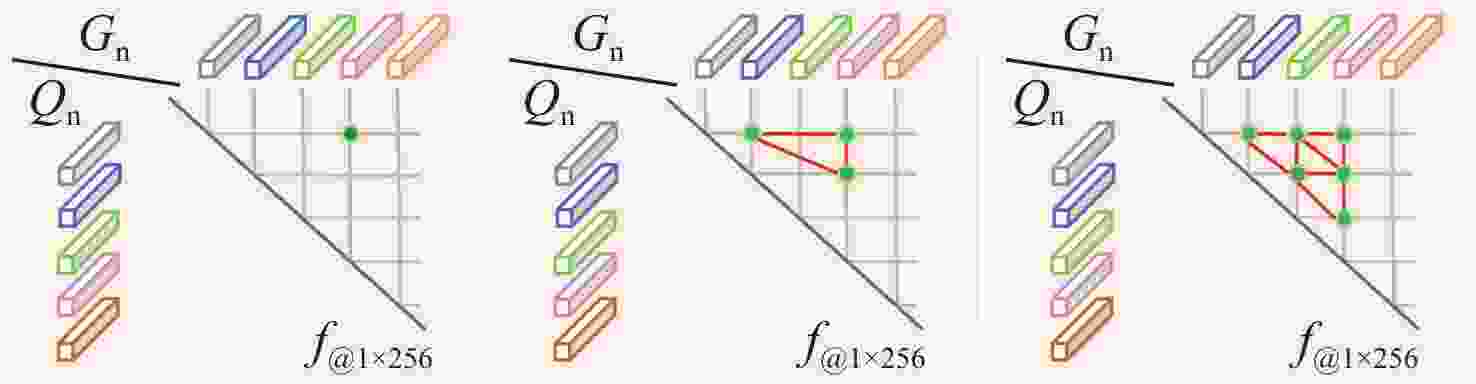
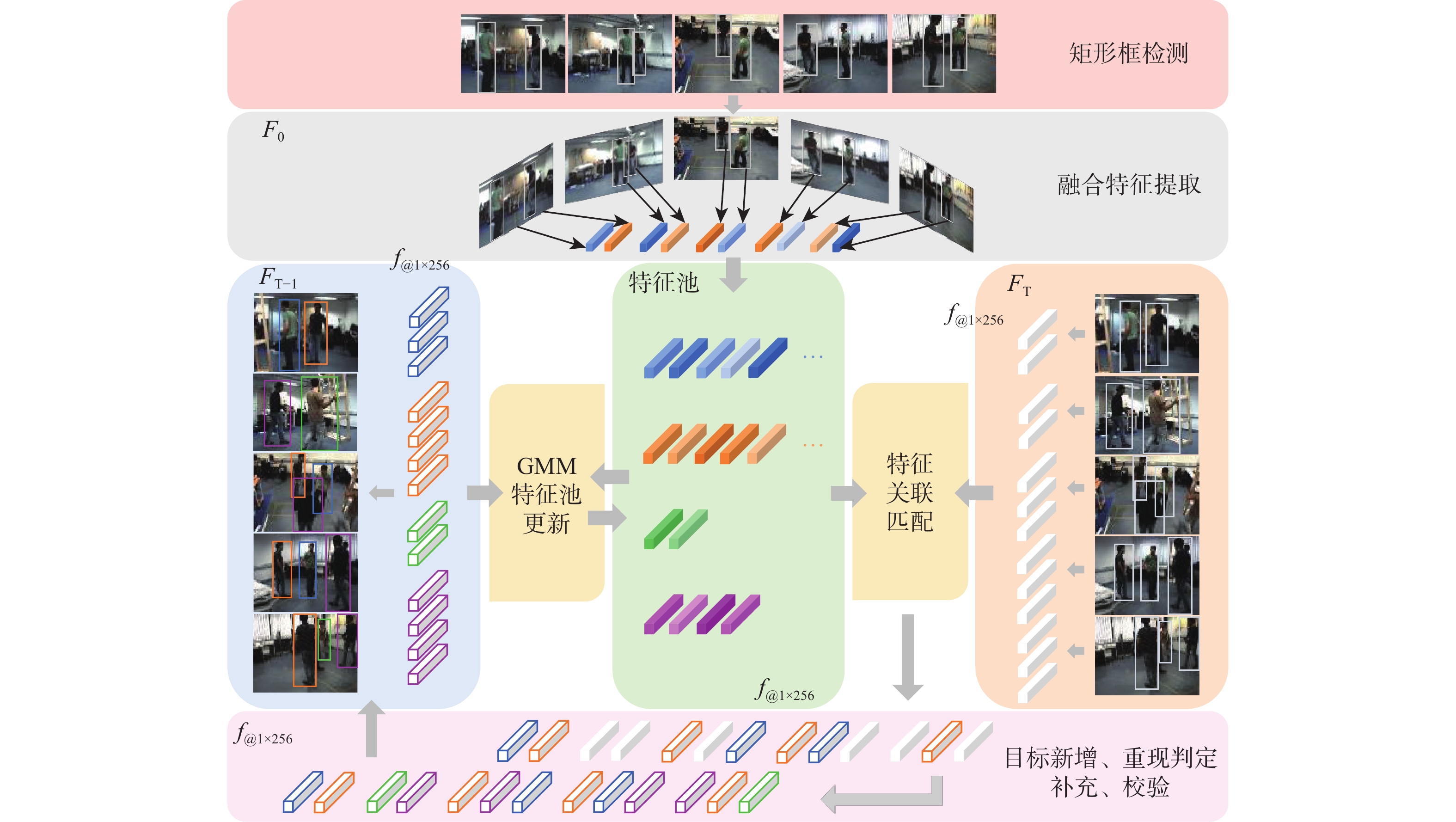
-
摘要:
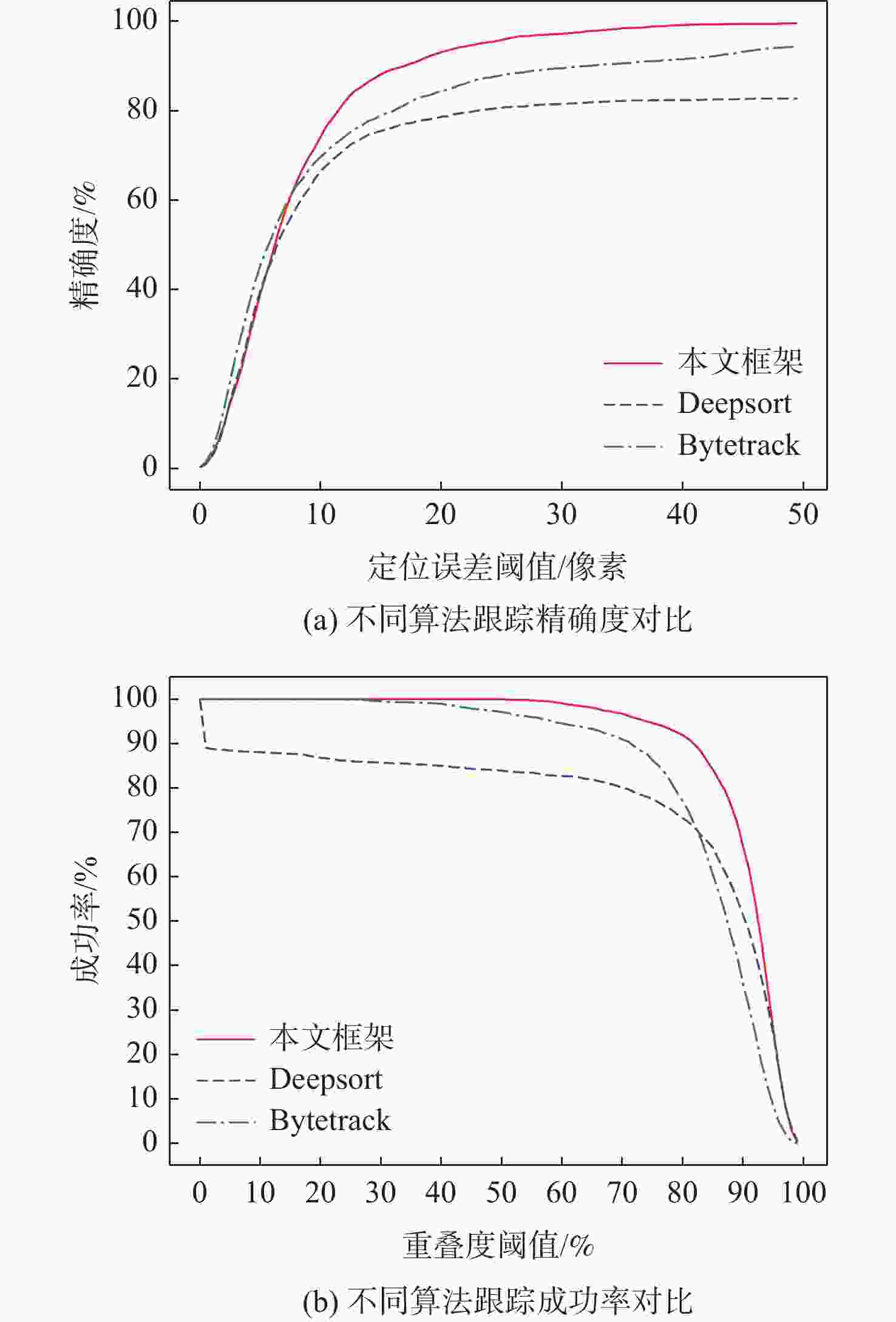
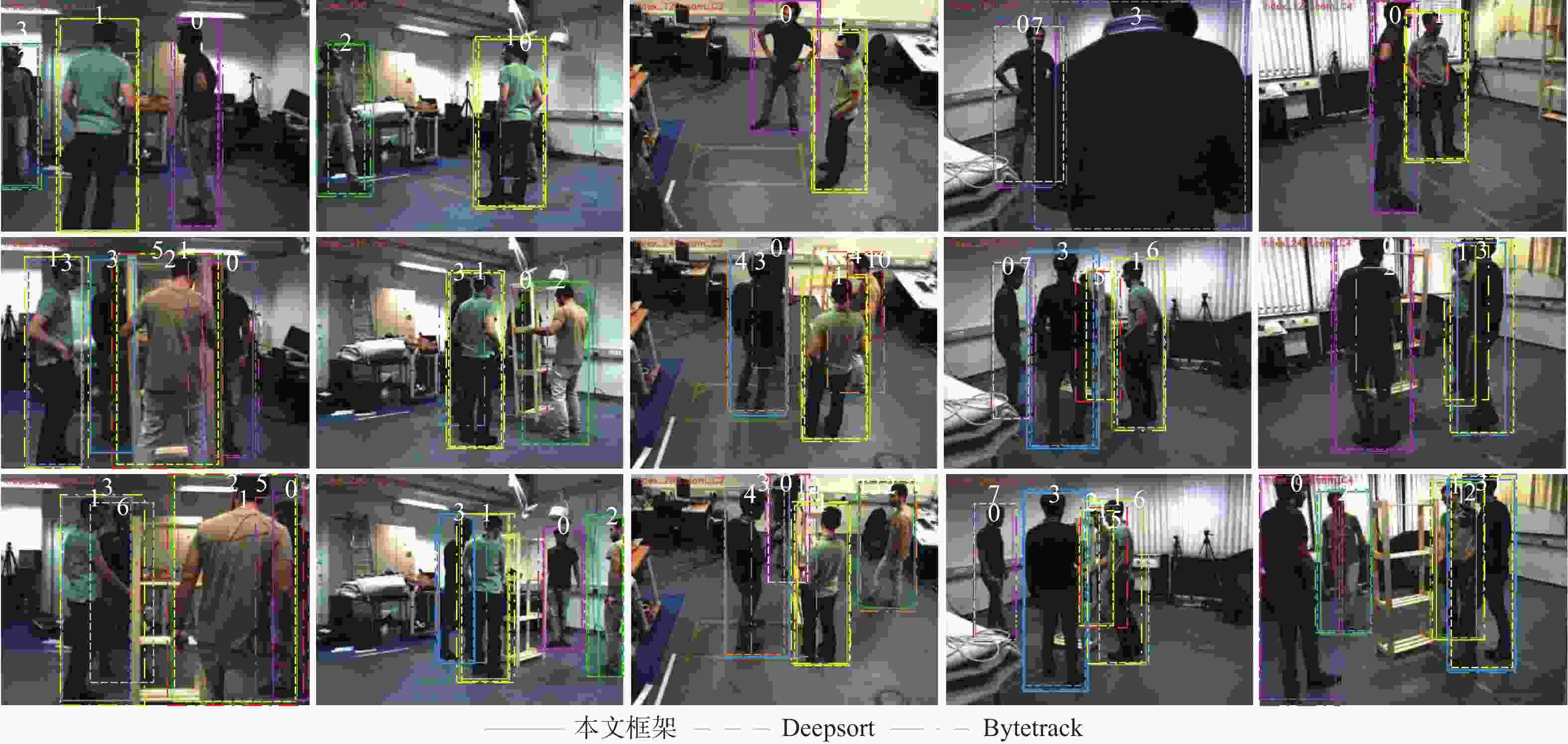
针对当前大部分计算机视觉跟踪方法仍不能有效解决目标受遮挡以及在摄像机视角中消失后重现等问题,基于融合特征相关性对多目标行人跟踪方法进行了研究:基于高斯混合模型(GMM)更新行人特征池以减少人员密集所导致的特征污染;基于K-means算法动态计算目标特征相似性阈值;利用融合特征相似性关联行人特征,加入单应性约束校验以判定行人的新增与重现。在公开数据集Shelf上进行实验,结果显示所提方法平均精确度相较其他算法分别提升16.05%、7.39%,平均成功率分别提升16.04%、4.16%。完整视频流下的平均错跟率为10.11%,在控制错跟数量方面取得显著效果之外还能够在行人重现后有效关联至原目标。
Abstract:Many multi-object pedestrian tracking algorithms have been proposed in computer vision, and great progress has been made in tracking efficiency and accuracy recently. Practical applications are severely hampered by the fact that the majority of tracking techniques now in use are still unable to address the issues of object occlusion and reappearance in camera perspectives. To tackle the above problems in dense crowds under multi-vision, the multi-target pedestrian tracking method is based on fusion feature correlation. The feature pool was updated based on GMM to reduce feature pollution caused by dense people. To ensure the tracking universality, the similarity threshold of target features was calculated dynamically based on K-means. The similarity of fused features is used to associate the pedestrian features, with the homography constraint check to determine the addition and reappearance of pedestrians, which reduces error and miss tracking. The results of experiments using several algorithms on the public dataset Shelf indicate that the suggested method's average accuracy is 16.05% and 7.39% higher than that of other methods, while its average success rate is 16.04% and 4.16% higher. The average error tracking rate under the complete video is 10.11%, which achieves significant results in controlling mistracking and effectively associates with the original ID after the pedestrian’s reappearance.
