-
摘要:
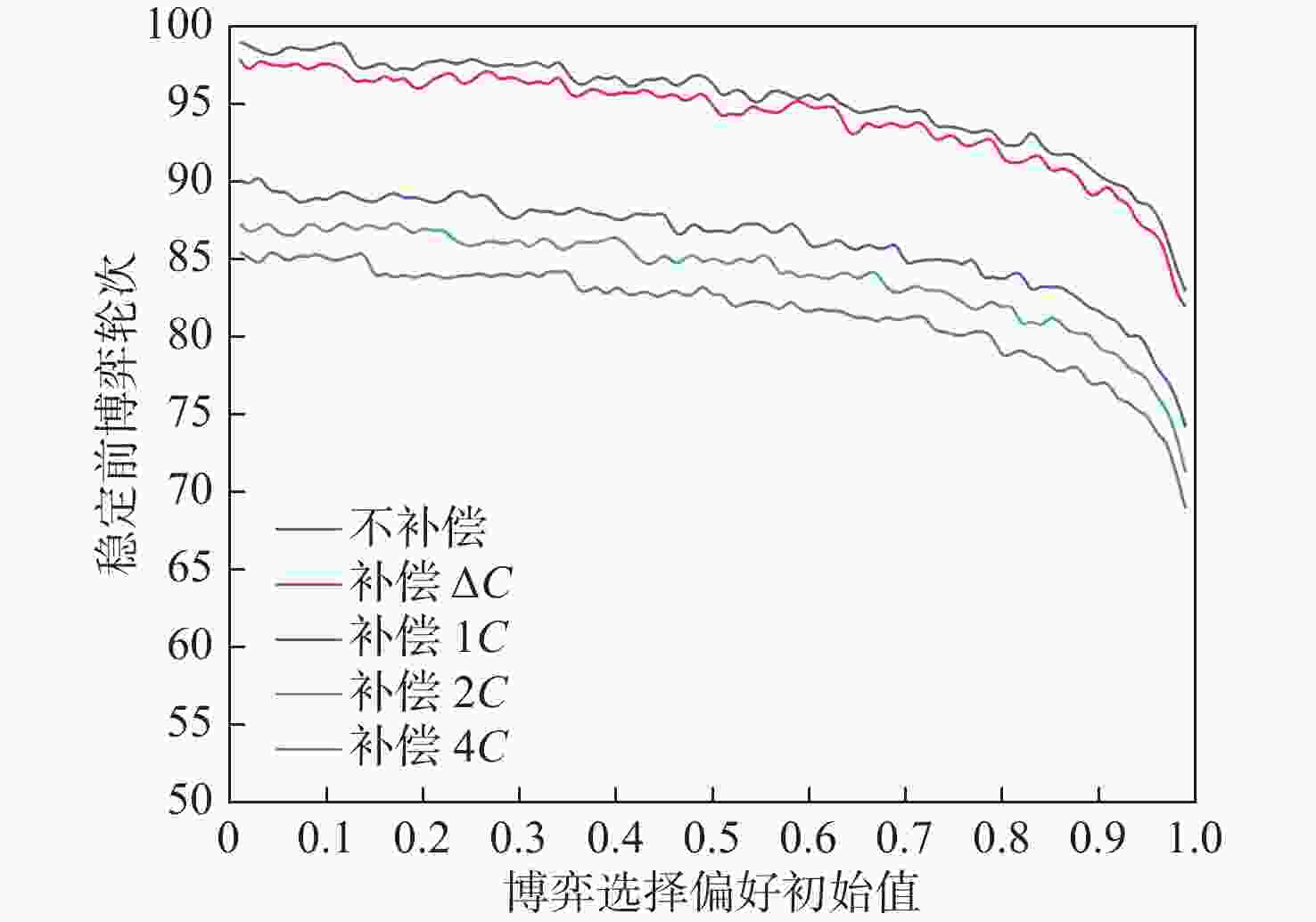
针对航空器自主路径规划问题,提出一种面向航空器自主冲突解脱的博弈协调方法,并研究了该方法在航空器各类博弈策略下达成均衡状态所需的计算周期。基于演化博弈论构建航空器冲突解脱博弈模型,通过计算博弈轮次间的复制动态方程,促进航空器迭代进化其博弈选择偏好,加速博弈系统达到局部均衡状态;构建雅可比矩阵分析博弈中各局部均衡解的稳定性,并证明博弈系统中有且仅有一个局部均衡解稳定,参与博弈的各航空器均会趋向于该均衡解;使用ZSSSAR01扇区空域数据进行仿真实验,设定多种航空器博弈策略并分析各策略达到均衡状态所需的博弈时间。仿真结果表明:理性博弈策略具有较高的博弈效率,在非极端情况下平均仅需5.31轮次博弈即达到均衡;激进和保守博弈策略分别会加快和减慢博弈均衡过程;不合作博弈策略会显著减慢博弈均衡过程,平均需要110.53轮次博弈,不合作博弈者进行的运行成本补偿策略则会缓解该趋势(平均需要86.87轮次)。
Abstract:To solve the problem of autonomous path planning for aircraft, this article proposes a game coordination method for aircraft autonomous conflict resolution, and discusses the game efficiency of this method under various game strategy settings for aircraft. First, based on evolutionary Game theory, a game model of aircraft conflict resolution is constructed. By calculating the replication dynamic equation between adjacent game rounds, the aircraft iterative evolution of its game selection preference is promoted, and the game system is accelerated to reach Partial equilibrium; Construct a Jacobian matrix and determinant to analyze the stability of each Partial equilibrium solution in the game, and prove that there is one and only one Partial equilibrium solution in the game system is stable, and all aircraft participating in the game will tend to this equilibrium solution; Conduct simulation experiments using ZSSSAR01 sector airspace data, set multiple aircraft game strategies, and analyze the game time required for each strategy to reach an equilibrium state. The simulation results show that rational gamers have high game efficiency and can reach equilibrium on average within 5.31 rounds of the game; Radical and conservative gamers will accelerate and slow down the equilibrium process of the game, respectively; Non cooperative gamers will significantly slow down the game equilibrium process, requiring an average of 110.53 rounds of gaming. The operating cost compensation strategy based on non-cooperative gamers will accelerate this process (with an average of 86.87 rounds).
-
表 1 双航空器路径选择决策-成本
Table 1. Dual aircrafts routing decision - cost
路径规划 航空器$ i $成本 航空器$ j $成本 航空器i
规避航空器i
不规避航空器j
规避航空器j
不规避航空器$ j $规避 $ {C_i} + \Delta {C_i} $ $ {C_i} $ $ {C_j} + \Delta {C_j} $ $ \begin{gathered} {C_j} + \Delta {C_j} + {\varphi _j} \end{gathered} $ 航空器$ j $不规避 $ \begin{gathered} {C_i} + \Delta {C_i} + {\varphi _i} \end{gathered} $ $ {D_i} $ $ {C_j} $ $ {D_j} $ 表 2 局部均衡状态稳定性判别
Table 2. Stability discrimination of local equilibrium state
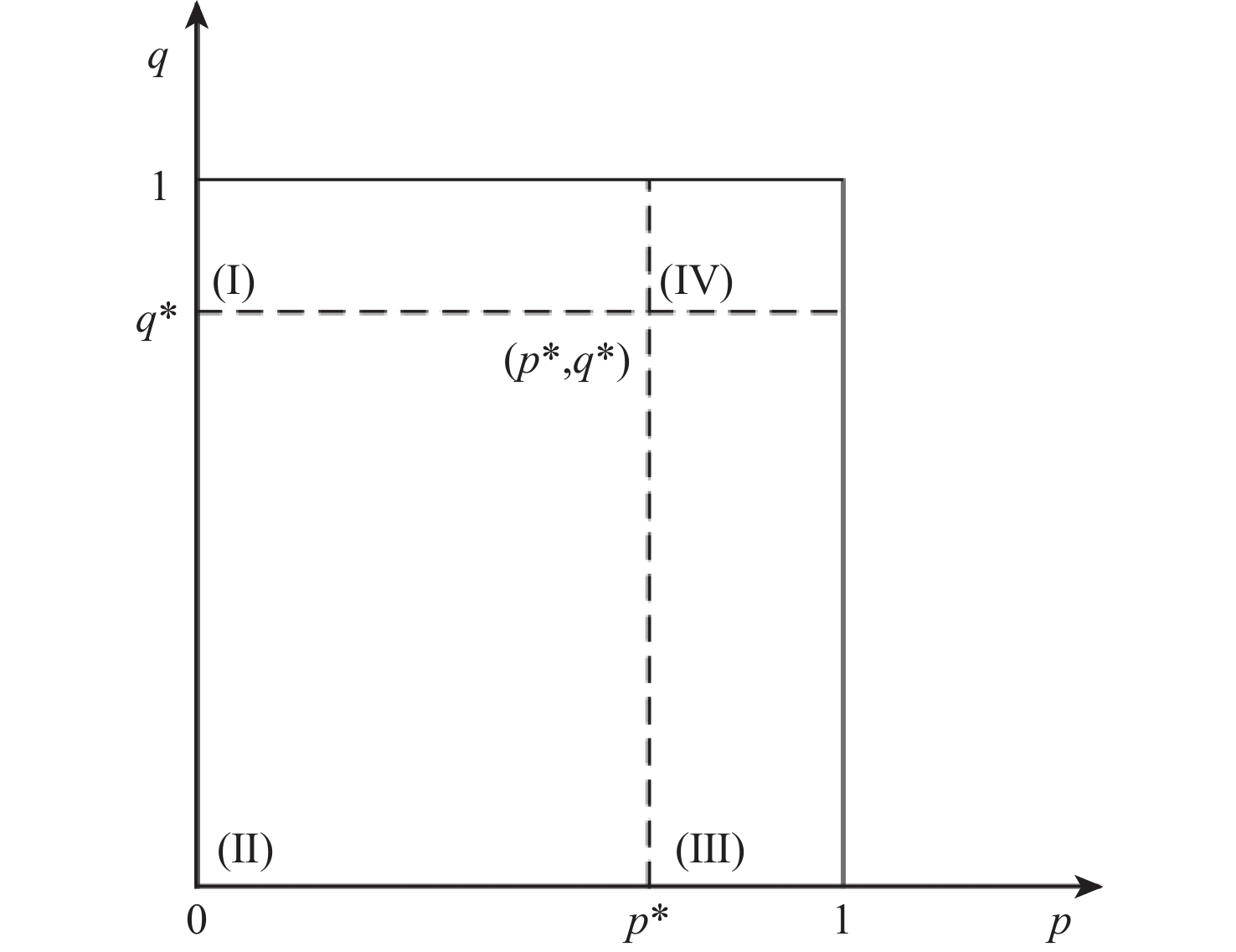
$ (p,q) $ $ \left| {\boldsymbol{J}} \right| $ $ \left| {\boldsymbol{J}} \right| $的正负性 $ {\mathrm{tr}}({\boldsymbol{J}}) $ $ {\mathrm{tr}}({\boldsymbol{J}}) $的正负性 稳定状态 $ (0,0) $ 0 0 不稳定 $ (0,1) $ 0 $ 2({C_j} + \Delta {C_j} - {D_j} + {\varphi _j}) $ 负 不稳定 $ (1,0) $ 0 $ 2({C_i} + \Delta {C_i} - {D_i} + {\varphi _i}) $ 负 不稳定 $ (1,1) $ $ 4\Delta {C_i}\Delta {C_j} - {D_i}{D_j} - {C_i}{C_j} - {\varphi _i}{\varphi _j} $ 负 $ 2\Delta {C_i} + 2\Delta {C_j} $ 正 不稳定 $ (p*,q*) $ $ - \dfrac{{[({D_i} - {C_i} - {\varphi _i} - \Delta {C_i})({D_j} - {C_j} - {\varphi _j} - \Delta {C_j})]^2}}{{({D_i} - {C_i} - {\varphi _i})({D_j} - {C_j} - {\varphi _j})}} $ 负 0 鞍点 表 3 激进和保守博弈者在不同初始状态所需博弈轮次
Table 3. Number of game rounds required by aggressive and conservative players in different initial states
$ ({p_0},{q_0}) $ 正常博弈者所需轮次 激进博弈者所需轮次 激进较正常博弈者的变化比例/% 保守博弈者所需轮次 保守较正常博弈者的变化比例/% (0.01,0.01) 113.95 81.59 −28.39 160.04 40.44 (0.10,0.10) 18.85 13.48 −28.48 28.01 48.59 (0.20,0.20) 13.25 10.29 −22.34 18.91 42.71 (0.30,0.30) 10.34 7.64 −26.11 16.09 55.60 (0.40,0.40) 8.50 7.41 −12.82 11.72 37.88 (0.50,0.50) 7.74 5.79 −25.19 9.64 24.54 (0.60,0.60) 7.46 5.28 −29.22 8.98 20.37 (0.70,0.70) 5.98 5.01 −16.38 7.88 31.77 (0.80,0.80) 5.23 4.04 −22.75 6.83 30.59 (0.90,0.90) 5.08 3.59 −29.33 5.96 17.32 (0.99,0.99) 3.62 3.29 −9.12 4.21 16.29 表 4 不合作博弈者在不同初始状态所需博弈轮次
Table 4. Number of rounds required by non-cooperative players in different initial states
$ {q_0} $ 正常博弈者$ {p_0} = {q_0} $ 不合作博弈者$ {p_0} = p = 0.9 $ 不合作博弈者$ {p_0} = p = 0.7 $ 不合作博弈者$ {p_0} = p = 0.5 $ 不合作博弈者$ {p_0} = p = 0.3 $ 0.01 113.95 18.43 42.50 99.60 301.03 0.10 18.85 16.42 41.15 99.48 299.33 0.20 13.25 16.93 41.47 98.61 298.44 0.30 10.34 17.29 42.00 97.98 297.18 0.40 8.50 16.99 41.77 97.89 294.66 0.50 7.74 16.78 41.67 96.83 293.12 0.60 7.46 17.78 41.12 96.05 290.49 0.70 5.98 17.58 41.31 94.74 288.53 0.80 5.23 16.43 40.27 93.13 283.68 0.90 5.08 16.76 39.70 90.46 275.83 0.99 3.62 15.56 35.95 83.17 252.16 表 5 成本补偿策略在不同初始状态所需博弈轮次
Table 5. Number of game rounds required by cost compensation strategy in different initial states
$ {q_0} $ 不合作博弈者,不补偿 不合作博弈者,补偿$ \Delta {C_j} $ 不合作博弈者,补偿$ {C_j} $ 不合作博弈者,补偿$ 2{C_j} $ 不合作博弈者,补偿$ 4{C_j} $ 0.01 99.60 98.17 90.19 87.68 86.22 0.10 99.48 98.47 89.59 86.99 85.17 0.20 98.61 96.17 89.12 87.99 84.29 0.30 97.98 97.25 88.24 86.41 84.30 0.40 97.89 96.16 87.52 86.84 83.80 0.50 96.83 95.11 87.29 85.29 83.23 0.60 96.05 94.94 86.16 84.30 82.14 0.70 94.74 93.51 84.89 83.43 81.29 0.80 93.13 92.21 84.17 82.36 79.01 0.90 90.46 89.28 81.99 79.34 77.16 0.99 83.17 82.95 74.69 72.15 69.54 表 6 碰撞损失成本调整在不同初始状态所需博弈轮次
Table 6. Number of rounds required by collision loss cost adjustment in different initial states
$ {q_0} $ 碰撞损失成本为$ D $ 碰撞损失成本为$ 0.9D $ 碰撞损失成本为$ 0.7D $ 碰撞损失成本为$ 0.5D $ 碰撞损失成本为$ 0.3D $ 碰撞损失成本为$ 0.1D $ 0.01 113.95 118.82 134.53 159.93 201.07 328.30 0.10 18.85 20.34 23.03 27.31 34.71 57.47 0.20 13.25 13.08 15.58 18.23 23.28 39.39 0.30 10.34 10.23 12.63 14.79 19.15 31.97 0.40 8.50 9.52 10.41 14.10 16.40 27.87 0.50 7.74 8.92 8.83 11.23 16.12 24.47 0.60 7.46 7.36 7.83 10.69 13.97 20.91 0.70 5.98 6.34 7.32 8.79 12.49 18.95 0.80 5.23 5.82 7.26 7.64 10.57 15.12 0.90 5.08 4.20 5.86 7.93 8.05 12.07 0.99 3.62 3.25 4.22 3.98 5.33 5.51 -
[1] International Civil Aviation Organization. Global air traffic management operational concept[Z]. Montreal: ICAO, 2005. [2] Federal Aviation Administration. NextGen implementation plan[Z]. Washington, D. C. : FAA, 2017. [3] 蔡开泉, 赵鹏. 空中交通自主间隔管控技术研究[J]. 南京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2022, 54(4): 688-699.CAI K Q, ZHAO P. Key technologies on air traffic self-separation management[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2022, 54(4): 688-699(in Chinese). [4] HAO S Q, CHENG S W, ZHANG Y P. A multi-aircraft conflict detection and resolution method for 4-dimensional trajectory-based operation[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2018, 31(7): 1579-1593. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2018.04.017 [5] 陈雨童, 胡明华, 杨磊, 等. 受限航路空域自主航迹规划与冲突管理技术[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(9): 324045.CHEN Y T, HU M H, YANG L, et al. Autonomous trajectory planning and conflict management technology in restricted airspace[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(9): 324045(in Chinese). [6] CHEN Y T, HU M H, YANG L. Autonomous planning of optimal four-dimensional trajectory for real-time en-route airspace operation with solution space visualisation[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2022, 140: 103701. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2022.103701 [7] DEGAS A, KADDOUM E, GLEIZES M P, et al. Cooperative multi-agent model for collision avoidance applied to air traffic management[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 102: 104286. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104286 [8] STRYSZOWSKI M, LONGO S, D’ALESSANDRO D, et al. A framework for self-enforced optimal interaction between connected vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(10): 6152-6161. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2988150 [9] WANG H, MENG Q, CHEN S K, et al. Competitive and cooperative behaviour analysis of connected and autonomous vehicles across unsignalised intersections: a game-theoretic approach[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2021, 149: 322-346. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2021.05.007 [10] 马庆禄, 聂振宇. 基于博弈论的无信号交叉口冲突消解方法[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 35(10): 144-151.MA Q L, NIE Z Y. Conflict resolution method based on game theory at unsignalized intersection[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2021, 35(10): 144-151(in Chinese). [11] 雷爱国, 胡启洲, 李慧慧, 等. 无信号交叉口过街行人与司机演化博弈行为研究[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2020, 44(6): 705-714.LEI A G, HU Q Z, LI H H, et al. Evolutionary game behavior between crossing pedestrians and drivers at unsignalized intersections[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2020, 44(6): 705-714(in Chinese). [12] AGNEL TONY L, GHOSE D, CHAKRAVARTHY A. Correlated-equilibrium-based unmanned aerial vehicle conflict resolution[J]. Journal of Aerospace Information Systems, 2022, 19(4): 283-304. doi: 10.2514/1.I011001 [13] 张宏宏, 甘旭升, 孙静娟, 等. 针对合作型无人机的最优防相撞策略[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(4): 290-297.ZHANG H H, GAN X S, SUN J J, et al. Optimal anti-collision strategy for cooperative UAV[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(4): 290-297(in Chinese). [14] ALBABA B M, MUSAVI N, YILDIZ Y. A 3D game theoretical framework for the evaluation of unmanned aircraft systems airspace integration concepts[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 133: 103417. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2021.103417 [15] PANG Y T, ZHAO X Y, HU J M, et al. Bayesian spatio-temporal grAph tRansformer network (B-STAR) for multi-aircraft trajectory prediction[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 249(5): 108998. [16] PARK S G, MENON P K. Game-theoretic trajectory-negotiation mechanism for merging air traffic management[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2017, 40(12): 3061-3074. doi: 10.2514/1.G002716 [17] TANG X M, LU X N, ZHENG P C. Aircraft autonomous separation assurance based on cooperative game theory[J]. Aerospace, 2022, 9(8): 421. doi: 10.3390/aerospace9080421 [18] 韩丹, 蒋豪, 陈亚青. 微分对策理论在配对进近防撞安全间隔研究中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(5): 2617-2623.HAN D, JIANG H, CHEN Y Q. Application of differential game in collision safety limit for paired approach[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(5): 2617-2623(in Chinese). [19] QIAN X W, MAO J F, CHEN C H, et al. Coordinated multi-aircraft 4D trajectories planning considering buffer safety distance and fuel consumption optimization via pure-strategy game[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2017, 81: 18-35. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2017.05.008 [20] 蒋旭瑞, 吴明功, 温祥西, 等. 基于合作博弈的多机飞行冲突解脱策略[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(11): 2482-2489.JIANG X R, WU M G, WEN X X, et al. Conflict resolution of multi-aircraft based on the cooperative game[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(11): 2482-2489(in Chinese). [21] 王红勇, 郭宇鹏. 终端区离场航空器自主路径规划研究[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2025, 51(2): 446-456.WANG H Y, GUO Y P. Research on autonomous path planning of departing aircraft in terminal area[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2025, 51(2): 446-456(in Chinese). [22] FREY E. Evolutionary game theory: theoretical concepts and applications to microbial communities[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2010, 389(20): 4265-4298. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.02.047 [23] International Air Transport Association. 2022 airline safety performance[EB/OL]. (2023-03-07)[2023-07-15]. http://www.iata.org/en/pressroom/2023-releases/2023-03-07-01/. -







 下载:
下载: