-
摘要:
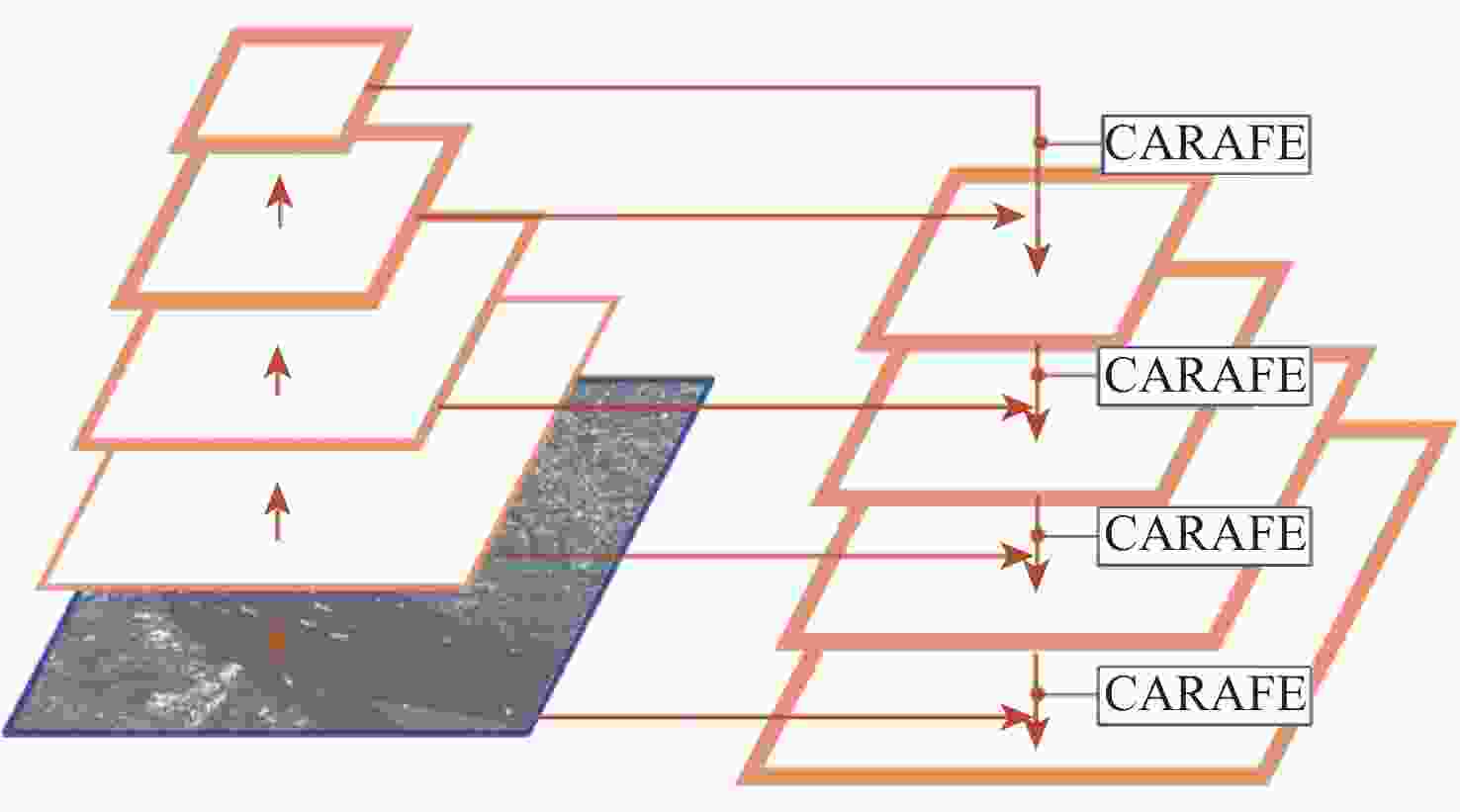
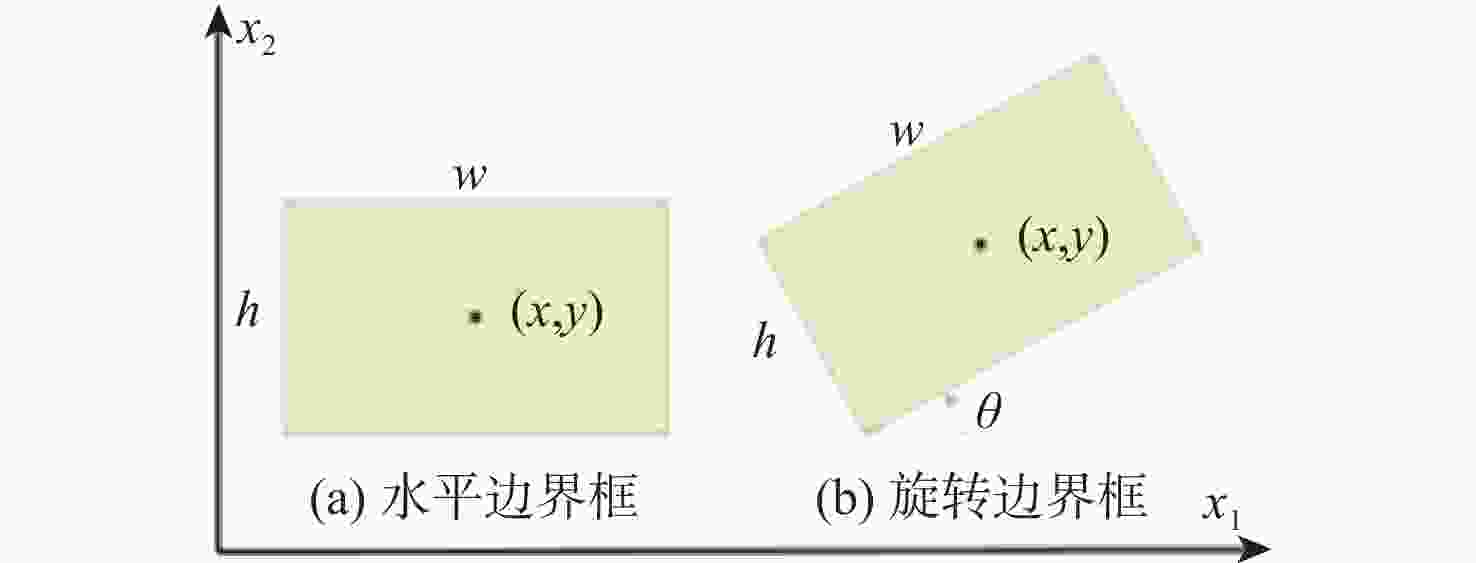
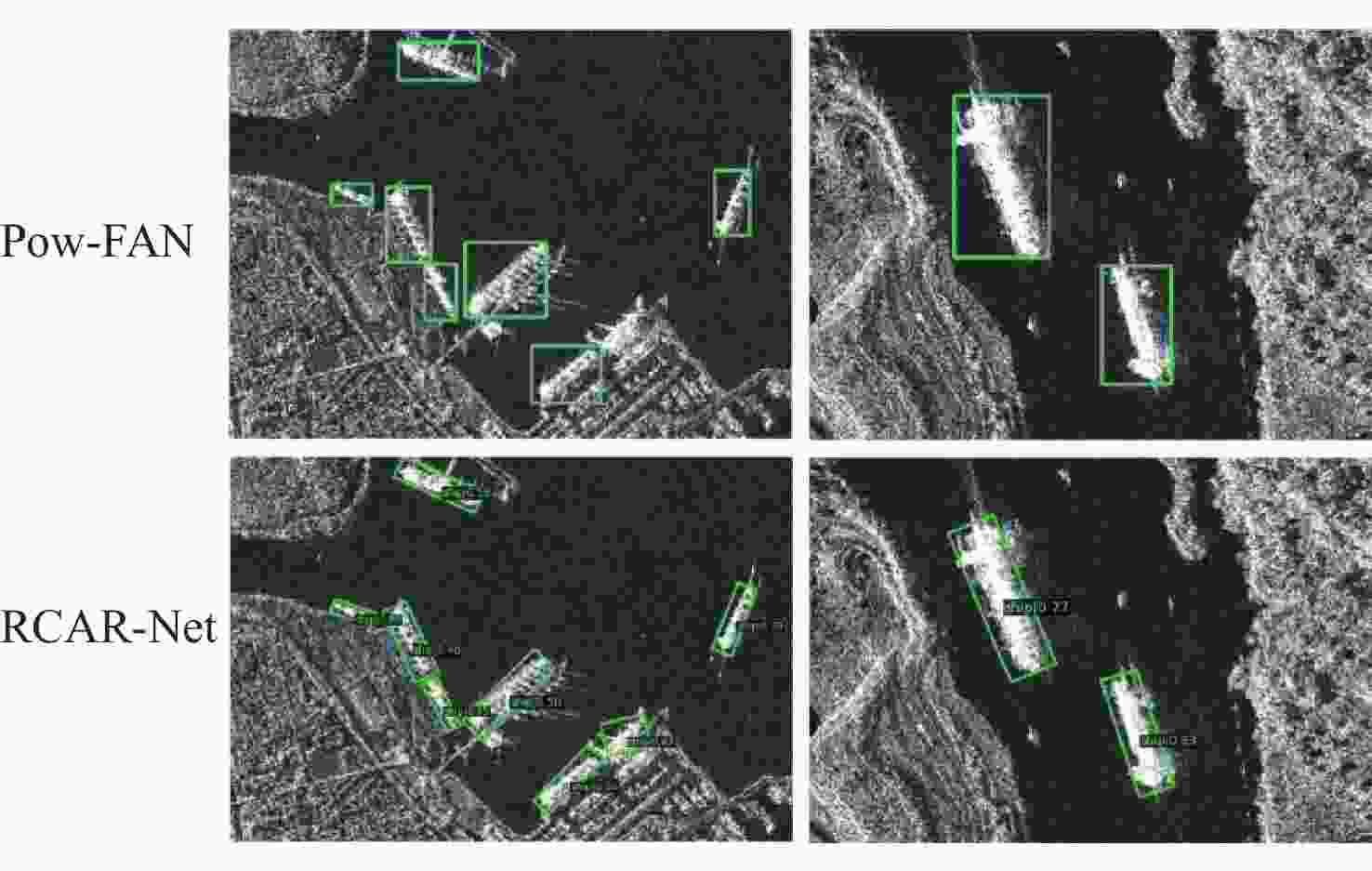
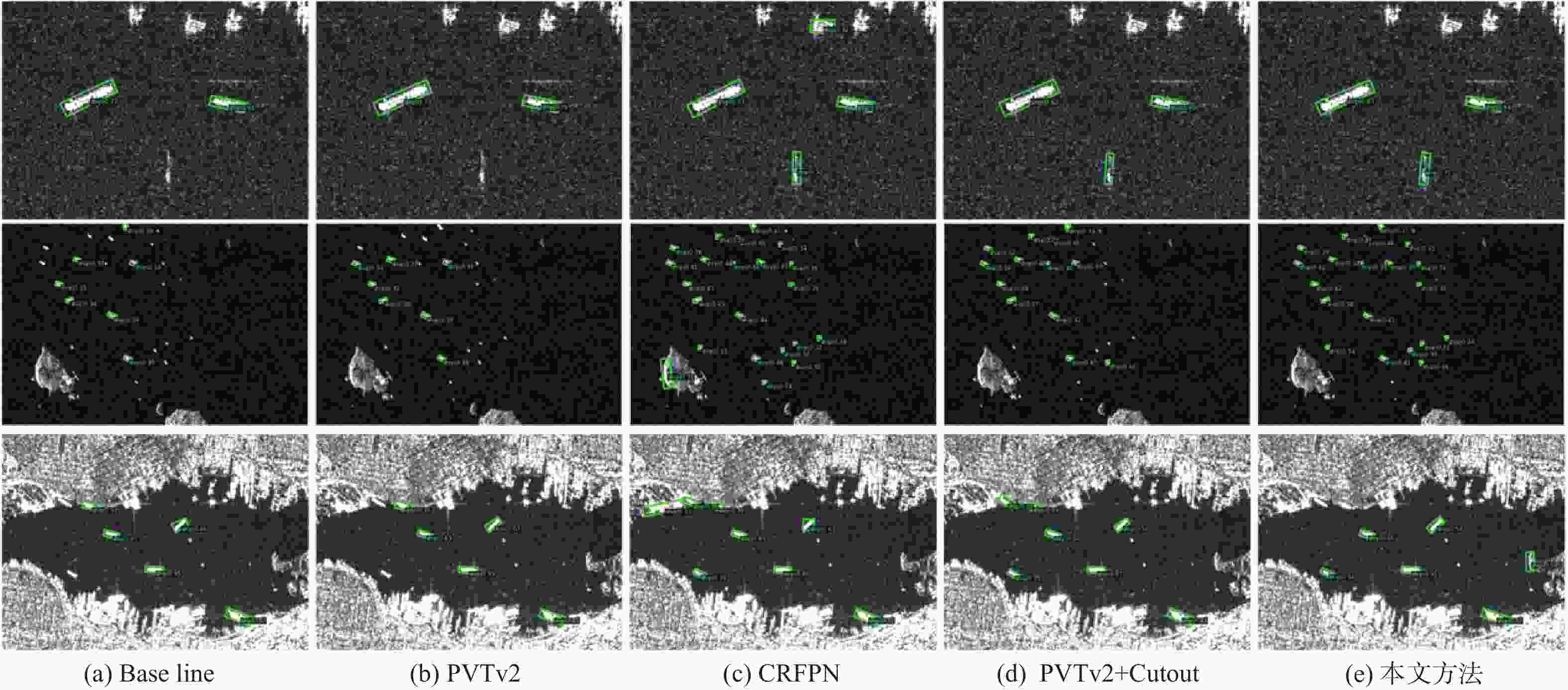
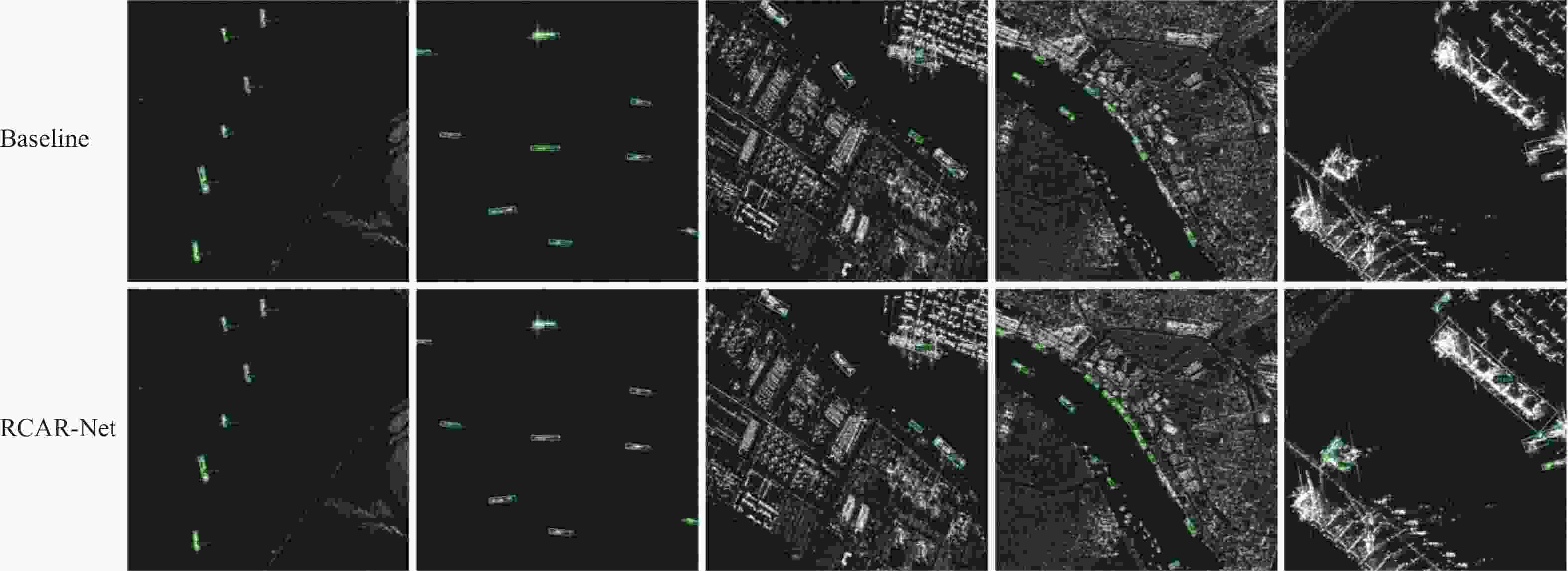
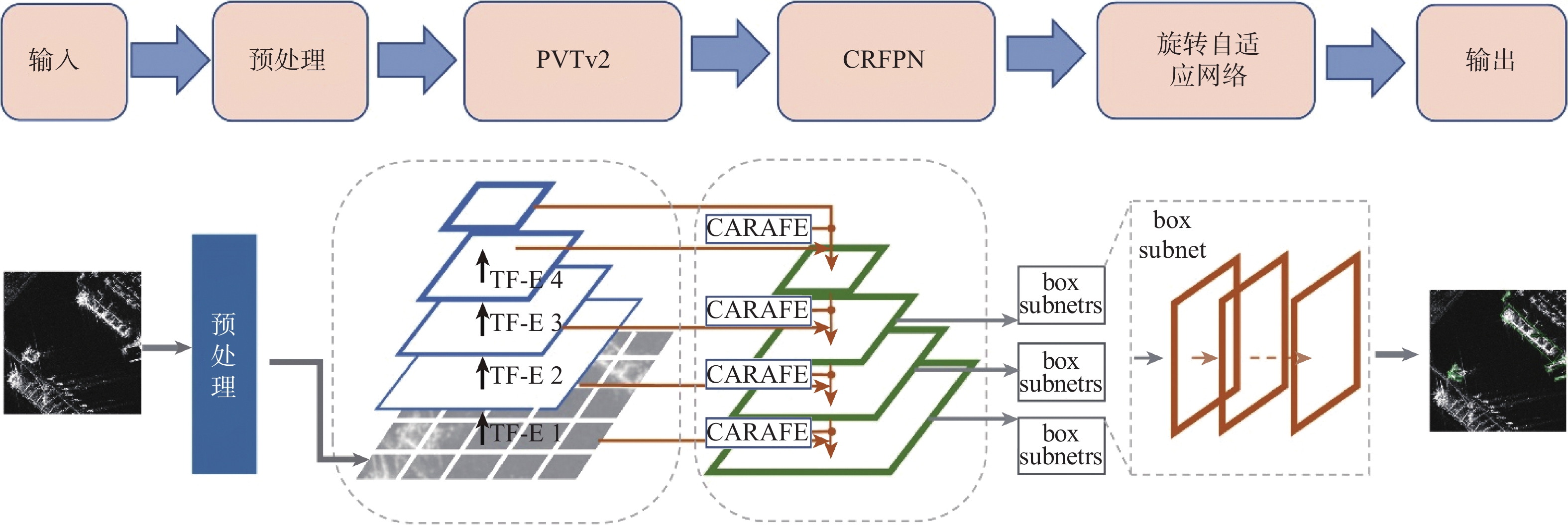
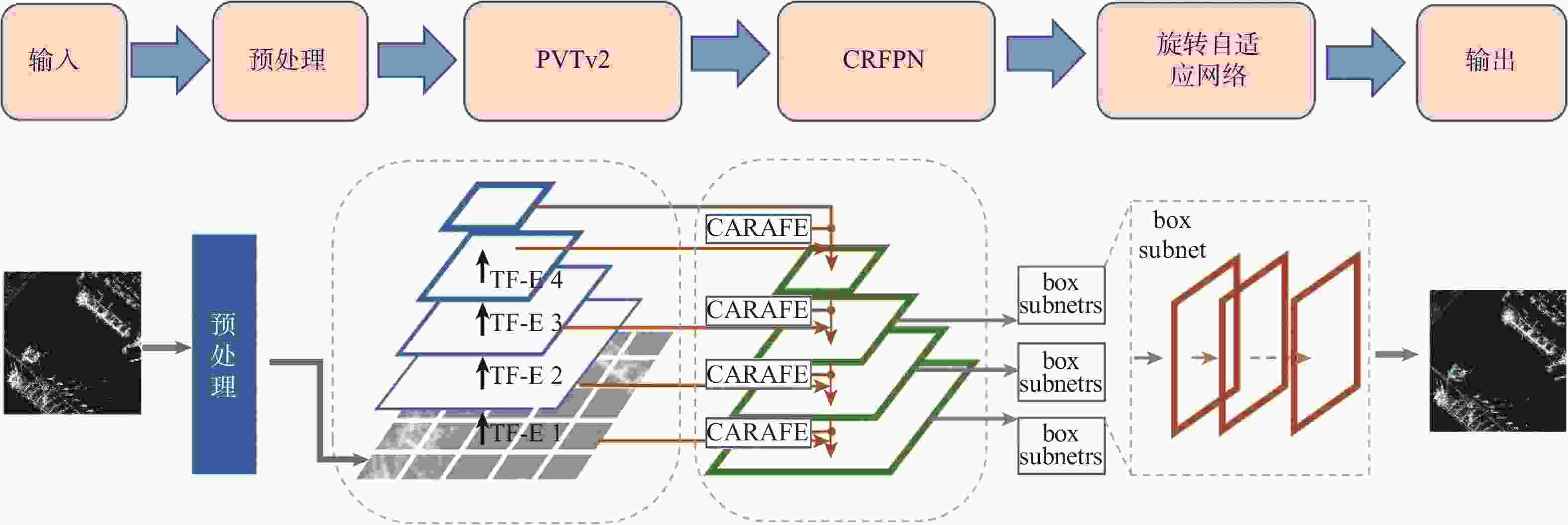
目标尺寸变化多样且干扰因素多,目标有多种方向且训练样本数据量有限是当前合成孔径雷达(SAR)船舶检测方法主要面临的2个难题。为此,提出了一种用于SAR图像船舶检测的旋转目标感知网络RCAR-Net。主干网络使用基于多尺度Transformer架构的PVTv2,可以更好地保留特征图的局部连续性,同时更好地融合图像的多尺度特征;将旋转边界框与RetinaNet结合,有效减少了背景冗余以及噪声的干扰;引入Cutout方法进行数据增强,用现有样本的部分遮挡来扩大数据集,提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力;为了在保证检测精度的同时节省计算和内存开销,使用高效的CARAFE 算子对低分辨率的特征图进行上采样,提高多尺度融合效果。RCAR-Net在SSDD和HRSID这2个SAR船舶检测数据集的平均精度分别达到93.63%和90.37%,明显优于DPAN、PANet等方法,对于目标尺寸变化和噪声干扰具有较强的适应性。
Abstract:Current synthetic aperture radar (SAR) ship detection methods primarily encounter two challenges: 1) the variability of target sizes and the abundance of interfering factors; 2) multiple orientations of targets and a limited quantity of training samples. To address these issues, this paper introduces a Rotating Target-Aware Network for SAR image ship detection, RCAR-Net. Firstly, the backbone network employs the PVTv2 based on a multi-scale Transformer architecture, which better preserves the local continuity of feature maps while enhancing the integration of multi-scale image features. In conjunction, a combination of rotating bounding boxes with RetinaNet effectively reduces background redundancy and noise interference. The model's generalizability and robustness are further enhanced by the introduction of the Cutout data augmentation technique, which uses partial occlusion of current samples to enlarge the dataset. Finally, the effective CARAFE operator is used to upsample low-resolution feature maps, improving the multi-scale fusion effect, reducing computational and memory costs while maintaining detection accuracy. RCAR-Net achieves an average precision of 93.63% and 90.37% on the SSDD and HRSID SAR ship detection datasets, respectively, significantly outperforming current methods such as DPAN and PANet, demonstrating strong adaptability to changes in target size and noise interference.
-
Key words:
- synthetic aperture radar /
- ship detection /
- rotated bounding box /
- deep learning /
- attention mechanism
-
表 1 RCAR-Net 消融实验
Table 1. RCAR-Net ablation experiment
Baseline PVTv2 CARAFE Cutout mAP/% 实验设置 69.42 √ 72.07 √ 73.09 √ √ 73.26 √ √ √ 76.39 表 2 本文方法与当前方法在 SSDD 和 HRSID 数据集上的对比
Table 2. Comparison of the proposed method with current methods on SSDD and HRSID datasets
方法 mAP/% SSDD HRSID Faster R-CNN[26] 92.07 81.80 Cascade RCNN[27] 91.61 81.89 YOLOv4[28] 92.16 83.23 SSD300[29] 87.06 79.05 SSD512[29] 89.19 82.50 DAPN[17] 90.60 88.20 Double-Head R-CNN[18] 91.17 80.41 PANet[19] 91.73 80.11 RetinaNet[8] 86.37 77.32 Quad-FPN[30] 92.84 86.12 LFG-Net[31] 93.01 88.50 RCAR-Net (本文) 93.63 90.37 -
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6-43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [2] REIGBER A, SCHEIBER R, JAGER M, et al. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: signal processing and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2013, 101(3): 759-783. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2220511 [3] CUI J Y, JIA H C, WANG H P, et al. A fast threshold neural network for ship detection in large-scene SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 6016-6032. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3192455 [4] ZHANG T W, ZHANG X L, LI J W, et al. SAR ship detection dataset (SSDD): official release and comprehensive data analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3690. doi: 10.3390/rs13183690 [5] WEI S J, ZENG X F, QU Q Z, et al. HRSID: a high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 120234-120254. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005861 [6] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 580-587. [7] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [8] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2999-3007. [9] LI J W, QU C W, SHAO J Q. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [10] WANG Y Y, WANG C, ZHANG H, et al. Automatic ship detection based on RetinaNet using multi-resolution Gaofen-3 imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 531. doi: 10.3390/rs11050531 [11] ZHOU Z, CHEN J, HUANG Z X, et al. HRLE-SARDet: a lightweight SAR target detection algorithm based on hybrid representation learning enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5203922. [12] CHEN S W, CUI X C, WANG X S, et al. Speckle-free SAR image ship detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 5969-5983. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3089936 [13] DEVRIES T, TAYLOR G W, ASSIRI Y. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout[EB/OL]. (2017-11-29)[2023-06-01]. http://arXiv.org/abs/1708.04552v2. [14] WANG W H, XIE E Z, LI X, et al. PVT v2: improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2022, 8(3): 415-424. doi: 10.1007/s41095-022-0274-8 [15] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale[EB/OL]. (2021-06-03)[2023-06-02]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1708.04552. [16] WANG W, XIE E, LI X, et al. Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions[C]// 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 548- 558. [17] CUI Z Y, LI Q, CAO Z J, et al. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi- scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8983-8997. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923988 [18] WU Y, CHEN Y P, YUAN L, et al. Rethinking classification and localization for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10183-10192. [19] LIU S, QI L, QIN H F, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2018/CVF IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8759-8768. [20] NOH H, HONG S, HAN B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1520-1528. [21] WANG J, CHEN K, XU R, et al. CARAFE: content-aware ReAssembly of FEatures[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3007-3016. [22] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2117-2125. [23] XIAO M, HE Z, LI X Y, et al. Power transformations and feature alignment guided network for SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4509405. [24] EVERINGHAM M, VAN GOOL L, WILLIAMS C K, et al. The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303-338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [25] LOSHCHILOV I, HUTTER F. Decoupled weight decay regularization[EB/OL]. (2019-01-04)[2023-06-07]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1711.05101. [26] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1137-1149. [27] CAI Z W, VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: delving into high quality object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 6154-6162. [28] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H M. Scaled-YOLOv4: scaling cross stage partial network[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13024-13033. [29] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: single shot multi-box detector[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [30] ZHANG T W, ZHANG X L, KE X. Quad-FPN: a novel quad feature pyramid network for SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(14): 2771. doi: 10.3390/rs13142771 [31] WEI S J, ZENG X F, ZHANG H, et al. LFG-net: low-level feature guided network for precise ship instance segmentation in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5231017. -






 下载:
下载:
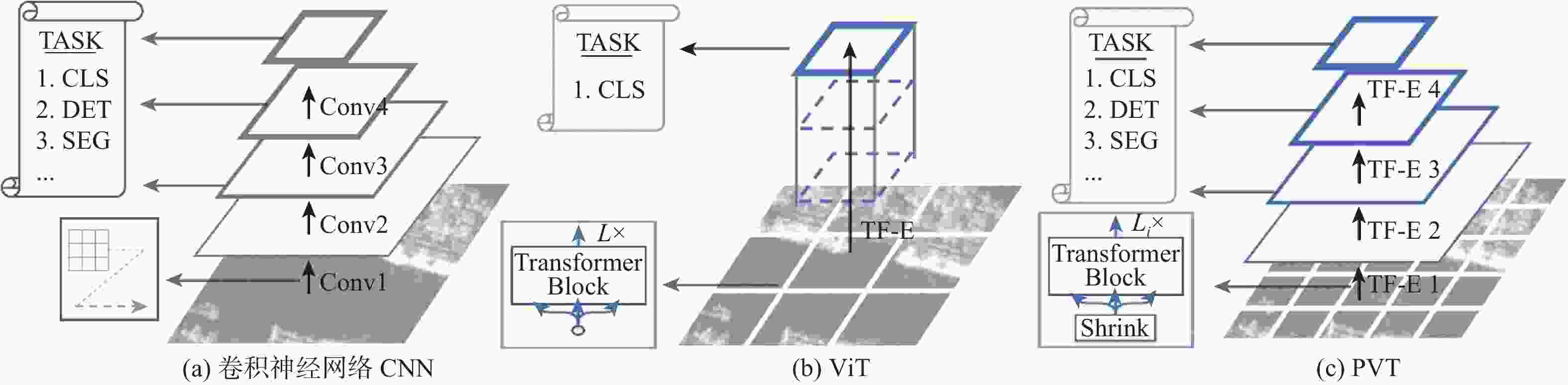
 图 2 卷积神经网络 CNN、ViT 与 PVT 的架构对比
图 2 卷积神经网络 CNN、ViT 与 PVT 的架构对比