-
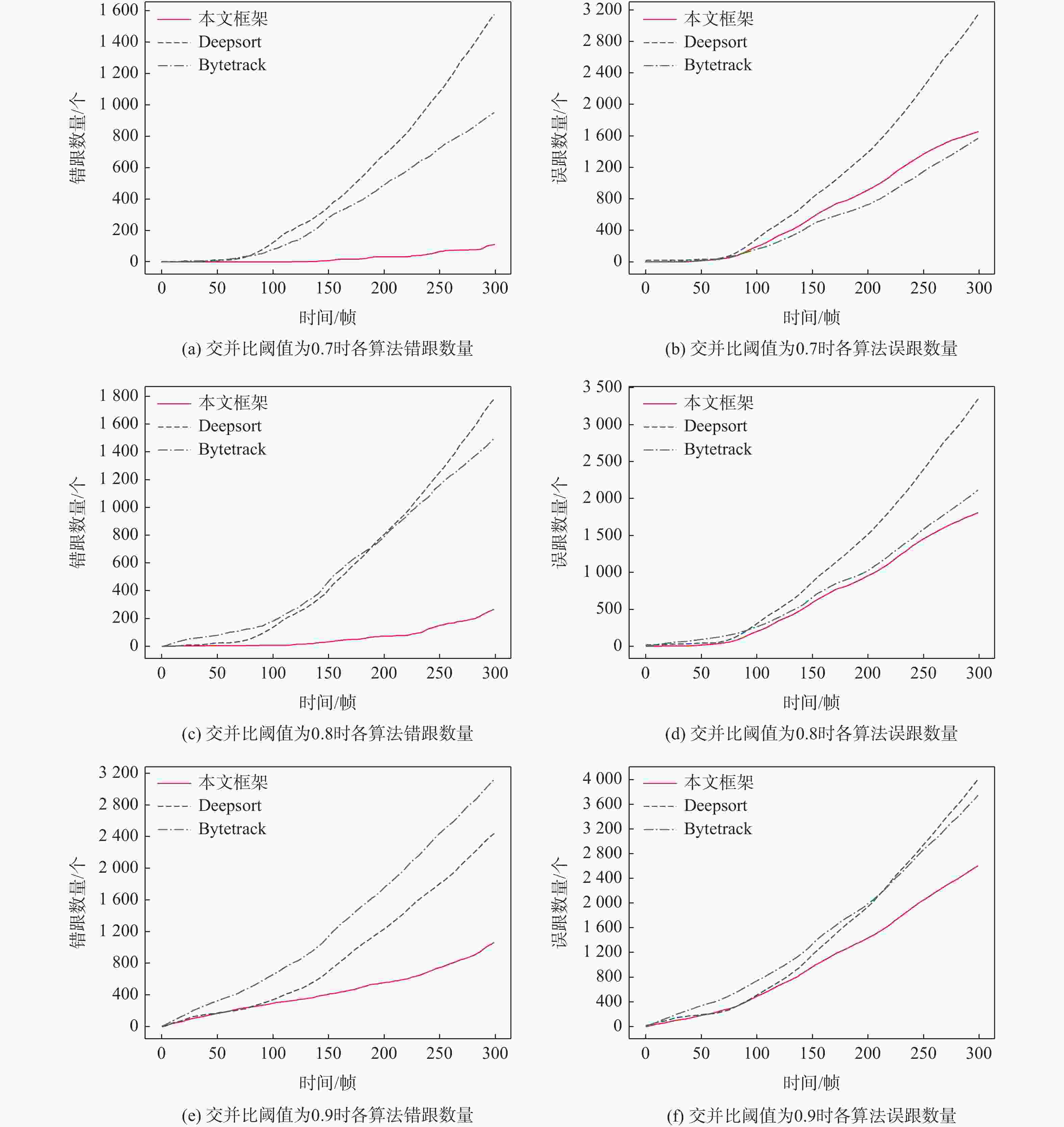
表 1 各算法在不同阈值下的错跟数量
Table 1. The number of error-tracking at different thresholds for each algorithm
算法 阈值 0.7 0.8 0.9 本文框架 110 265 1 060 Deepsort 1 577 1 782 2 440 Bytetrack 951 1 498 3 126 表 2 各算法在不同阈值下的误跟数量
Table 2. The number of mismatches at different thresholds for each algorithm
算法 阈值 0.7 0.8 0.9 本文框架 1 654 1 809 2 604 Deepsort 3 144 3 349 4 007 Bytetrack 1 571 2 118 3 746 -
[1] ZHUANG B H, LU H C, XIAO Z Y, et al. Visual tracking via discriminative sparse similarity map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(4): 1872-1881. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2308414 [2] BERCLAZ J, FLEURET F, TÜRETKEN E, et al. Multiple object tracking using K-shortest paths optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(9): 1806-1819. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.21 [3] WU T F, LU Y, ZHU S C. Online object tracking, learning and parsing with and-or graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2465-2480. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644963 [4] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [5] SIKDAR A, CHATTERJEE D, BHOWMIK A, et al. Open-set metric learning for person re-identification in the wild[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2356-2360. [6] HAGER G D, BELHUMEUR P N. Efficient region tracking with parametric models of geometry and illumination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(10): 1025-1039. doi: 10.1109/34.722606 [7] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [8] KWON O H, TANKE J, GALL J. Recursive Bayesian filtering for multiple human pose tracking from multiple cameras[C]// Computer Vision – ACCV 2020. Berlin: Springer, 2021: 438-453. [9] BEWLEY A, GE Z Y, OTT L, et al. Simple online and realtime tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 3464-3468. [10] WOJKE N, BEWLEY A, PAULUS D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3645-3649. [11] COMANICIU D, RAMESH V, MEER P. Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift[C]//Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2000: 142-149. [12] ZHANG Y F, SUN P Z, JIANG Y, et al. ByteTrack: multi-object tracking byAssociating every detection box[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. Berlin: Springer, 2022: 1-21. [13] ZHU X K, LYU S C, WANG X, et al. TPH-YOLOv5: improved YOLOv5 based on transformer prediction head for object detection on drone-captured scenarios[EB/OL]. (2021-08-26)[2023-05-25]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.21081.1539. [14] HARTIGAN J A, WONG M A. Algorithm AS 136: a K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Applied Statistics, 1979, 28(1): 100. doi: 10.2307/2346830 [15] LIU Z, LIN Y T, CAO Y, et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 9992-10002. [16] IOFFE S , SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]// Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: ACM, 2015, 37: 448-456. [17] HINTON G E, SRIVASTAVA N, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors[EB/OL]. (2012-07-03)[2023-05-28]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1207.0580. [18] YU E, LI Z L, HAN S D, et al. RelationTrack: relation-aware multiple object tracking with decoupled representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2022, 25: 2686-2697. [19] LI W, XIONG Y J, YANG S, et al. Semi-TCL: semi-supervised track contrastive representation learning[EB/OL]. (2021-07-06)[2023-05-29]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2107.02396. [20] CHEN K, SONG X, ZHAI X, et al. An integrated deep learning framework for occluded pedestrian tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 26060-26072. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2900296 [21] BAE S H, YOON K J. Robust online multiobject tracking with data association and track management[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(7): 2820-2833. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2320821 [22] BRASO G, LEAL-TAIXE L. Learning a neural solver for multiple object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6246-6256. [23] HORNAKOVA A, HENSCHEL R, ROSENHAHN B, et al. Lifted disjoint paths with application in multiple object tracking[EB/OL]. (2020-06-25)[2023-06-01]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2006.14550. [24] ZENG F G, DONG B, ZHANG Y A, et al. MOTR: end-to-end multiple-object tracking withTransformer[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. Berlin: Springer, 2022: 659-675. [25] DAI P, WENG R L, CHOI W, et al. Learning a proposal classifier for multiple object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 2443-2452. [26] WANG Z D, ZHENG L, LIU Y X, et al. Towards real-time multi-object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2020. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 107-122. [27] WANG Q, ZHENG Y, PAN P, et al. Multiple object tracking with correlation learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 3875-3885. [28] MEINHARDT T, KIRILLOV A, LEAL-TAIXÉ L, et al. TrackFormer: multi-object tracking with transformers[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 8834-8844. [29] STADLER D, BEYERER J. Improving multiple pedestrian tracking by track management and occlusion handling[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 10953-10962. [30] NIGAM J, RAMESHAN R M. EgoTracker: pedestrian tracking with re-identification in egocentric videos[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 980-987. [31] KHAN S M, SHAH M. A multiview approach to tracking people in crowded scenes using a planar homography constraint[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2006. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 133-146. [32] BELAGIANNIS V, AMIN S, ANDRILUKA M, et al. 3D pictorial structures for multiple human pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1669-1676. [33] WU Y, LIM J, YANG M H. Online object tracking: a benchmark[C]//Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2411-2418. -






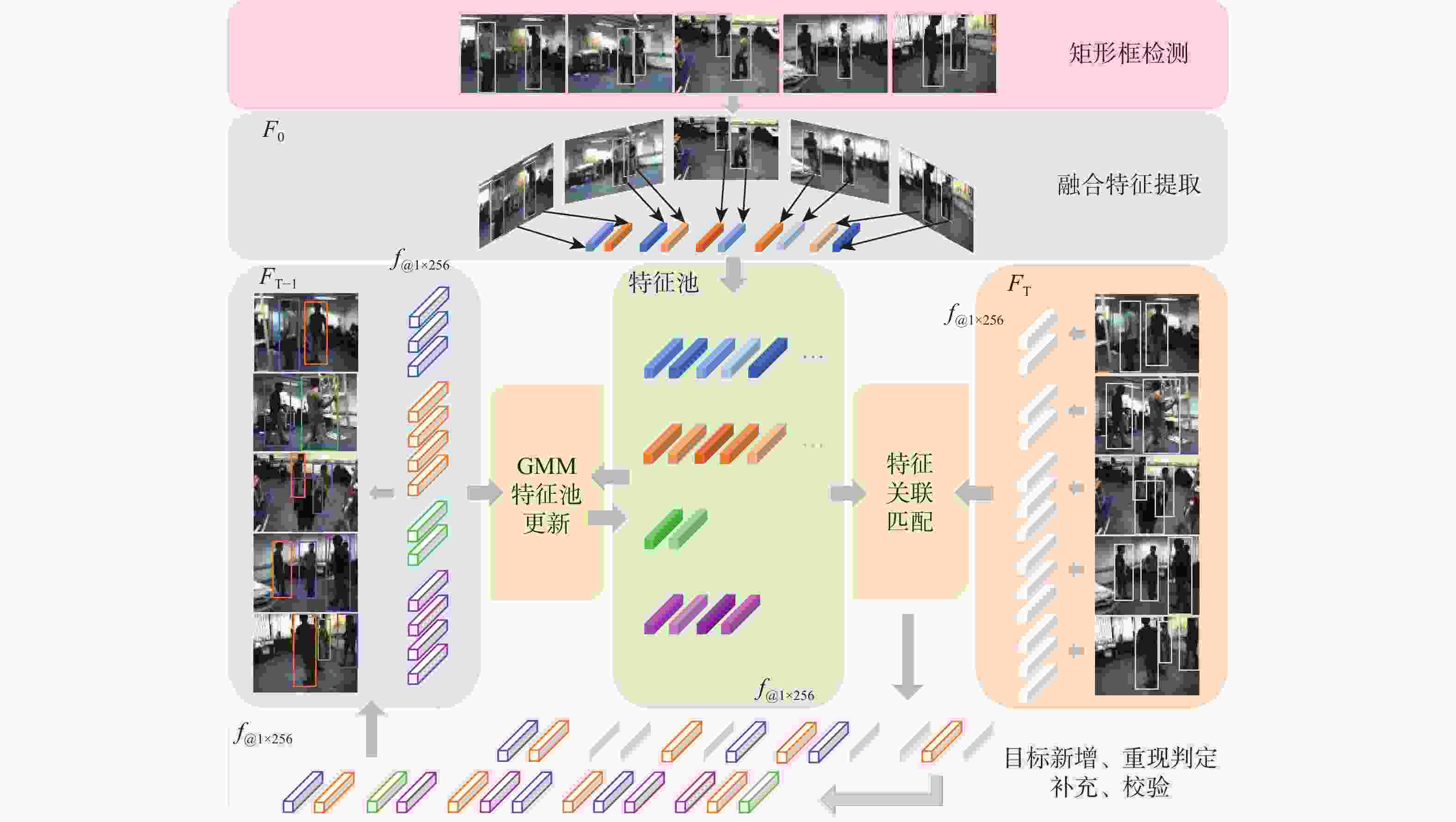
 下载:
下载: