-
摘要:
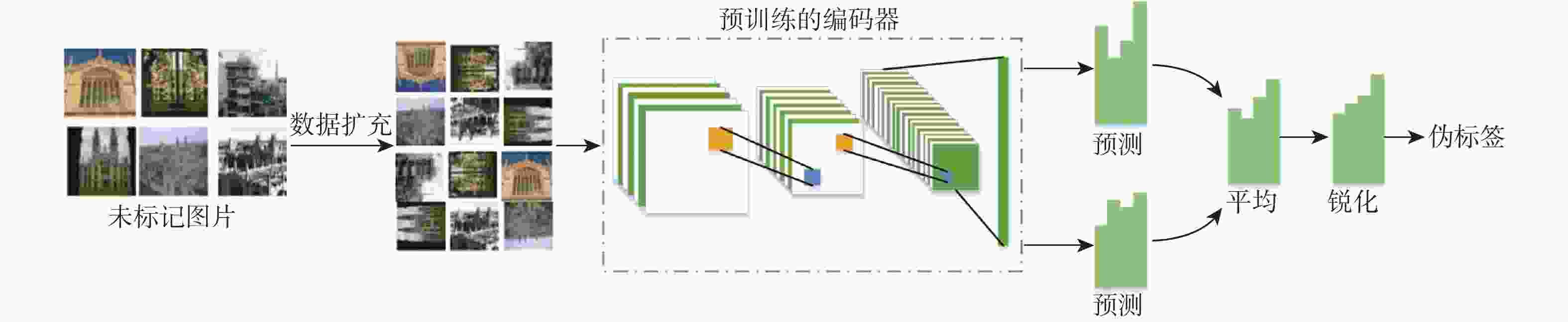
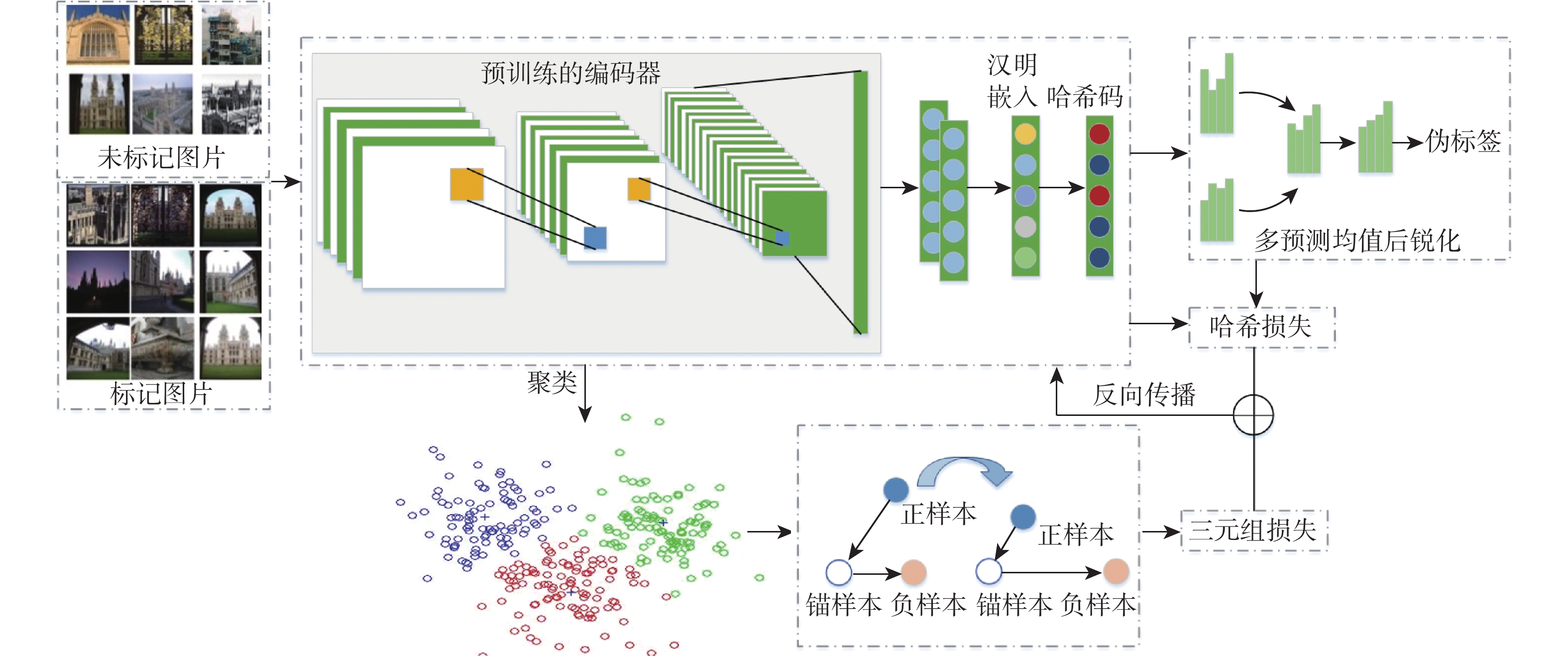
目前大多数基于深度学习的图像检索方法是在有监督条件下进行的,需要大量的标签数据,但实际应用中获取大量标签数据困难且成本高昂。此外,现有基于欧氏距离的三元组损失计算不够精确,使模型对图像相似性学习的能力欠佳。采用熵最小化伪标签、三元组损失和半监督学习技术,提出了一种新的半监督哈希图像检索模型(SSITL)。应用多阶段模型联合与锐化技术为未标记数据生成伪标签,并通过熵最小化处理以提高伪标签的置信度。同时,利用标记数据和未标记数据的聚类结果选择三元组,并采用基于通道权重矩阵的三元组哈希损失(CWT loss)帮助SSITL学习图像相似性。为了生成更好的哈希码,在2个汉明嵌入间使用MixUp进行混洗得到新的汉明嵌入以改善图像检索性能。实验结果表明:相较于其他方法,SSITL在相仿的时间开销下,在CIFAR-10和NUS-WIDE数据集上的检索平均准确率分别提高了1.2%和0.7%,强有力地验证了SSITL是一种优秀的半监督哈希图像检索模型。
Abstract:Currently, most of the image retrieval methods based on deep learning are supervised techniques, which require massive labeled data. However, it is very difficult and expensive to label so much data in real applications. Furthermore, the network learned picture similarity poorly since the triple loss functions that were in place were computed using Euclidean distance. In this work, a novel semi-supervised hash image retrieval model (SSITL) is proposed that mixes the pseudo-labels with entropy minimization, triplet hash loss and semi-supervised learning. The multi-stage model union and sharpening technique are used to generate pseudo-labels, and the pseudo-labels are processed with entropy minimization to improve their confidence. The triplet hash loss based on the channel weight matrix is utilized to assist SSITL in learning the similarity of images, while the triples are chosen concurrently depending on the clustering outcomes of labeled and unlabeled data. In order to generate a better hash code, Mix Up is used to shuffle between two Hamming embeddings to obtain a new Hamming embedding for image retrieval. The abundant experimental results show that compared with other methods, SSITL improves the average retrieval accuracy by 1.2% and 0.7% respectively on CIFAR-10 and NUS-WIDE datasets under similar time cost, which strongly demonstrates that SSITL is an excellent semi-supervised hash framework for image retrieval.
-
Key words:
- image retrieval /
- triplet hash loss /
- semi-supervised learning /
- pseudo-labels /
- deep learning
-
表 1 CIFAR-10数据集上不同方法的平均精度
Table 1. MAP scores of different methods on CIFAR-10
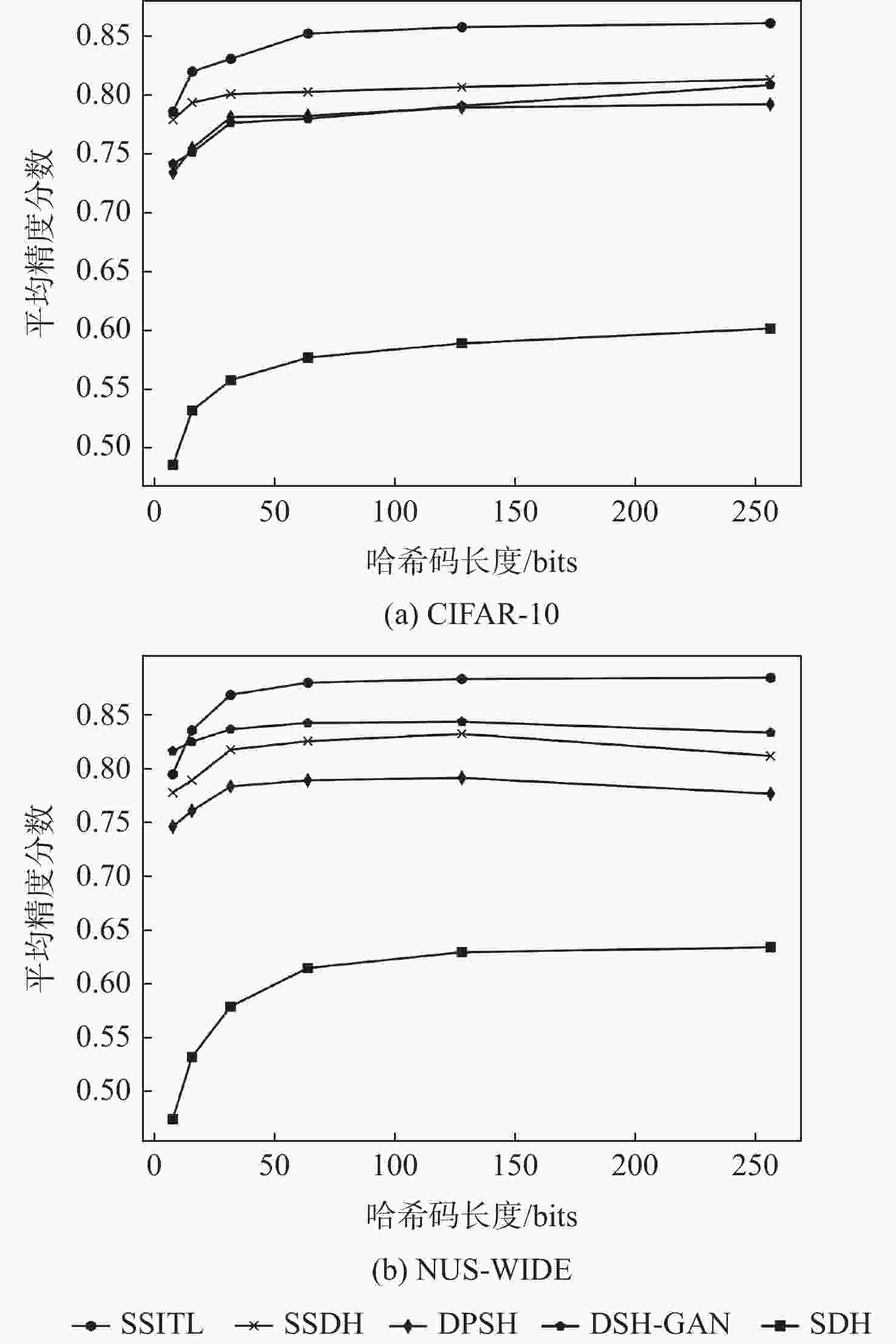
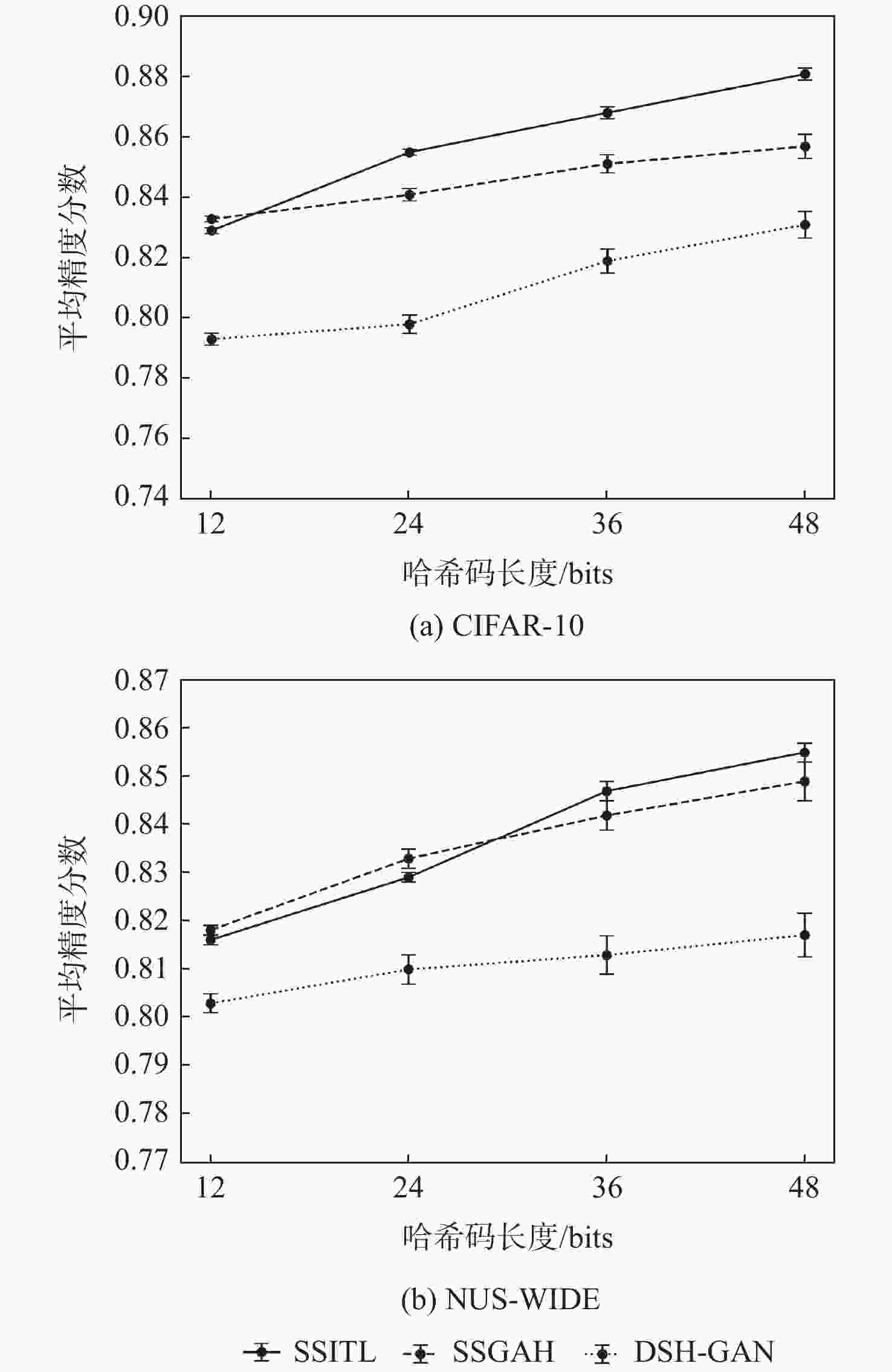
方法 CIFAR-10 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits SSITL 0.818 0.838 0.853 0.854 ABML[19] 0.815 0.832 0.850 0.851 CPQN[18] 0.817 0.830 0.848 0.852 BGDH[30] 0.805 0.824 0.826 0.833 DSH-GAN[31] 0.751 0.801 0.807 0.811 SSDH[17] 0.802 0.810 0.816 0.819 DPSH[27] 0.737 0.775 0.801 0.798 DSDH[29] 0.738 0.784 0.795 0.818 DRSCH[28] 0.616 0.625 0.630 0.629 SDH[25] 0.438 0.520 0.558 0.587 ITQ[26] 0.219 0.242 0.250 0.252 表 2 NUS-WIDE数据集上不同方法的平均精度
Table 2. MAP scores of different methods on NUS-WIDE dataset
方法 NUS-WIDE 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits SSITL 0.838 0.857 0.880 0.873 ABML[19] 0.835 0.851 0.872 0.869 CPQN[18] 0.833 0.849 0.869 0.870 BGDH[30] 0.805 0.824 0.826 0.833 DSH-GAN[31] 0.828 0.843 0.848 0.851 SSDH[17] 0.803 0.808 0.826 0.833 DPSH[27] 0.767 0.778 0.795 0.798 DSDH[29] 0.772 0.804 0.821 0.831 DRSCH[28] 0.616 0.623 0.627 0.627 SDH[25] 0.541 0.548 0.579 0.621 ITQ[26] 0.663 0.700 0.707 0.723 表 3 CIFAR-10和NUS-WIDE数据集上SSITL不同模型的平均精度分数
Table 3. MAP scores of different SSITLs on CIFAR-10 and NUS-WIDE datasets
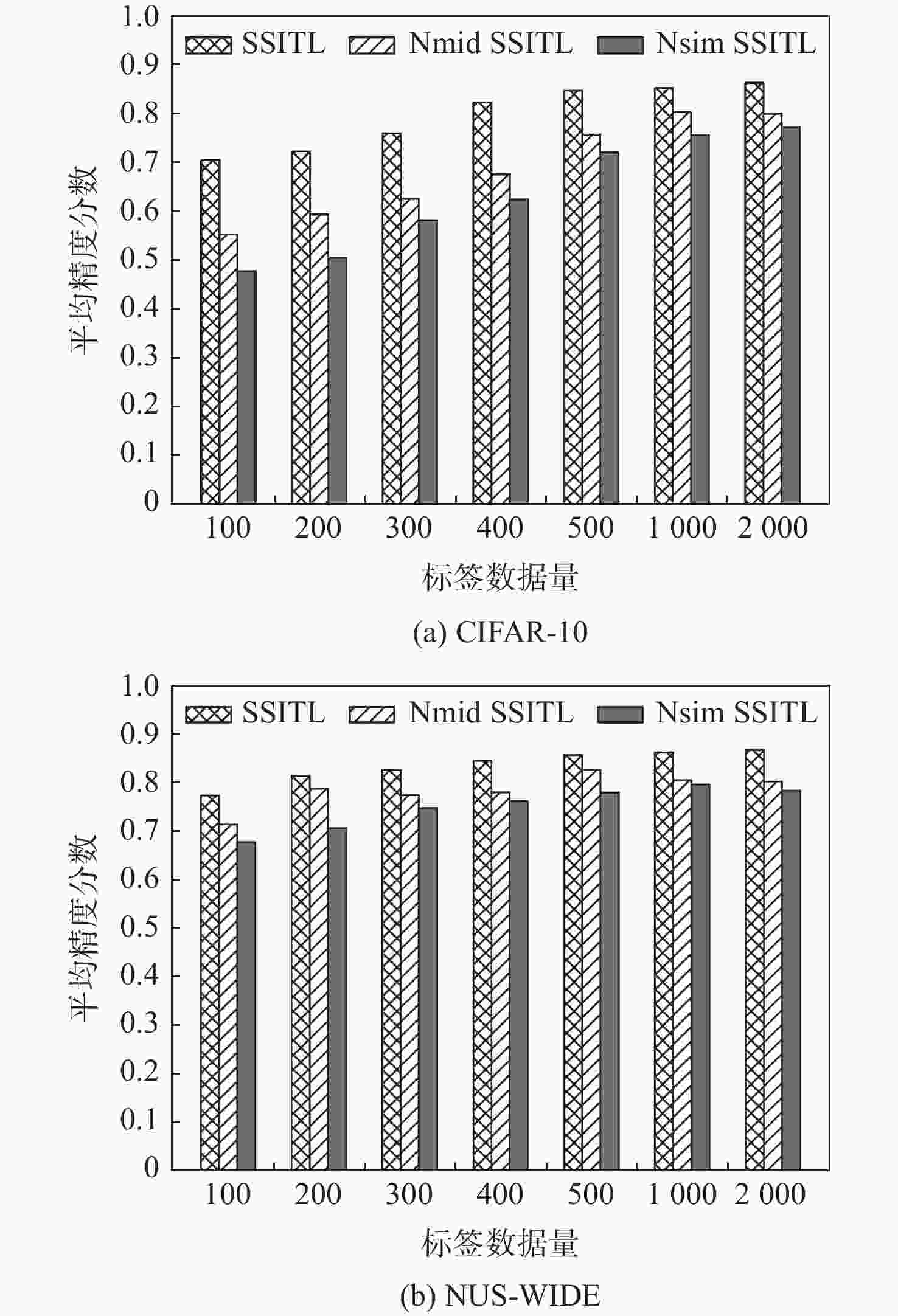
方法 CIFAR-10 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits SSITL 0.818 0.838 0.853 0.854 Nmid SSITL 0.781 0.812 0.828 0.831 Nsim SSITL 0.737 0.764 0.785 0.778 方法 NUS-WIDE 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits SSITL 0.838 0.857 0.880 0.873 Nmid SSITL 0.807 0.823 0.844 0.857 Nsim SSITL 0.775 0.788 0.815 0.820 表 4 CIFAR-10数据集上不同方法对不可见类的检索精度
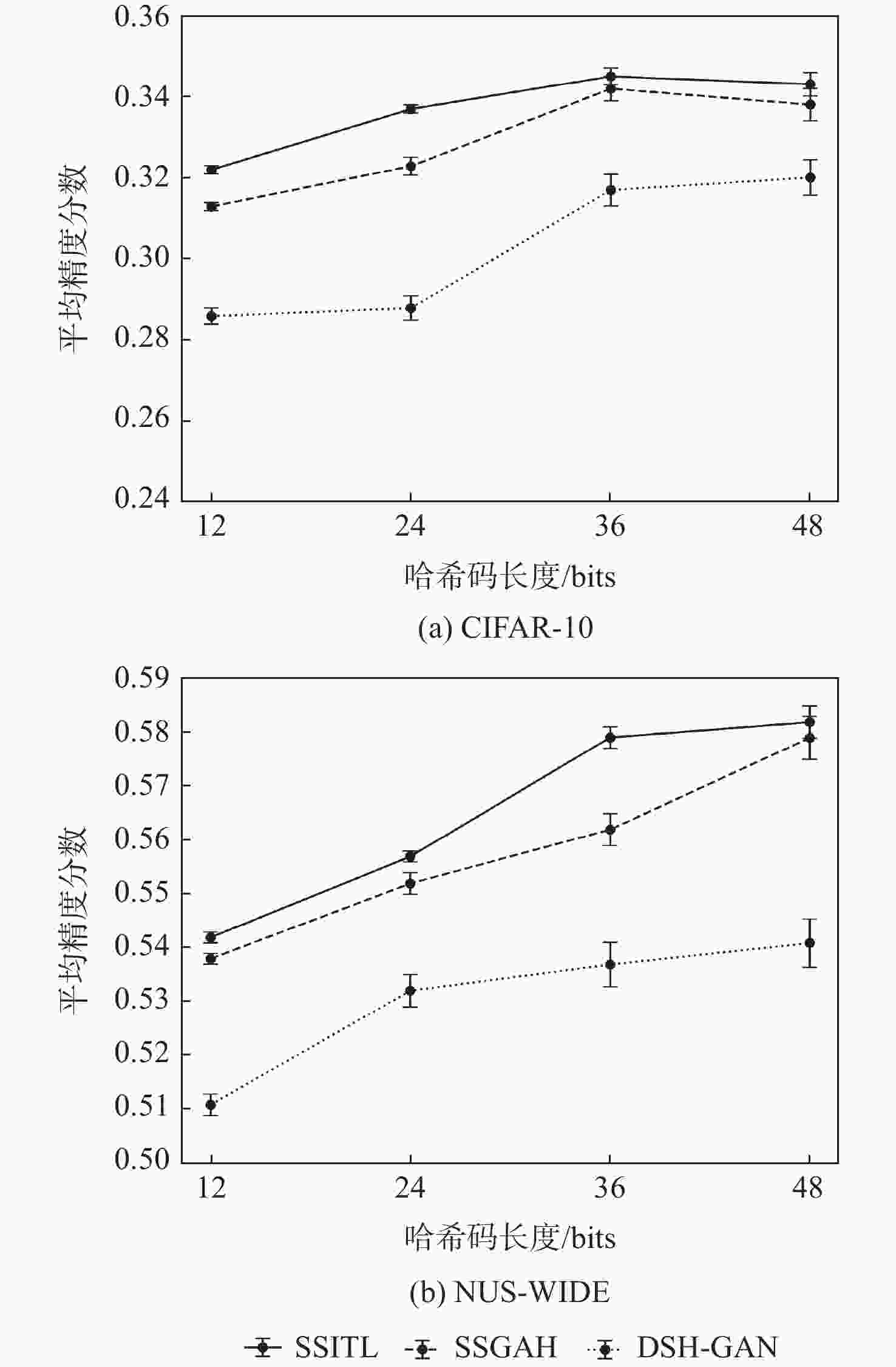
Table 4. MAP scores of unseen class retrieval with different methods with on CIFAR-10 datasets
方法 CIFAR-10 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits SSITL 0.319 0.327 0.349 0.358 ABML[19] 0.316 0.325 0.337 0.348 BGDH[30] 0.267 0.279 0.284 0.294 DSH-GAN[31] 0.281 0.288 0.299 0.310 SSDH[17] 0.287 0.291 0.309 0.317 DPSH[27] 0.264 0.275 0.281 0.293 DSDH[29] 0.255 0.263 0.278 0.288 DRSCH[28] 0.217 0.218 0.233 0.251 SDH[25] 0.190 0.192 0.197 0.206 ITQ[26] 0.153 0.162 0.192 0.199 表 5 NUS-WIDE数据集上不同方法对不可见类检索的平均精度
Table 5. MAP scores of unseen class retrieval with different methods on NUS-WIDE datasets
方法 NUS-WIDE 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits SSITL 0.537 0.553 0.581 0.584 ABML[19] 0.532 0.550 0.574 0.582 BGDH[30] 0.511 0.529 0.545 0.538 DSH-GAN[31] 0.508 0.539 0.542 0.541 SSDH[17] 0.514 0.534 0.538 0.549 DPSH[27] 0.487 0.512 0.514 0.527 DSDH[29] 0.255 0.263 0.278 0.288 DRSCH[28] 0.458 0.463 0.471 0.468 SDH[25] 0.468 0.489 0.491 0.505 ITQ[26] 0.490 0.486 0.493 0.507 表 6 CIFAR-10数据集上使用不同层激活通道的不可见类检索
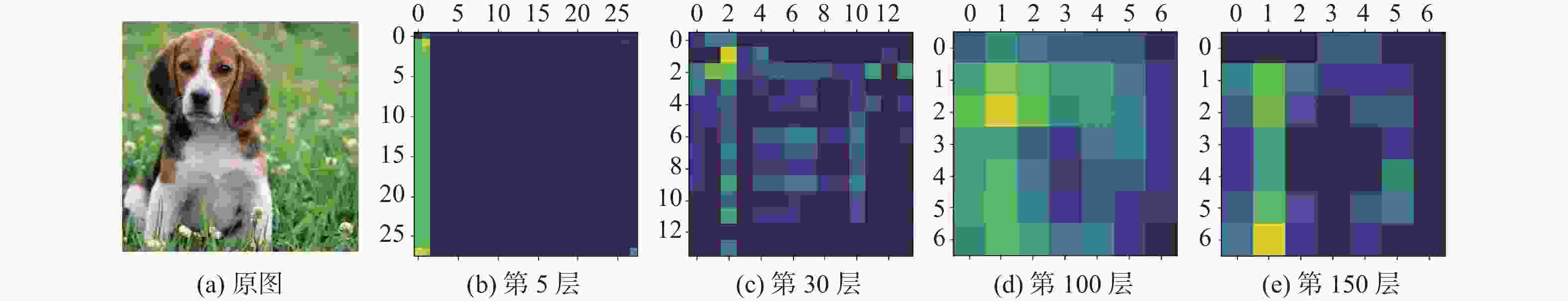
Table 6. Unseen class retrieval using activation channels of different layers on CIFAR-10 datasets
不同层激活通道 CIFAR-10 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits 第5层 0.226 0.233 0.251 0.273 第30层 0.286 0.305 0.329 0.343 第100层 0.319 0.327 0.349 0.358 第150层 0.308 0.319 0.346 0.354 表 7 NUS-WIDE数据集上使用不同层激活通道的不可见类检索
Table 7. Unseen class retrieval using activation channels of different layers on NUS-WIDE datasets
不同层激活通道 NUS-WIDE 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits 第5层 0.462 0.473 0.481 0.483 第30层 0.504 0.511 0.539 0.542 第100层 0.537 0.553 0.581 0.584 第150层 0.518 0.532 0.574 0.579 表 8 CIFAR-10数据集上不同权重的不可见类检索
Table 8. Unseen class retrieval using different weight values on CIFAR-10 datasets
权重值 CIFAR-10 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits ${\lambda _2} = 0$ 0.275 0.286 0.305 0.311 ${\lambda _2} = 0.2$ 0.302 0.311 0.332 0.343 ${\lambda _2} = 0.5$ 0.319 0.327 0.349 0.358 ${\lambda _2} = 1$ 0.284 0.306 0.329 0.338 ${\lambda _2} = 2$ 0.265 0.281 0.297 0.301 表 9 NUS-WIDE数据集上不同权重值的不可见类检索
Table 9. Unseen class retrieval using different weight values on NUS-WIDE datasets
权重值 NUS-WIDE 12 bits 24 bits 32 bits 48 bits ${\lambda _2} = 0$ 0.508 0.517 0.526 0.539 ${\lambda _2} = 0.2$ 0.519 0.542 0.559 0.571 ${\lambda _2} = 0.5$ 0.537 0.553 0.581 0.584 ${\lambda _2} = 1$ 0.513 0.537 0.541 0.564 ${\lambda _2} = 2$ 0.497 0.511 0.530 0.543 -
[1] LI W, DUAN L X, XU D, et al. Text-based image retrieval using progressive multi-instance learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 2049-2055. [2] LIU Y, ZHANG D S, LU G J, et al. A survey of content-based image retrieval with high-level semantics[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2007, 40(1): 262-282. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2006.04.045 [3] CHEN R Y, PAN L L, LI C, et al. An improved deep fusion CNN for image recognition[J]. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2020, 65(2): 1691-1706. [4] LAI H J, PAN Y, YE L, et al. Simultaneous feature learning and hash coding with deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3270-3278. [5] CHEN Y B, MANCINI M, ZHU X T, et al. Semi-supervised and unsupervised deep visual learning: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(3): 1327-1347. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3201576 [6] 刘颖, 程美, 王富平, 等. 深度哈希图像检索方法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(7): 1296-1317. doi: 10.11834/jig.190518LIU Y, CHENG M, WANG F P, et al. Deep Hashing image retrieval methods[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(7): 1296-1317(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.190518 [7] ZHU X, GOLDBERG A B. Introduction to semi-supervised learning[J]. Synthesis Lectures on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, 2009, 3(1): 1-130. [8] SCHROFF F, KALENICHENKO D, PHILBIN J. FaceNet: a unified embedding for face recognition and clustering[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 815-823. [9] SONG H O, XIANG Y, JEGELKA S, et al. Deep metric learning via lifted structured feature embedding[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4004-4012. [10] 郑大刚, 刘光杰, 茅耀斌, 等. 基于三元组损失函数的深度人脸哈希方法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2021, 19(2): 313-318. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2018108ZHENG D G, LIU G J, MAO Y B, et al. Deep face Hashing based on ternary-group loss function[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2021, 19(2): 313-318(in Chinese). doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2018108 [11] 杜雨佳, 李海生, 姚春莲, 等. 基于三元组网络的单图三维模型检索[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2020, 46(9): 1691-1700.DU Y J, LI H S, YAO C L, et al. Monocular image based 3D model retrieval using triplet network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(9): 1691-1700(in Chinese). [12] 刘晗煜, 黄宏恩, 郑世宝. 基于视角一致性三元组损失的车辆重识别技术[J]. 测控技术, 2021, 40(8): 47-53,63.LIU H Y, HUANG H E, ZHENG S B. View consistency triplet loss for vehicle re-identification[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2021, 40(8): 47-53,63 (in Chinese). [13] LIAO S C, SHAO L. Graph sampling based deep metric learning for generalizable person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 7349-7358. [14] YANG S, ZHANG Y F, ZHAO Q H, et al. Prototype-based support example miner and triplet loss for deep metric learning[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(15): 3315. doi: 10.3390/electronics12153315 [15] LI Z, KO B, CHOI H J. Naive semi-supervised deep learning using pseudo-label[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2019, 12(5): 1358-1368. doi: 10.1007/s12083-018-0702-9 [16] BERTHELOT D, CARLINI N, GOODFELLOW I, et al. MixMatch: a holistic approach to semi-supervised learning[EB/OL]. (2019-10-23)[2023-05-23]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.02249. [17] ZHANG J, PENG Y X. SSDH: Semi-supervised deep hashing for large scale image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 29(1): 212-225. [18] GUO Z T, HONG C Q, ZHUANG W W, et al. CPQN: central product quantization network for semi-supervised image retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 3183-3190. [19] WANG G A, HU Q H, YANG Y, et al. Adversarial binary mutual learning for semi-supervised deep hashing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(8): 4110-4124. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3055834 [20] 魏翔, 王靖杰, 张顺利, 等. ReLSL: 基于可靠标签选择与学习的半监督学习算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(6): 1147-1160. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01147WEI X, WANG J J, ZHANG S L, et al. ReLSL: reliable label selection and learning based algorithm for semi-supervised learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(6): 1147-1160(in Chinese). doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01147 [21] ZHANG H Y, CISSE M, DAUPHIN Y N, et al. Mixup: beyond empirical risk minimization[EB/OL]. (2018-04-27)[2023-05-25]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1710.09412. [22] WANG G A, HU Q H, YANG Y, et al. Adversarial binary mutual learning for semi-supervised deep hashing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 33(8): 4110-4124. [23] KRIZHEVSKY A, HINTON G. Convolutional deep belief networks on cifar-10[J]. Unpublished Manuscript, 2010, 40(7): 1-9. [24] CHUA T S, TANG J H, HONG R C, et al. NUS-WIDE: a real-world web image database from National University of Singapore[C]// Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2009: 1-9. [25] SHEN F M, SHEN C H, LIU W, et al. Supervised discrete hashing[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 37-45. [26] GONG Y C, LAZEBNIK S, GORDO A, et al. Iterative quantization: a Procrustean approach to learning binary codes for large-scale image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(12): 2916-2929. [27] LI W J, WANG S, KANG W C. Feature learning based deep supervised hashing with pairwise labels[EB/OL]. (2016-04-21)[2023-05-27]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1511.03855. [28] ZHANG R M, LIN L, ZHANG R, et al. Bit-scalable deep hashing with regularized similarity learning for image retrieval and person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 4766-4779. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2467315 [29] LI Q, SUN Z, HE R, et al. Deep supervised discrete hashing[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: Curran Associates, 2017: 2479-2488. [30] YAN X, ZHANG L, LI W J. Semi-supervised deep Hashing with a bipartite graph[C]//Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Melbourne: IJCAJ, 2017: 3238-3244. [31] QIU Z F, PAN Y W, YAO T, et al. Deep semantic hashing with generative adversarial networks[C]// Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2017: 225-234. [32] WANG G A, HU Q H, CHENG J, et al. Semi-supervised generative adversarial hashing for image retrieval[C]// Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 491-507. -






 下载:
下载: