-
摘要:
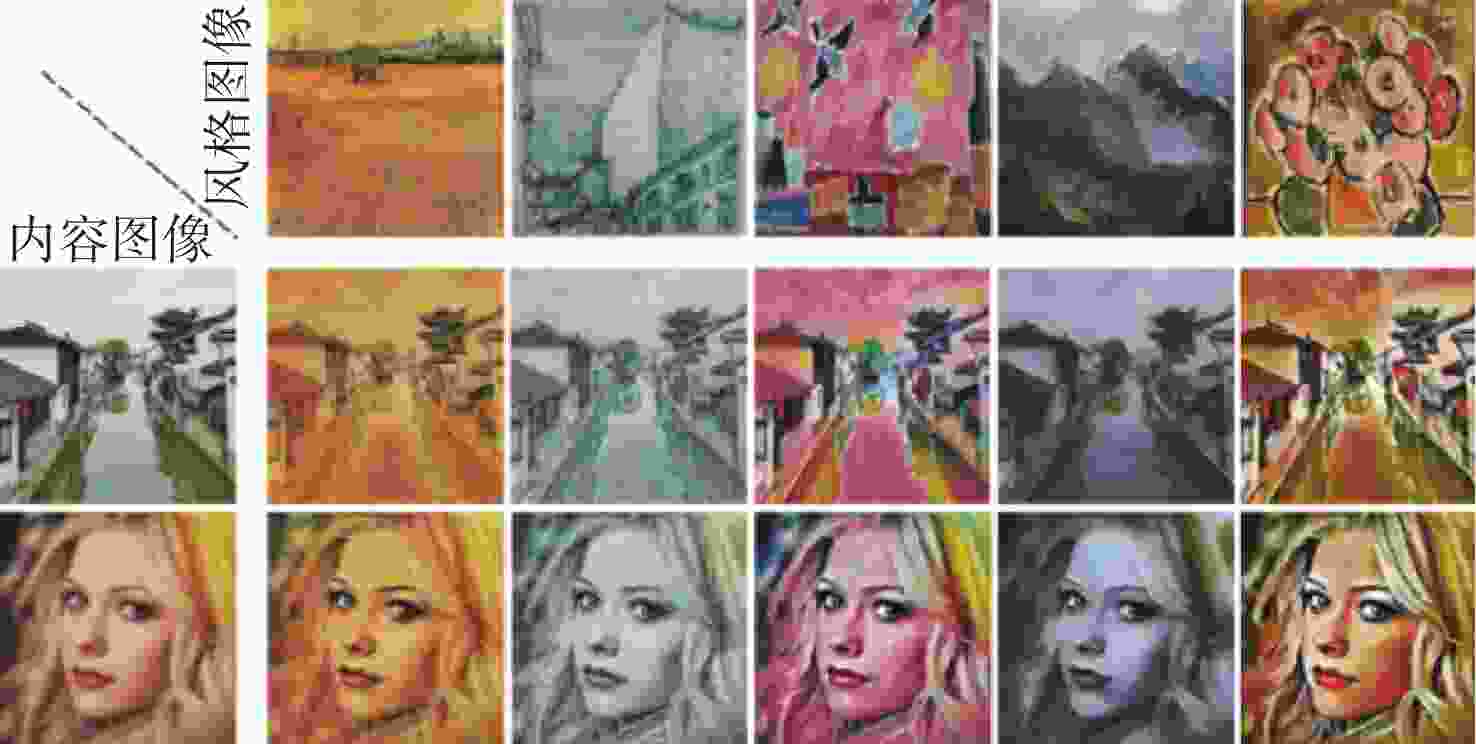
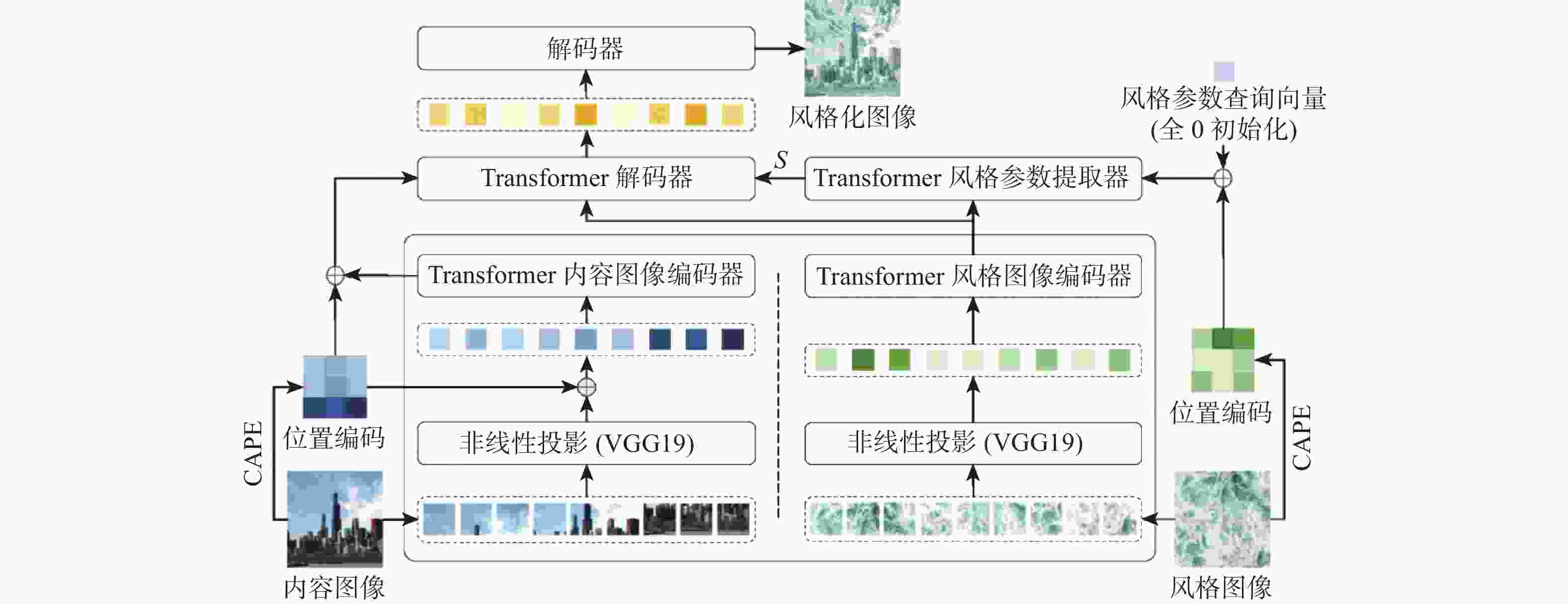
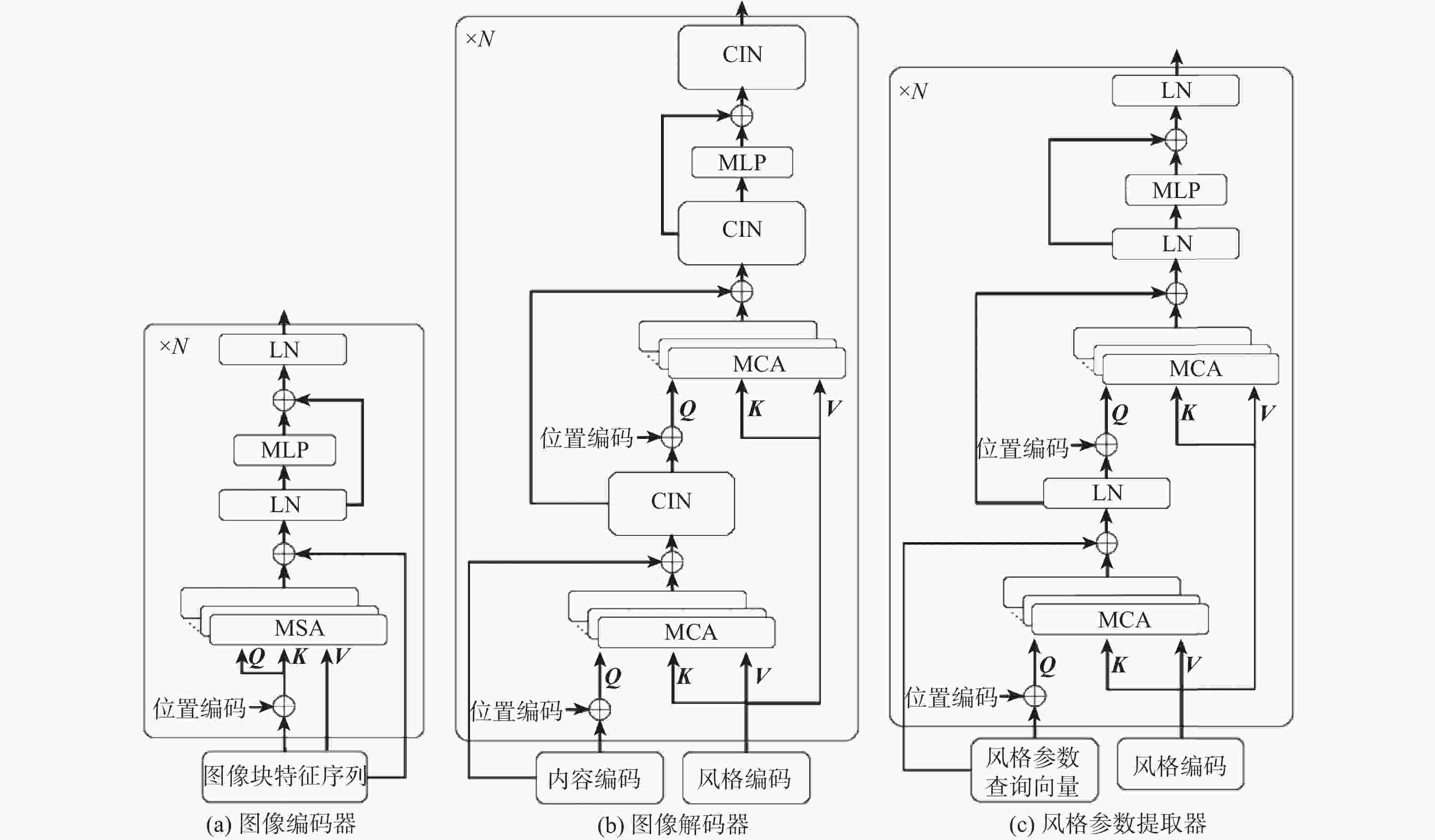
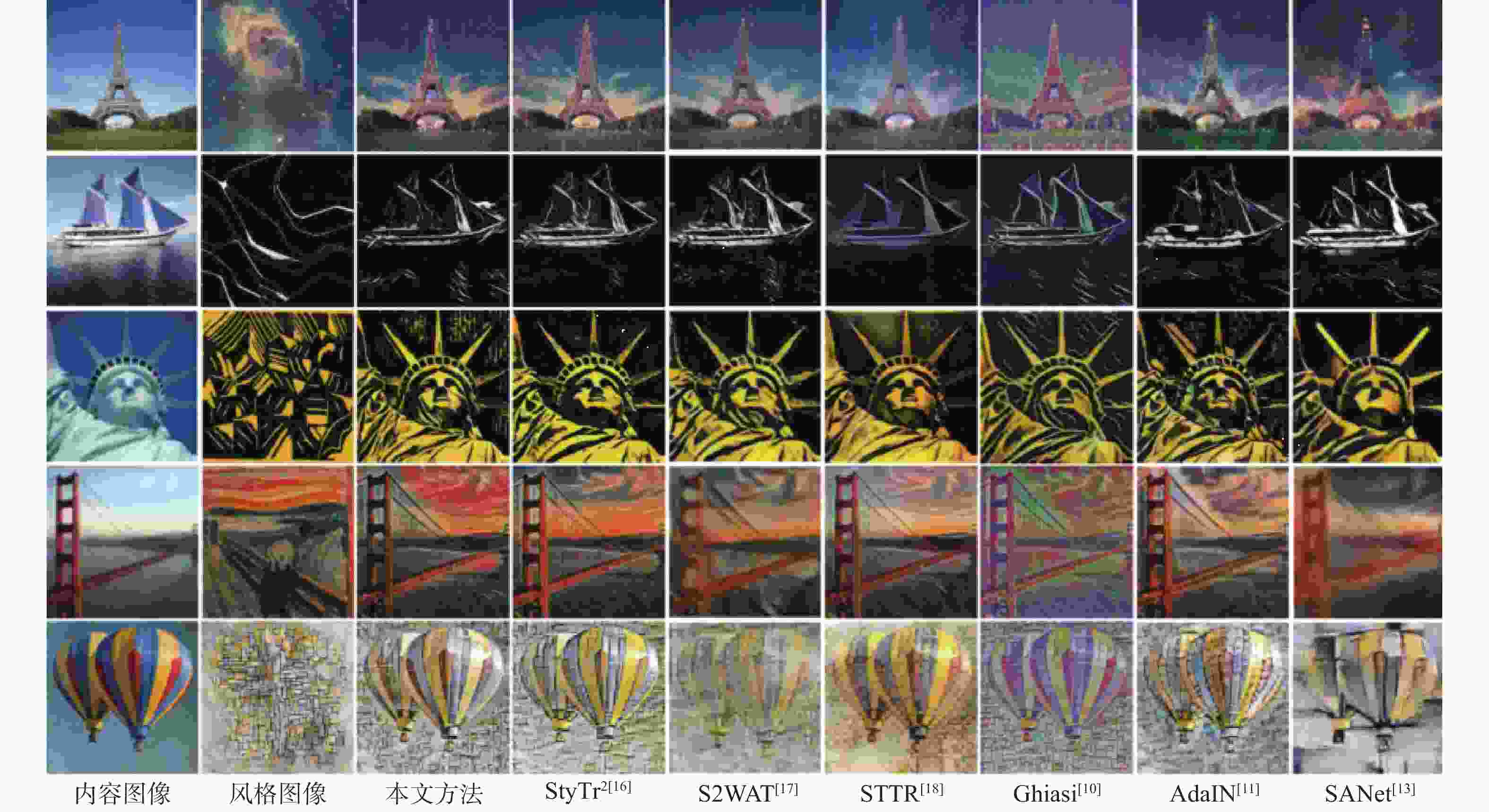
图像风格迁移旨在根据风格图像调整内容图像的视觉属性,使其保留原始内容的同时呈现出特定风格样式,从而生成具有视觉吸引力的风格化图像。针对现有代表性方法大多未考虑不同图像域间的编码差异,专注提取图像局部特征而忽视了全局上下文信息的重要性,提出一种新型的基于双路视觉Transformer的图像风格迁移方法Bi-Trans,对内容图像域和风格图像域进行独立编码,提取风格参数向量以离散化表征图像风格,通过交叉注意力机制与条件实例归一化(CIN)将内容图像标定至目标域风格,从而生成风格化图像。实验结果表明,该方法无论是内容保留度还是风格还原度均优于现有方法。
-
关键词:
- 图像风格迁移 /
- 视觉Transformer /
- 任意风格化 /
- 条件实例归一化 /
- 注意力机制
Abstract:Image style transfer aims to adjust the visual properties of a content image based on a style reference image, preserving the original content while presenting specific styles to generate visually appealing stylized images. Most existing representative methods focus on extracting local image features without considering the encoding differences between different image domains or the importance of global contextual information. To address this issue, Bi-Trans, a novel image style transfer method based on a dual-channel vision Transformer was proposed. This method encoded the content and style image domains independently, extracting style parameter vectors to discretely represent the image style. By using a cross-attention mechanism and conditional instance normalization (CIN), the content image was calibrated to the target style domain, generating the stylized image. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method is superior to existing methods in terms of both content preservation and style restoration.
-
表 1 本文方法与基于CNN的方法平均风格化损失对比
Table 1. Comparison of average stylization loss between proposed method and CNN-based methods
表 2 本文方法与基于视觉Transformer的方法平均风格化损失对比
Table 2. Comparison of average stylization loss between proposed method and vision Transformer based methods
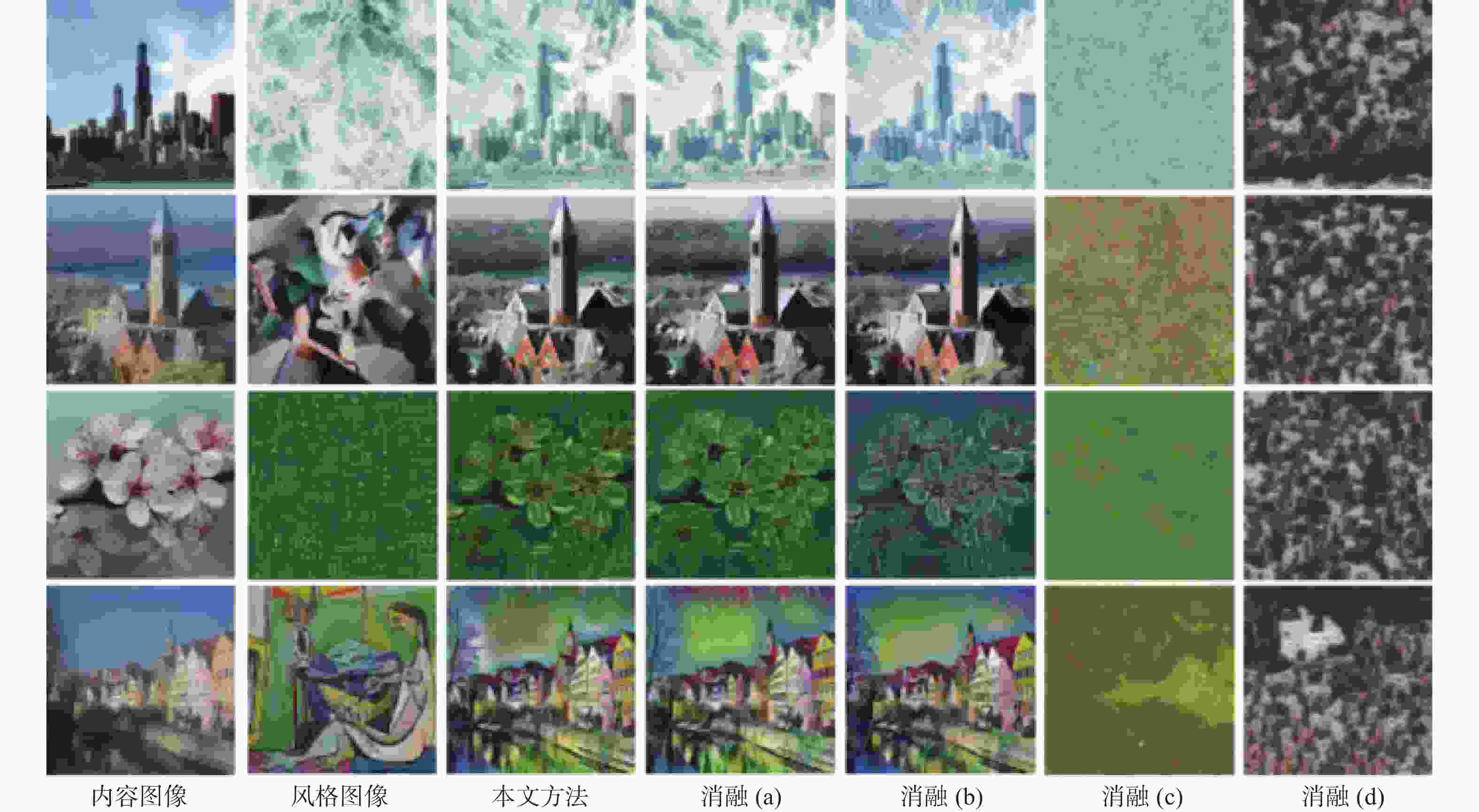
表 3 不同消融设置下的平均风格化损失对比
Table 3. Comparison of average stylization loss under different ablation settings
方法 $ \mathscr{L}_{\text {con}} $ $ \mathscr{L}_{\text {sty}}^{\mu, \sigma}$ $\mathscr{L}_{\text {sty}}^{{\mathrm{Gram}}} $ 消融(a) 0.70 1.02 3.15 消融(b) 0.64 1.37 4.71 消融(c) 1.88 11.36 18.61 消融(d) 1.93 6.75 16.05 完整方法 0.69 0.94 3.02 -
[1] ZHANG Y, HUANG N, TANG F, et al. Inversion-based style transfer with diffusion models[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 10146-10156. [2] ZHANG Y X, DONG W M, TANG F, et al. ProSpect: prompt spectrum for attribute-aware personalization of diffusion models[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. [3] WANG Z, ZHAO L, XING W. Stylediffusion: controllable disentangled style transfer via diffusion models[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 7677-7689. [4] ROMBACH R, BLATTMANN A, LORENZ D, et al. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 10674-10685. [5] JING Y C, YANG Y Z, FENG Z L, et al. Neural style transfer: a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2020, 26(11): 3365-3385. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2019.2921336 [6] GATYS L A, ECKER A S, BETHGE M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural network [C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 2414-2423. [7] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, LI F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV . Cham: Springer, 2016: 694-711. [8] ULYANOV D, LEBEDEV V, VEDALDI A, et al. Texture networks: feed-forward synthesis of textures and stylized images[EB/OL]. (2016-03-10)[2023-01-10]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.03417v1. [9] LIN T W, MA Z Q, LI F, et al. Drafting and revision: Laplacian pyramid network for fast high-quality artistic style transfer[C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 5137-5146. [10] GHIASI G, LEE H, KUDLUR M, et al. Exploring the structure of a real-time arbitrary neural artistic stylization network[C]//British Machine Vision Conference. Great Britain: BMVA, 2017: 1-27. [11] HUANG X, BELONGIE S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1510-1519. [12] LI Y, FANG C, YANG J, et al. Universal style transfer via feature transforms[C]//Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. La Jolla: NIPS, 2017: 1-11. [13] PARK D Y, LEE K H. Arbitrary style transfer with style-attentional networks[C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition . Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5873-5881. [14] LIU S H, LIN T W, HE D L, et al. AdaAttN: revisit attention mechanism in arbitrary neural style transfer[C]//IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 6629-6638. [15] CHANDRAN P, ZOSS G, GOTARDO P, et al. Adaptive convolutions for structure-aware style transfer [C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 7968-7977. [16] DENG Y Y, TANG F, DONG W M, et al. StyTr2: image style transfer with transformers[C]//IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 11316-11326. [17] ZHANG C, YANG J, WANG L, et al. S2WAT: image style transfer via hierarchical vision transformer using Strips Window Attention[EB/OL]. (2022-11-07)[2023-06-19]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12381. [18] WANG J B, YANG H, FU J L, et al. Fine-grained image style transfer with visual transformers[C]//Computer Vision-ACCV. Cham: Springer, 2023: 427-443. [19] ZHANG C Y, DAI Z Y, CAO P, et al. Edge enhanced image style transfer via transformers[C]//Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2023: 105-114. [20] FENG J X, ZHANG G, LI X H, et al. A compositional transformer based autoencoder for image style transfer[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(5): 1184. doi: 10.3390/electronics12051184 [21] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [22] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [23] GEIHOS R, RUBISCH P, MICHALIS C, et al. ImageNet-trained CNNs are biased towards texture; increasing shape bias improves accuracy and robustness[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. Washington DC: ICLR, 2019: 1-22. [24] WEI H P, DENG Y Y, TANG F, et al. A comparative study of CNN- and transformer-based visual style transfer[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2022, 37(3): 601-614. doi: 10.1007/s11390-022-2140-7 [25] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale [EB/OL]. (2021-06-03)[2023-06-19]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929. [26] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. La Jolla: NIPS, 2017: 5998-6008. [27] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: common objects in context[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV. Cham: Springer, 2014: 740-755. [28] PHILLIPS F, MACKINTOSH B. Wiki art gallery, inc. a case for critical thinking[J]. Issues in Accounting Education, 2011, 26(3): 593-608. doi: 10.2308/iace-50038 -






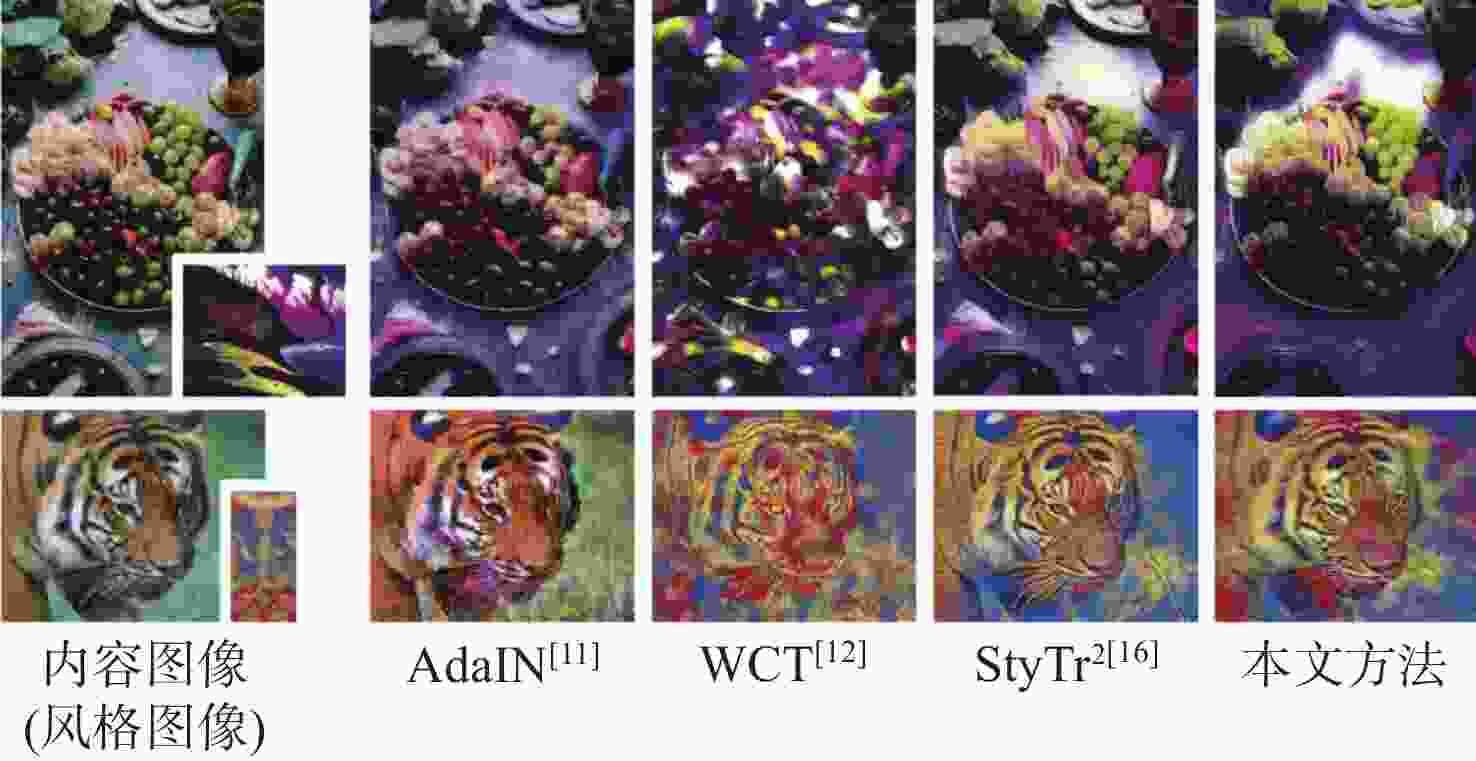
 下载:
下载: