-
摘要:
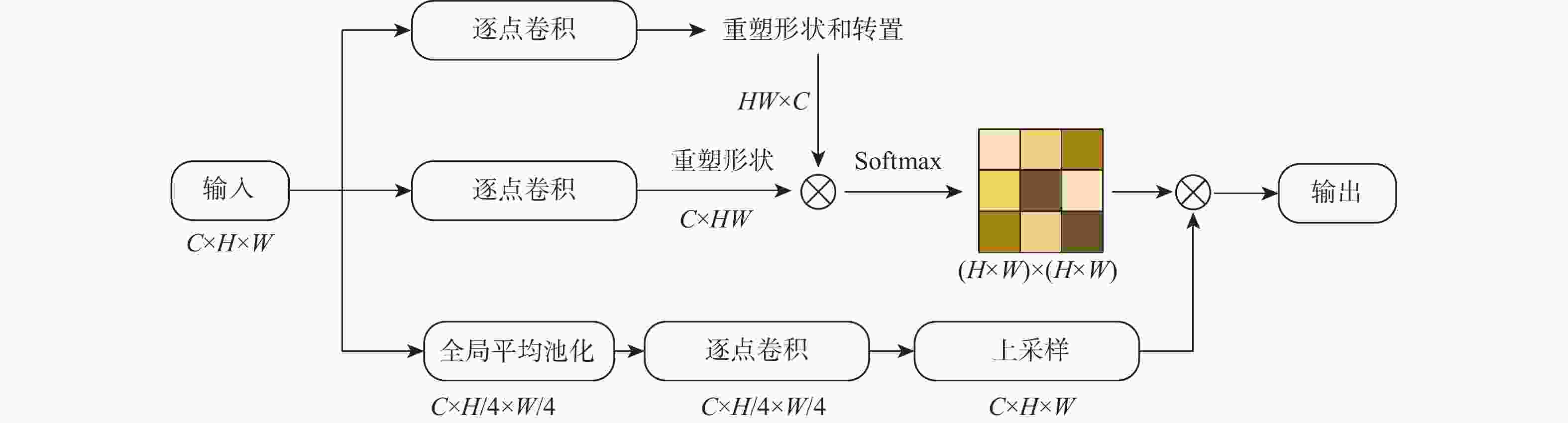
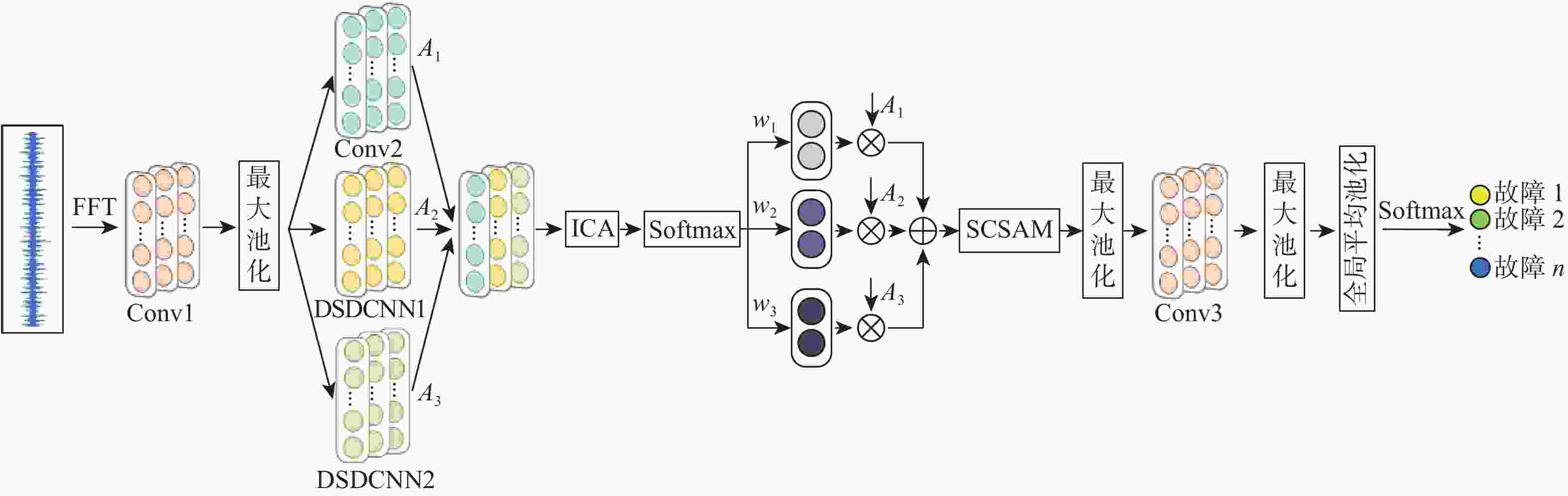
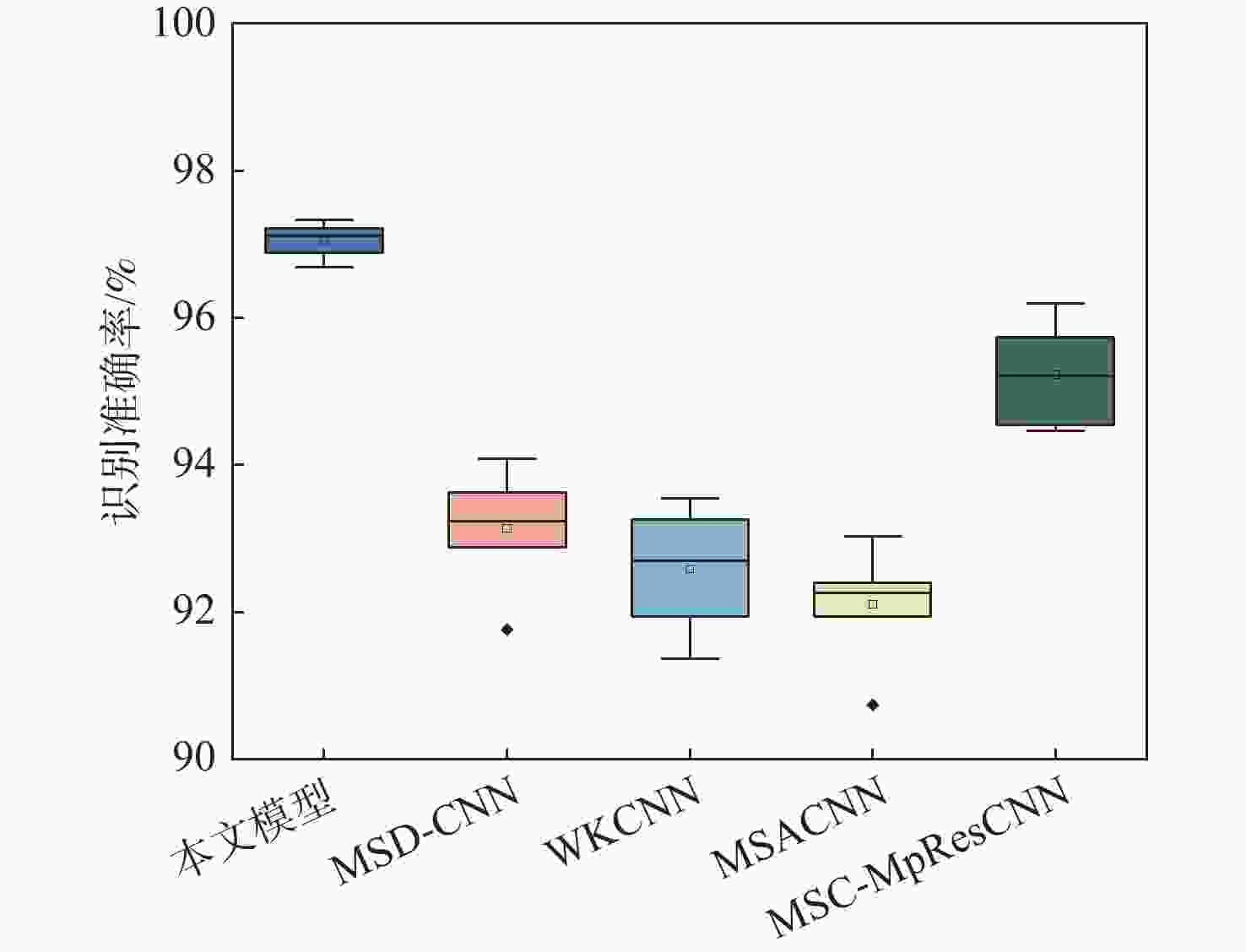
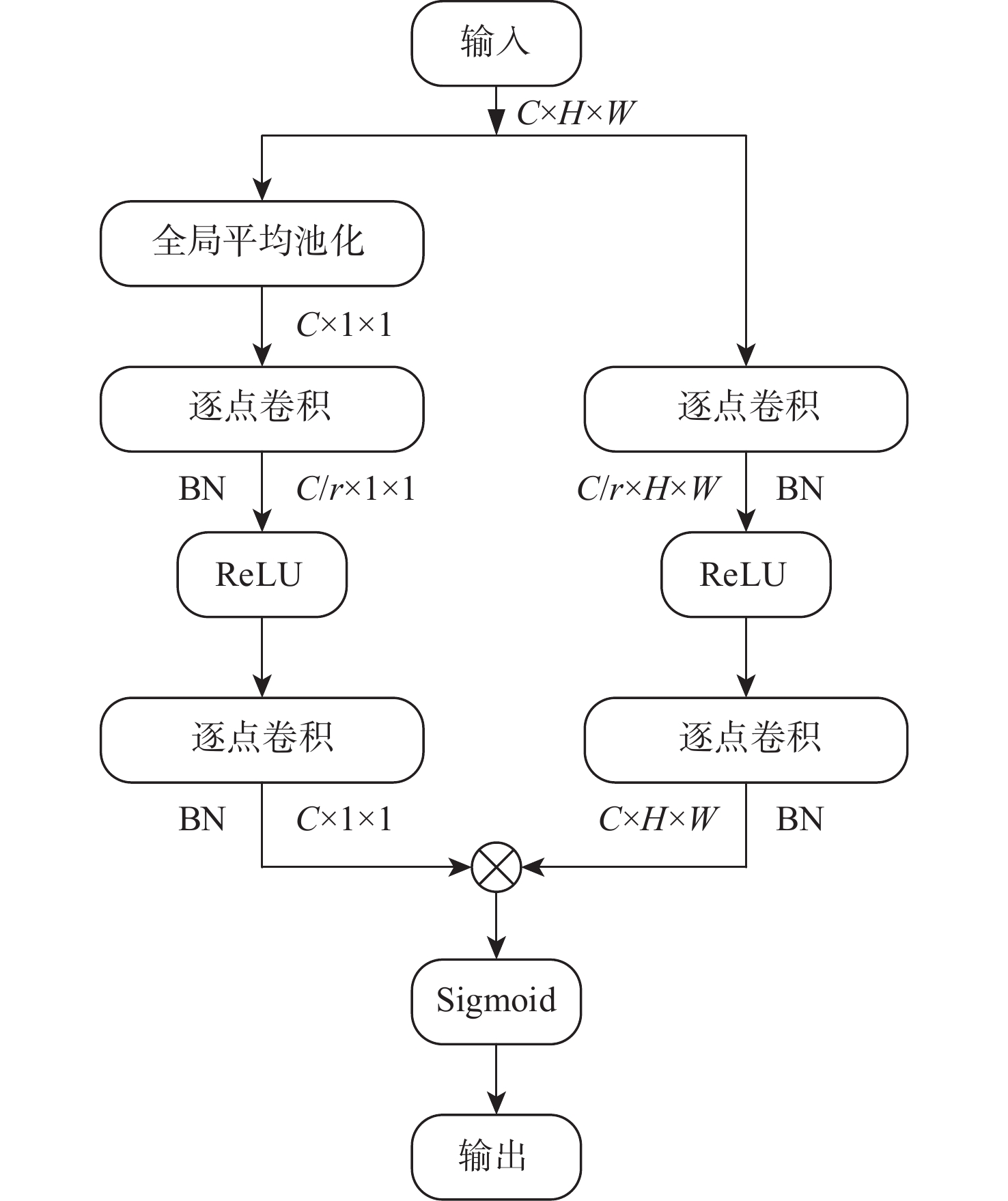
针对传统基于深度学习的轴承故障诊断方法存在抗噪性能差、计算复杂度高和泛化性能不足的问题,提出了一种基于多尺度动态卷积神经网络(MSDCNN)的滚动轴承故障诊断方法。采用傅里叶变换将滚动轴承一维振动信号转换到频域进行表示,并通过宽卷积核进一步提取特征;提出一种多尺度动态卷积结构,利用改进的通道注意力机制,对不同大小的卷积核提取的特征信息赋予不同的权重;设计一种自校准空间注意力机制(SCSAM),将提取的特征信息输入到空间注意力机制中,捕获不同区域的重要程度;通过小卷积核进一步提取特征,利用Softmax分类器进行故障类别分类。使用2种不同数据集验证所提模型的故障诊断性能,实验结果表明:与多尺度深度卷积神经网络(MSD-CNN)、宽卷积核卷积神经网络(WKCNN)等智能模型相比,所提模型在强噪声背景下具有更高的分类精度、更好的泛化能力和更强的鲁棒性。
Abstract:To address the poor anti-noise performance, high computational complexity, and insufficient generalization performance of traditional bearing fault diagnosis methods based on deep learning, this paper proposed a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on multi-scale dynamic convolutional neural network (MSDCNN). Firstly, the one-dimensional vibration signal of the rolling bearing was transformed into frequency domain by Fourier transform, and the features werefurther extracted by wide convolution kernel. Secondly, a multi-scale dynamic convolution structure was presented, and an improved channel attention mechanism wasutilized to assign different weights to the feature information extracted by convolution kernels of different sizes. Then, a self-calibrating spatial attention mechanism (SCSAM) was designed to capture the importance of different regions by inputting the extracted feature information into the spatial attention mechanism. Finally, the features were further extracted by the small convolution kernel, and the Softmax classifier was used to classify faults. Two different data sets were used to verify the fault diagnosis performance of the proposed model. The experimental results show that the proposed model has higher classification accuracy, better generalization ability, and stronger robustness under strong noise background than other intelligent modelssuch as multi-scale deep convolutional neural network (MSD-CNN) and wide convolutional kernel convolutional neural network (WKCNN).
-
表 1 MSDCNN模型的结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of MSDCNN model
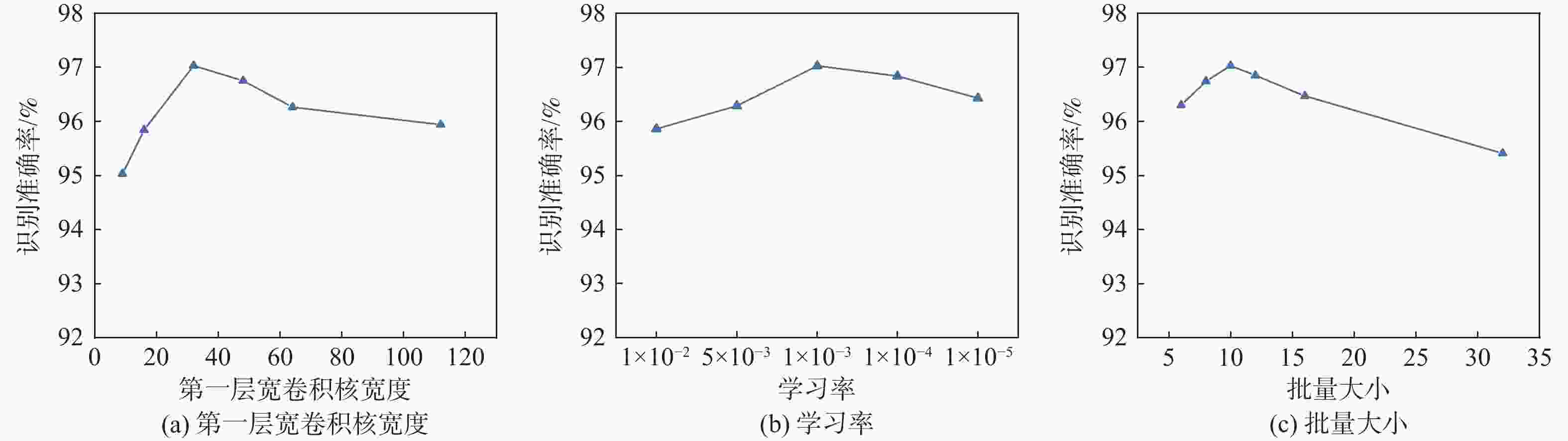
特征层 卷积核数量 卷积核大小 输出尺寸/像素 输入 1024 ×1Conv1 8 32 1024 ×8最大池化 512×8 Conv2 32 5 512×32 DSDCNN1 32 5(EDR=2) 512×32 DSDCNN2 32 5(EDR=3) 512×32 特征融合 512×96 ICA 512×96 特征融合 512×32 最大池化 256×32 SCSAM 256×32 Conv3 32 5 256×32 最大池化 128×32 全局平均池化 1×32 Softmax分类器 7 表 2 强噪声环境下变负载识别准确率
Table 2. Variable load recognition accuracy under strong noise environment
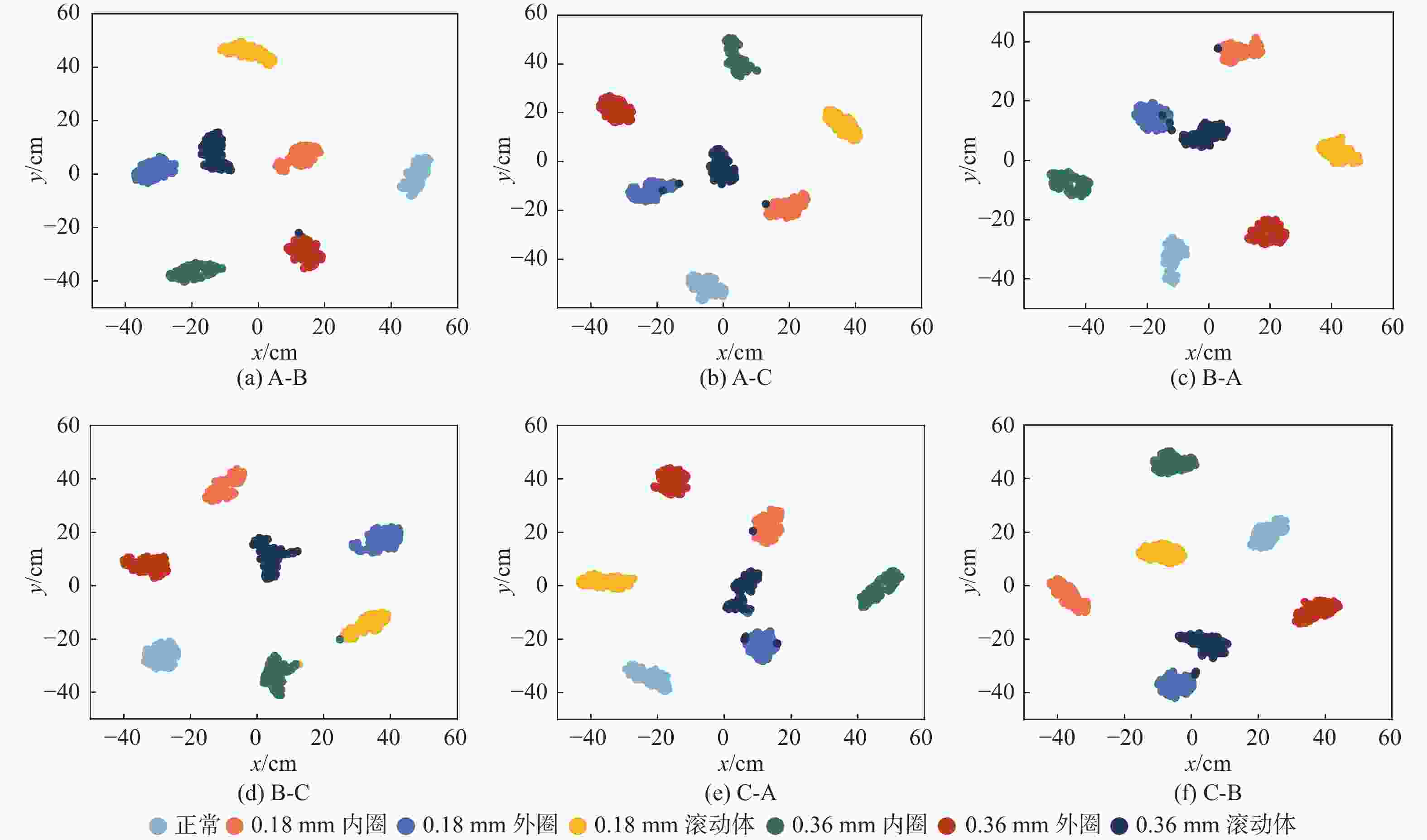
% 模型 识别准确率 均值 A-B A-C B-A B-C C-A C-B 本文模型 97.43 96.86 97.51 97.26 97.29 97.03 97.23 MSD-CNN 94.57 93.68 95.05 93.63 93.77 92.69 93.90 WKCNN 93.37 92.06 95.17 92.29 90.11 91.20 92.37 MSACNN 92.69 91.29 92.29 93.79 94.00 93.14 92.87 MSC-MpResCNN 96.23 95.48 96.85 96.54 96.31 95.83 96.21 表 3 强噪声环境下变转速识别准确率
Table 3. Variable speed recognition accuracy under strong noise environment
% 模型 识别准确率 均值 D-E D-F E-D E-F F-D F-E 本文模型 97.20 96.69 97.34 97.03 96.89 97.22 97.06 MSD-CNN 93.63 91.77 94.09 93.29 92.89 93.20 93.15 WKCNN 92.71 91.37 93.54 92.69 91.94 93.26 92.59 MSACNN 92.23 90.74 93.03 91.94 92.40 92.28 92.10 MSC-MpResCNN 95.25 94.54 95.74 96.20 94.46 95.17 95.23 表 4 XJTU-SY数据集早期故障样本分布
Table 4. Early fault sample distribution of XJTU-SY data set
故障类型 轴承编号 总实验
时长/min初始故障发
生时间点/min转速/(r·min−1) 外圈 Bearing1_1 123 77 2100 混合故障 Bearing1_5 52 33 2100 内圈 Bearing2_1 491 454 2250 保持架 Bearing2_3 533 325 2250 表 5 不同模型对早期故障的识别准确率
Table 5. Recognition accuracy of different models forearly faults
% 模型 识别准确率 识别准确率均值 外圈 混合故障 内圈 保持架 本文模型 94.8 98.8 100 98 97.9 MSD-CNN 62 75.2 100 79.6 79.2 WKCNN 41.4 41.6 99.6 62 61.15 MSACNN 47 96.6 100 91 83.65 MSC-MpResCNN 87.2 93 100 86.2 91.6 -
[1] LI W, ZHONG X, SHAO H D, et al. Multi-mode data augmentation and fault diagnosis of rotating machinery using modified ACGAN designed with new framework[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2022, 52: 101552. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2022.101552 [2] CHEN Z Y, GRYLLIAS K, LI W H. Mechanical fault diagnosis using convolutional neural networks and extreme learning machine[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 133: 106272. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106272 [3] SONG L Y, WANG H Q, CHEN P. Vibration-based intelligent fault diagnosis for roller bearings in low-speed rotating machinery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 67(8): 1887-1899. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2806984 [4] WANG B, LEI Y G, LI N P, et al. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 401-412. doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682 [5] XIAO Y M, SHAO H D, HAN S Y, et al. Novel joint transfer network for unsupervised bearing fault diagnosis from simulation domain to experimental domain[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 27(6): 5254-5263. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2022.3177174 [6] CHEN Z Y, LI W H. Multisensor feature fusion for bearing fault diagnosis using sparse autoencoder and deep belief network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(7): 1693-1702. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2017.2669947 [7] ZHAO J, YANG S P, LI Q, et al. A new bearing fault diagnosis method based on signal-to-image mapping and convolutional neural network[J]. Measurement, 2021, 176: 109088. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109088 [8] CHOUDHARY A, MIAN T, FATIMA S. Convolutional neural network based bearing fault diagnosis of rotating machine using thermal images[J]. Measurement, 2021, 176: 109196. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109196 [9] 曲建岭, 余路, 袁涛, 等. 基于一维卷积神经网络的滚动轴承自适应故障诊断算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2018, 39(7): 134-143.QU J L, YU L, YUAN T, et al. Adaptive fault diagnosis algorithm for rolling bearings based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2018, 39(7): 134-143(in Chinese). [10] 袁彩艳, 孙洁娣, 温江涛, 等. 多域信息融合结合改进残差密集网络的轴承故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(4): 200-208.YUAN C Y, SUN J D, WEN J T, et al. Bearing fault diagnosis based on information fusion and improved residual dense networks[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(4): 200-208(in Chinese). [11] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2017: 4278-4284. [12] 周奇才, 刘星辰, 赵炯, 等. 旋转机械一维深度卷积神经网络故障诊断研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(23): 31-37.ZHOU Q C, LIU X C, ZHAO J, et al. Fault diagnosis for rotating machinery based on 1D depth convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(23): 31-37(in Chinese). [13] LIU X P, XIA L J, SHI J, et al. A fault diagnosis method of rolling bearing based on improved recurrence plot and convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(10): 10767-10775. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3265409 [14] AN Z H, LI S M, WANG J R, et al. Generalization of deep neural network for bearing fault diagnosis under different working conditions using multiple kernel method[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 352: 42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.04.010 [15] 张玺君, 尚继洋, 余光杰, 等. 基于注意力的多尺度卷积神经网络轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 3009-3017.ZHANG X J, SHANG J Y, YU G J, et al. Bearing fault diagnosis based on attention for multi-scale convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 3009-3017(in Chinese). [16] 卞景艺, 刘秀丽, 徐小力, 等. 基于多尺度深度卷积神经网络的故障诊断方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(18): 204-211.BIAN J Y, LIU X L, XU X L, et al. Fault diagnosis method based on a multi-scale deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(18): 204-211(in Chinese). [17] PENG D D, WANG H, LIU Z L, et al. Multibranch and multiscale CNN for fault diagnosis of wheelset bearings under strong noise and variable load condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4949-4960. [18] WANG Y, NING D J, FENG S L. A novel capsule network based on wide convolution and multi-scale convolution for fault diagnosis[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(10): 3659. doi: 10.3390/app10103659 [19] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVFConference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [20] SMITH W A, RANDALL R B. Rolling element bearing diagnostics using the Case Western Reserve University data: a benchmark study[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 64: 100-131. [21] SHAO Z H, LI W Q, XIANG H, et al. Fault diagnosis method and application based on multi-scale neural network and data enhancement for strong noise[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies, 2024, 12(1): 295-308. [22] SONG X D, CONG Y Y, SONG Y F, et al. A bearing fault diagnosis model based on CNN with wide convolution kernels[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022, 13(8): 4041-4056. doi: 10.1007/s12652-021-03177-x [23] 丁雪, 邓艾东, 李晶, 等. 基于多尺度和注意力机制的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(1): 172-178.DING X, DENG A D, LI J, et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on multi-scale and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(1): 172-178(in Chinese). [24] CHAO Z Q, HAN T. A novel convolutional neural network with multiscale cascade midpoint residual for fault diagnosis of rolling bearings[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 506: 213-227. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.07.022 [25] BELKINA A C, CICCOLELLA C O, ANNO R, et al. Automated optimized parameters for T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding improve visualization and analysis of large datasets[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5415. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13055-y [26] 黄如意, 李霁蒲, 王震, 等. 基于多任务学习的装备智能诊断与寿命预测方法[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2022, 52(1): 123-137.HUANG R Y, LI J P, WANG Z, et al. Intelligent diagnostic and prognostic method based on multitask learning for industrial equipment[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2022, 52(1): 123-137(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: