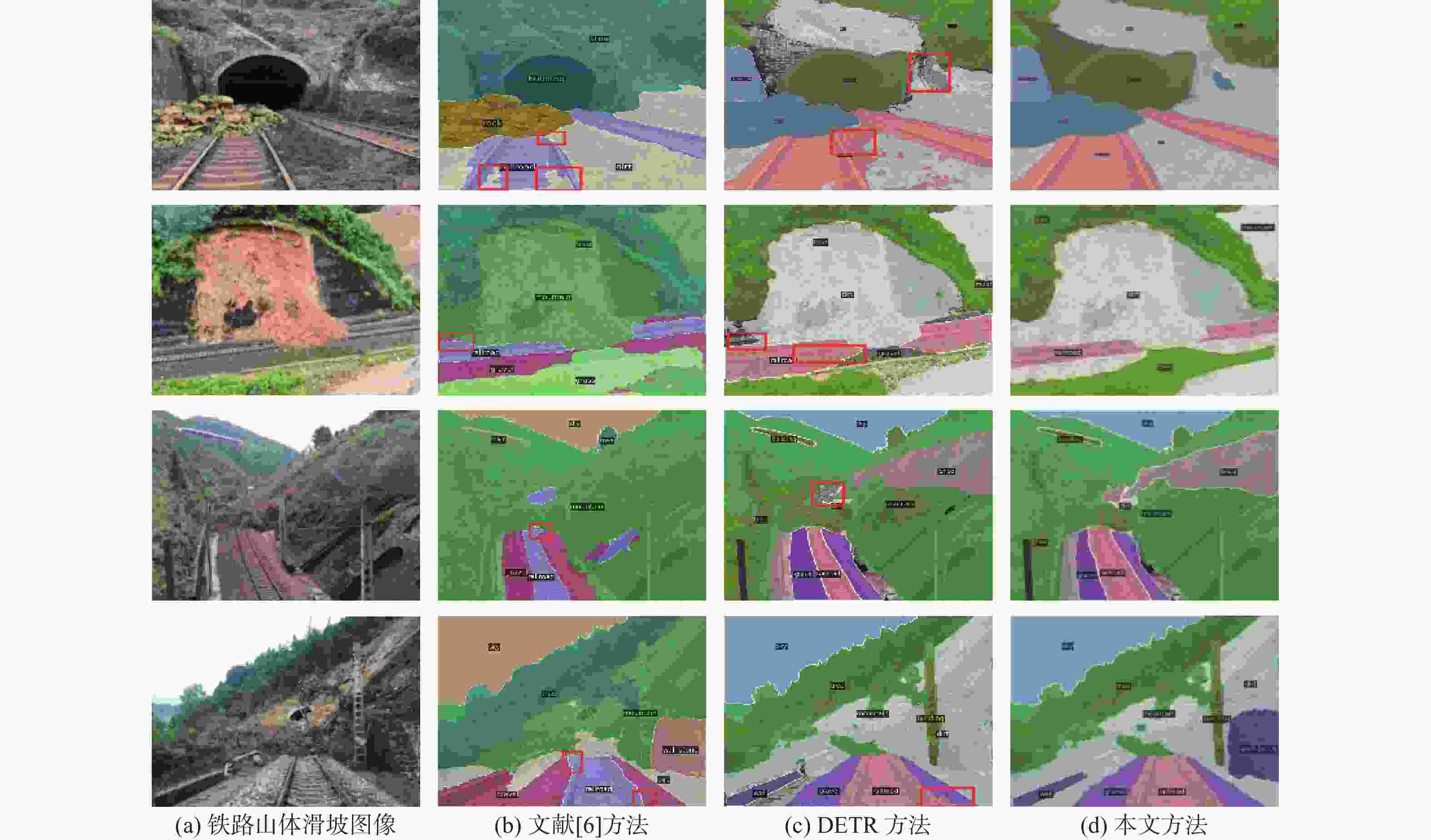
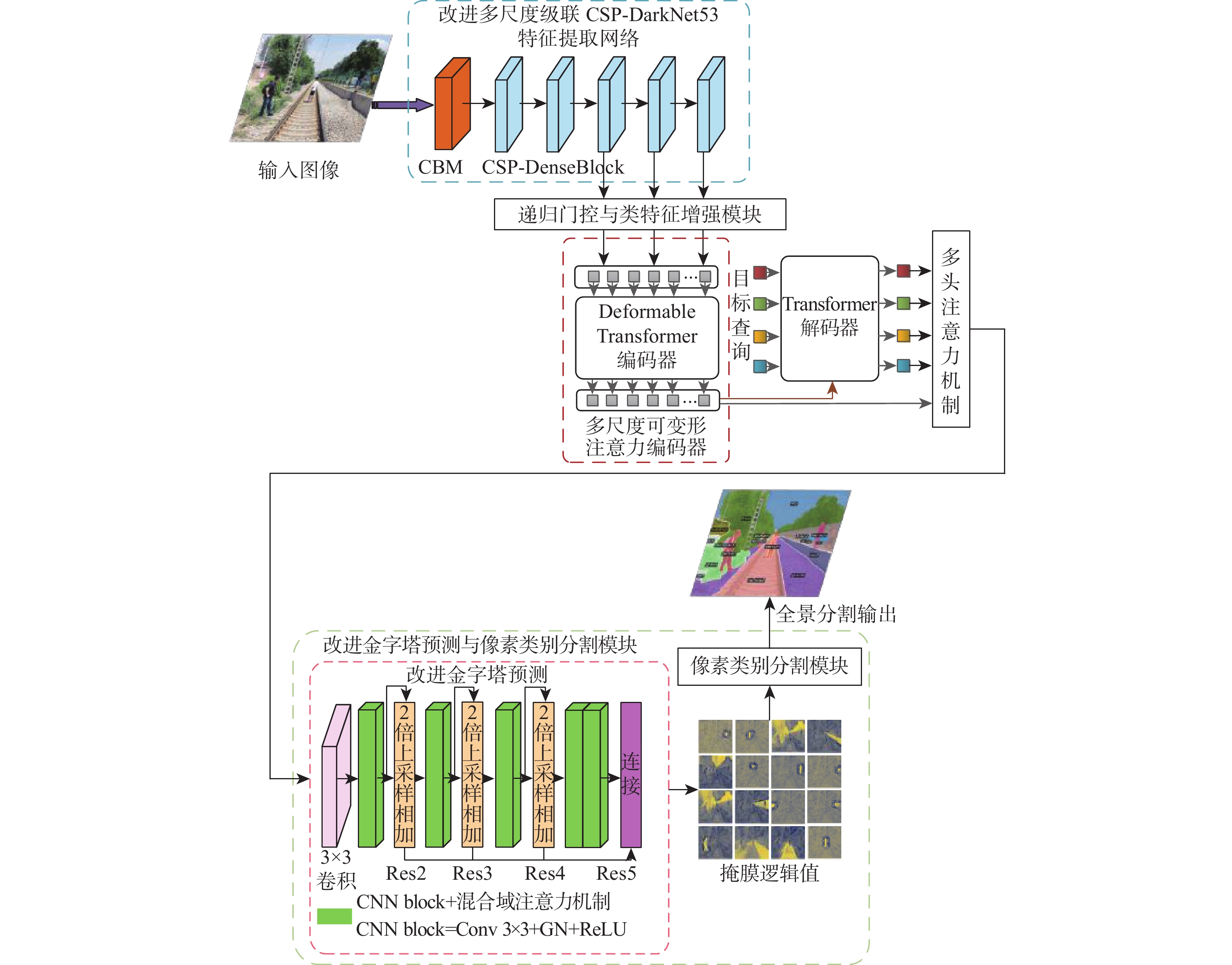
针对高速铁路场景全景分割时存在目标特征提取不充分、边缘轮廓分割模糊等问题,提出了一种递归门控增强与金字塔预测的铁路全景分割网络。在DETR模型的基础上,构建改进多尺度级联CSP-DarkNet53特征提取网络,提升对不同尺度的铁路场景目标特征提取能力;提出递归门控与类特征增强模块,获取更丰富的边缘特征信息,增强对边缘轮廓信息的提取和分割的能力;将多尺度可变形注意力引入编码骨干网络中,进一步捕获多尺度上下文信息,减少分割细节特征丢失;通过改进金字塔预测与像素类别分割模块,实现铁路全景的分割输出。实验结果表明:相比于原始DETR模型,所提方法的全景分割质量指标PQ提升了7.4%,前景实例目标评价指标PQTh提升了9.7%,背景填充区域质量评价指标PQSt提升了6.6%。所提方法在铁路场景下图像全景分割具有较好的性能,主观评价均优于对比方法。
Abstract:A recursive gated enhancement and pyramid prediction railway panoramic segmentation network is proposed to address the issues of insufficient target feature extraction and blurred edge contour segmentation in high-speed railway scene panoramic segmentation. On the basis of the DETR panoramic segmentation model, firstly, an improved multi-scale cascaded CSP-DarkNet53 feature network is constructed to enhance the ability to extract target features from railway scenes of different scales. Then, to improve the ability to extract and segment edge contour information and acquire richer edge feature information, a recursive gating and class feature augmentation module is proposed. Then, deformable attention is introduced into the coding backbone network to further capture context information and reduce the loss of segmentation details. Finally, by improving the pyramid prediction and pixel category segmentation module, the segmentation output of the railway panoramic view is achieved. The suggested approach enhances the original DETR model’s panorama segmentation quality index PQ by 7.4%, the foreground instance target’s panoramic quality index PQTh by 9.7%, and the background-filled area’s panoramic quality index PQSt by 6.6%, according to experimental data. The proposed method has good performance in panoramic image segmentation in railway scenes, and its subjective evaluation is superior to the comparison method.
-
Key words:
- panoramic segmentation /
- DETR /
- recursive gating enhancement /
- pyramid prediction /
- high-speed railway
-
表 1 不同全景分割方法性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different panoramic segmentation methods
% 方法 PQ PQTh PQSt 文献[6] 48.4 52.6 41.0 DETR 47.2 51.7 40.3 本文 54.6 61.4 46.9 表 2 模型消融实验比较
Table 2. Comparison of ablation experimental of model
基准 多尺度级联
CSP-DarkNet53
特征提取网络递归门控
与类特征
增强模块多尺度可
变形注意力
编码器改进金字塔
预测网络PQ/% √ 47.2 √ √ 48.5 √ √ √ 51.1 √ √ √ √ 52.5 √ √ √ √ √ 54.6 表 3 模型计算量对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparative experiment results of model calculation
方法 计算量 文献[6] 157 GFLOPs DETR 93 GFLOPs 本文 223 GFLOPs 注:GFLOPs为模型计算量的标准单位,表示10亿次浮点运算。 -
[1] 陈永, 王镇, 周方春. 空间定位与特征泛化增强的铁路异物跟踪检测[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2025, 51(1): 9-18.CHEN Y, WANG Z, ZHOU F C. Infrared railway foreign objects tracking based on spatial location and feature generalization enhancement[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2025, 51(1): 9-18(in Chinese). [2] LI C, XIE Z Y, QIN Y, et al. A multi-scale image and dynamic candidate region-based automatic detection of foreign targets intruding the railway perimeter[J]. Measurement, 2021, 185: 109853. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109853 [3] 路通, 余祖俊, 郭保青, 等. 网状多尺度与双向通道注意力的铁路场景语义分割[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2023, 23(2): 233-241.LU T, YU Z J, GUO B Q, et al. Semantic segmentation of railway scene based on reticulated multi-scale and bidirectional channel attention[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2023, 23(2): 233-241(in Chinese). [4] KIRILLOV A, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Panoptic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9396-9405. [5] KIRILLOV A, GIRSHICK R, HE K M, et al. Panoptic feature pyramid networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6392-6401. [6] ZHANG W, PANG J, CHEN K, et al. K-Net: towards unified image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2021-10-01)[2023-07-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.14855?context=cs.AI. [7] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with Transformers[C]//Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 213-229. [8] CHENG B, SCHWING A G, KIRILLOV A. Per-pixel classifica tion is not all you need for semantic segmentation[EB/OL]. (2021-10-31)[2023-07-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278?context=cs. [9] WANG H Y, ZHU Y K, ADAM H, et al. MaX-DeepLab: end-to-end panoptic segmentation with mask Transformers[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 5459-5470. [10] CHENG B W, COLLINS M D, ZHU Y K, et al. Panoptic-DeepLab: a simple, strong, and fast baseline for bottom-up panoptic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 12472-12482. [11] CHENG B W, MISRA I, SCHWING A G, et al. Masked-attention mask Transformer for universal image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1280-1289. [12] YANG T J, COLLINS M D, ZHU Y, et al. DeeperLab: single-shot image parser[C]//Proceedings of theIEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1902-5093. [13] 毛琳, 任凤至, 杨大伟, 等. 实例特征深度链式学习全景分割网络[J]. 光学精密工程, 2020, 28(12): 2665. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2665MAO L, REN F Z, YANG D W, et al. INFNet: deep instance feature chain learning network for panoptic segmentation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 2665(in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2665 [14] 宁欣, 田伟娟, 于丽娜, 等. 面向小目标和遮挡目标检测的脑启发CIRA-DETR全推理方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(10): 2080-2092. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.02080NING X, TIAN W J, YU L N, et al. Brain-inspired CIRA-DETR full inference model for small and occluded object detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(10): 2080-2092(in Chinese). doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.02080 [15] CHEN Y T, CHEN S F. Localizing plucking points of tea leaves using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 171: 105298. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105298 [16] ZHAO Z Q, ZHENG P, XU S T, et al. Object detection with deep learning: a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(11): 3212-3232. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2876865 [17] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [18] WANG Z M, WANG J S, YANG K, et al. Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images based on a class feature attention mechanism fused with Deeplabv3+[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 2022, 158: 104969. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104969 [19] RAO Y M, ZHAO W L, TANG Y S, et al. HorNet: efficient high-order spatial interactions with recursive gated convolutions[EB/OL]. (2022-10-11)[2023-07-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2207.14284v3. [20] 冷冰, 冷敏, 常智敏, 等. 基于Transformer结构的深度学习模型用于外周血白细胞检测[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2023, 44(5): 113-120.LENG B, LENG M, CHANG Z M, et al. Deep learning model based on Transformer architecture for peripheral blood leukocyte detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2023, 44(5): 113-120(in Chinese). [21] ZHU X, SU W, LU L, et al. Deformable DETR: deformable Transformers for end-to-end object detection[EB/OL]. (2021-05-18)[2023-07-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.04159?context=cs. [22] 李飞, 胡坤, 张勇, 等. 基于混合域注意力YOLOv4的输送带纵向撕裂多维度检测[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2022, 56(11): 2156-2167.LI F, HU K, ZHANG Y, et al. Multi-dimensional detection of longitudinal tearing of conveyor belt based on YOLOv4 of hybrid domain attention[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2022, 56(11): 2156-2167(in Chinese). [23] WANG Q L, WU B G, ZHU P F, et al. ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11531-11539. [24] YING X Y, WANG Y Q, WANG L G, et al. A stereo attention module for stereo image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 496-500. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2973813 [25] REZATOFIGHI H, TSOI N, GWAK J, et al. Generalized intersection over union: a metric and a loss for bounding box regression[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 658-666. -






 下载:
下载: