-
摘要:
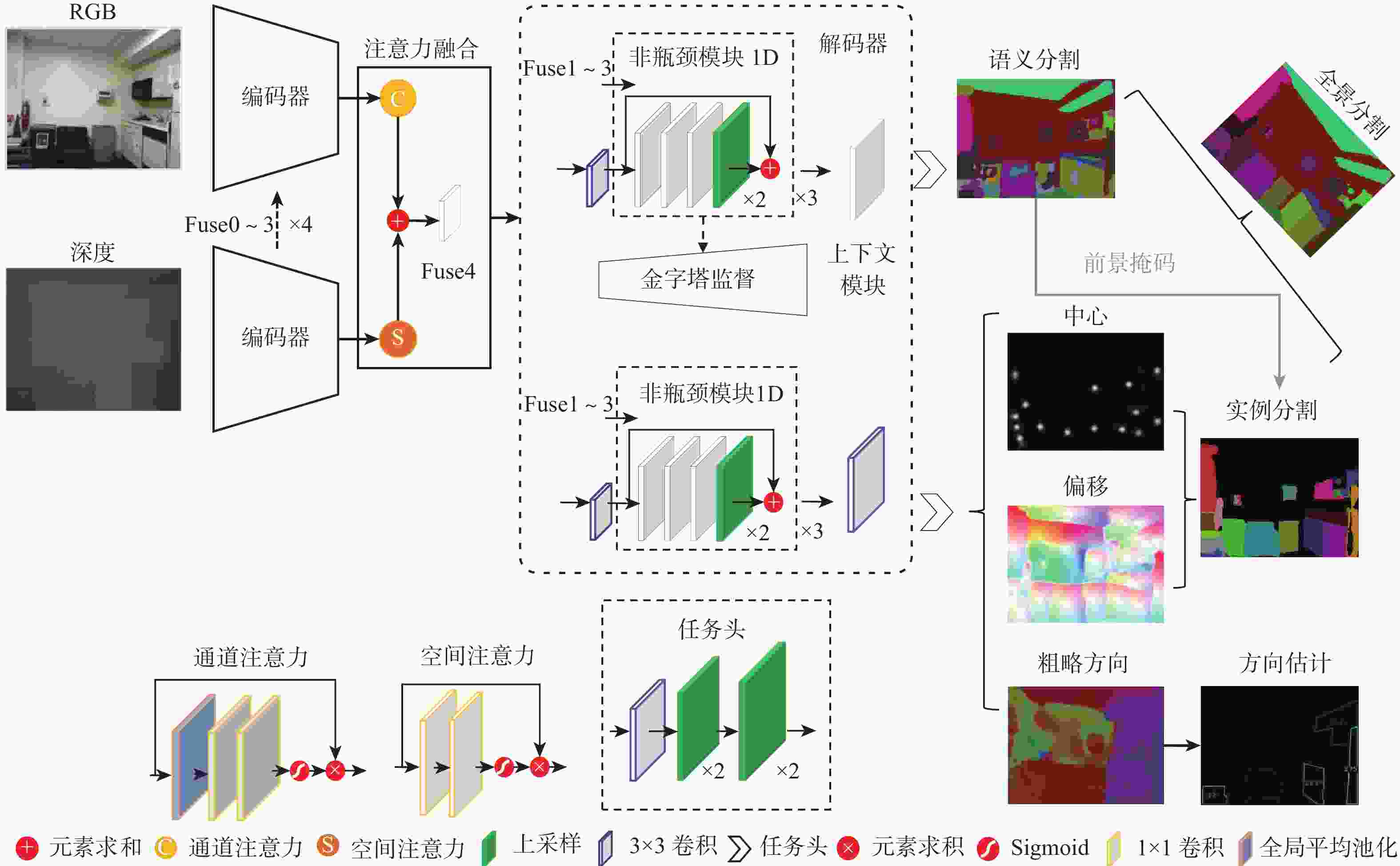
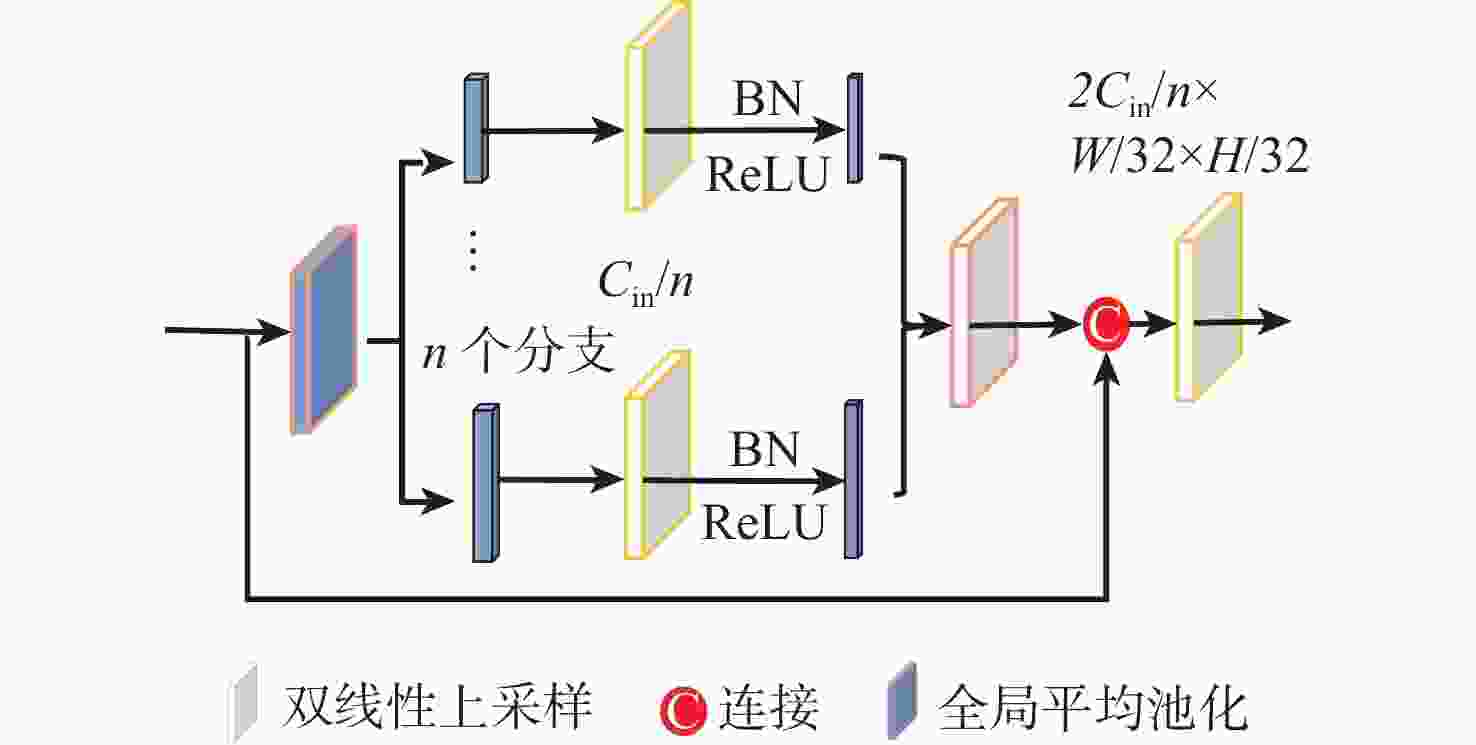
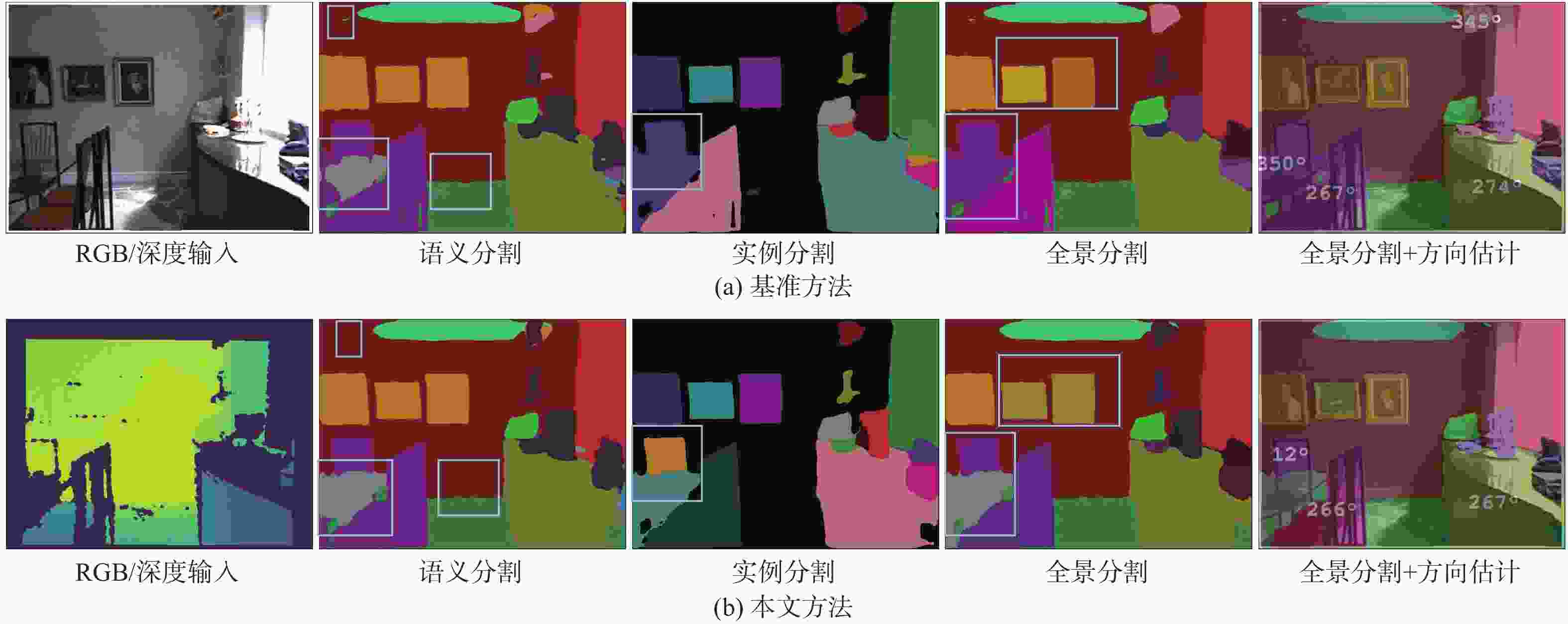
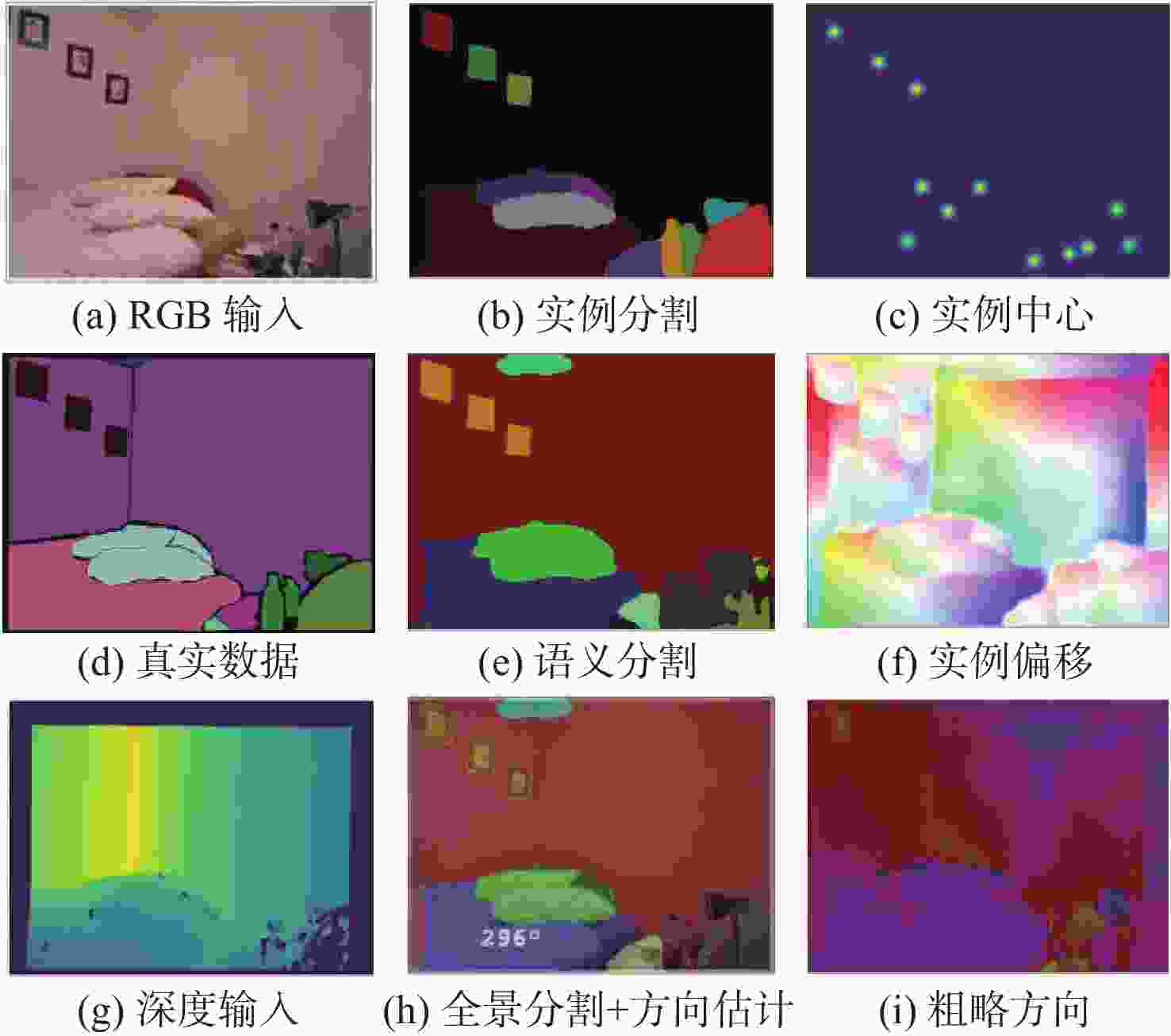
移动机器人在探索三维空间时需要获取大量场景信息,这些信息包含语义、实例对象、位置关系等多个方面。理解场景信息的准确性和计算复杂性是移动端关注的2个焦点。基于此,提出了一种适用于室内场景理解的空间信息增强的多任务学习方法。该方法由包含通道-空间注意力融合模块的编码器及多任务头的解码器组成,可同时实现语义分割、全景分割(实例分割)和方向估计多个任务。其中,通道-空间注意力融合模块旨在增强RGB和深度各自的模态特征,由简单卷积构成的空间注意力机制可降低收敛速度,与通道注意力机制信息融合后,进一步强化全局信息的位置特征。语义分支的上下文模块位于解码器后,为像素级语义信息提供有力支持,有助于减小模型大小。同时,设计了一种基于硬参数共享且能均衡训练任务的损失函数,探讨合适的轻量级骨干网络和任务数量对提升场景理解算法性能的影响。在新增标签注释的室内数据集NYUv2和SUN RGB-D上,评估了多任务学习方法的有效性,综合性全景分割精度分别提高了2.93%和4.87%。
Abstract:To explore 3D space, mobile robots need to obtain a large amount of scene information, which includes semantic, instance objects, and positional relationships. The accuracy and computational complexity of scene analysis are the two focuses of mobile terminals. Therefore, a spatial information-enhanced multi-task learning method for indoor scene understanding was proposed. This method consists of an encoder with a channel-spatial attention fusion module and a decoder with multi-task heads for semantic segmentation, panoptic segmentation (instance), and orientation estimation. The channel-spatial attention fusion module aims to enhance the modal characteristics of RGB and depth, and the spatial attention mechanism, composed of simple convolutions, can reduce the convergence speed. After fusing with the channel attention mechanism, it further strengthens the position features of global information. The context module of the semantic branch is located after the decoder, providing strong support for pixel-level semantic classification and helping to reduce the model size. A loss function based on hard parameter sharing was designed, enabling balanced training tasks. The influence of an appropriate lightweight backbone network and the number of tasks on improving the performance of scene understanding was discussed. Finally, on the NYUv2 and SUN RGB-D indoor datasets with newly added label annotations, the effectiveness of the proposed multi-task learning method was evaluated. Results show that the comprehensive panoramic segmentation accuracy is improved by 2.93% and 4.87%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- scene understanding /
- multi-task learning /
- RGB-D /
- spatial information /
- indoor scene
-
表 1 多任务数据标签
Table 1. Multi-task data label
主要任务 NYUv2 SUN RGB-D 训练集
样本数量测试集
样本数量训练集
样本数量测试集
样本数量语义分割 795 654 5285 5050 实例分割 12092 9874 18171 16961 方向估计 2696 2096 13076 12440 表 2 注意力融合方式和上下文位置的消融实验结果
Table 2. Ablation experiment results on attention fusion mode and context position
% 方法 融合方式 上下文位置 实例分割 全景分割 语义分割 PQ MAAE mIoU PQ RQ SQ MAAE mIoU 基准 2×SENet[8] 解码器前 60.99 17.59* 49.31 42.30 50.73 82.32* 16.83 50.16 方法1 2×CBAM[9] 解码器前 60.71 17.71 50.27 42.70 51.30 82.17 15.79* 50.35 方法2 2×NonLocal[10] 解码器前 61.75* 18.08 50.52* 42.98 51.75* 82.13 16.07 50.61* 方法3 SENet/Excite 解码器前 61.42 17.95 49.68 43.41* 51.39 82.21 15.94 49.97 方法4 2×SENet[8] 解码器后 61.61 18.33 49.19 42.79 51.48 82.68 16.10 49.76 方法5 2×NonLocal[10] 解码器后 61.02 19.11 48.42 41.85 50.19 82.31 16.52 48.45 本文方法 SENet/Excite 解码器后 61.88 18.45 49.36 43.54 52.08 82.60 15.76 49.75 注:“*”标志的数据表示注意力消融实验的最佳结果;SENet表示通道注意力模块,Excite表示空间注意力模块。 表 3 在NYUv2数据集中验证不同任务的组合效果
Table 3. Combination effect of different tasks verified on NYUv2 dataset
任务 任务权重 学习率 实例分割 全景分割 语义分割 PQ/% MAAE/% mIoU/% PQ/% RQ/% SQ/% MAAE/% mIoU/% 语义分割+实例分割 1∶3 0.03 61.81 48.56 42.98 51.33 82.43 48.77 实例分割+方向估计 3∶1 0.04 59.72 17.66 语义分割+实例分割+方向估计(本文) 1∶3∶1 0.04 61.88 18.45 49.36 43.54 52.08 82.60 15.76 49.75 语义分割+实例分割+方向估计+分类 1∶0.25∶3∶1 0.04 60.14 18.64 49.63 42.02 50.34 82.45 16.70 49.33 表 4 在SUN RGB-D数据集中验证不同任务的组合效果
Table 4. Combination effect of different tasks verified on SUN RGB-D dataset
任务 任务权重 学习率 实例分割 全景分割 语义分割 PQ/% MAAE/% mIoU/% PQ/% RQ/% SQ/% MAAE/% mIoU/% 语义分割+实例分割+方向估计(基准) 1∶2∶0.5 0.005 60.64 16.29 45.51 48.46 55.90 83.08 14.10 47.79 语义分割+实例分割+方向估计(本文) 1∶2∶0.5 0.005 61.17 16.01 45.00 50.82 58.96 85.05 14.66 47.75 语义分割+实例分割+方向估计+分类 1∶0.25∶2∶0.5 0.005 61.00 16.00 44.91 50.81 58.88 84.87 13.76 47.96 表 5 在NYUv2数据集上与最先进方法的比较
Table 5. Comparison with state-of-the-art methods on NYUv2 dataset
% 方法 骨干网络 模态 mIoU PQ MTI-Net[13] HRNet48 RGB 49.00 RefineNet[14] ResNet152 RGB 47.60 3DGNN[15] ResNet101 RGB-D 48.60 SGNet[16] ResNet101 RGB-D 49.00 Link-RGBD[26] ResNet50 RGB-D 49.50 SGACNet[27] ResNet34-NBt1D RGB-D 49.40 Panoptic-DeepLab[20] ResNet50 RGB 39.42 30.99 ResNet101 RGB 42.55 35.32 EMSANet[31] ASMLP-S RGB-D 36.02 28.52 ResNet18-NBt1D RGB-D 47.35 40.04 ResNet34-NBt1D RGB 44.16 36.38 ResNet34-NBt1D RGB-D 50.16 42.30 本文方法 ResNet34-NBt1D RGB-D 49.75 43.54 表 6 在SUN RGB-D数据集上与最先进方法的比较
Table 6. Comparison with state-of-the-art methods on SUN RGB-D dataset
方法 骨干网络 模态 mIoU/% 参数量 RefineNet[14] ResNet152 RGB 45.90 129.50×106 Link-RGBD[26] ResNet50 RGB-D 48.40 116.00×106 3DGNN[15] ResNet101 RGB-D 45.90 SGNet[16] ResNet101 RGB-D 47.10 64.70×106 ESANet[32] ResNet34-NBt1D RGB-D 47.46 46.95×106 SGACNet[27] ResNet34-NBt1D RGB-D 46.73 35.65×106 EMSANet[31] ResNet34-NBt1D RGB 45.41 49.37×106 ResNet34-NBt1D RGB-D 47.96 64.24×106 本文方法 ResNet34-NBt1D RGB-D 47.75 63.50×106 -
[1] 马素刚, 张子贤, 蒲磊, 等. 结合空间注意力机制的实时鲁棒视觉跟踪[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2024, 50(2): 419-432.MA S G, ZHANG Z X, PU L, et al. Real-time robust visual tracking based on spatial attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(2): 419-432(in Chinese). [2] WENGEFELD T, SEICHTER D, LEWANDOWSKI B, et al. Enhancing person perception for mobile robotics by real-time RGB-D person attribute estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2024: 914-921. [3] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [4] HE Y, XIAO L, SUN Z G, et al. Bimodal feature propagation and fusion for real-time semantic segmentation on RGB-D images[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1897-1902. [5] ISLAM M A, ROCHAN M, BRUCE N D B, et al. Gated feedback refinement network for dense image labeling[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4877-4885. [6] QUAN T M, HILDEBRAND D G C, JEONG W K. FusionNet: a deep fully residual convolutional neural network for image segmentation in connectomics[J]. Frontiers in Computer Science, 2021, 3: 613981. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2021.613981 [7] FU J, LIU J, TIAN H J, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3141-3149. [8] ZHANG R F, LI G B, LI Z, et al. Adaptive context selection for polyp segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 253-262. [9] YANG C L, ZHANG C C, YANG X Q, et al. Performance study of CBAM attention mechanism in convolutional neural networks at different depths[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 18th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 1373-1377. [10] ZOU W B, PENG Y Q, ZHANG Z Y, et al. RGB-D gate-guided edge distillation for indoor semantic segmentation[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(25): 35815-35830. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11395-w [11] ZHAO H S, QI X J, SHEN X Y, et al. ICNet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 418-434. [12] GE W X, YANG X B, JIANG R, et al. CD-CTFM: a lightweight CNN-transformer network for remote sensing cloud detection fusing multiscale features[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 4538-4551. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3361933 [13] VANDENHENDE S, GEORGOULIS S, VAN GOOL L. MTI-Net: multi-scale task interaction networks for multi-task learning[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 527-543. [14] LIN G S, LIU F Y, MILAN A, et al. RefineNet: multi-path refinement networks for dense prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(5): 1228-1242. [15] CAO J M, LENG H C, COHEN-OR D, et al. RGB × D: learning depth-weighted RGB patches for RGB-D indoor semantic segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 462: 568-580. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.08.009 [16] CHEN L Z, LIN Z, WANG Z Q, et al. Spatial information guided convolution for real-time RGBD semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2313-2324. [17] BORSE S, PARK H, CAI H, et al. Panoptic, instance and semantic relations: a relational context encoder to enhance panoptic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1259-1269. [18] XIONG Y W, LIAO R J, ZHAO H S, et al. A unified panoptic segmentation network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8810-8818. [19] MOHAN R, VALADA A. EfficientPS: efficient panoptic segmentation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(5): 1551-1579. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01445-z [20] CHENG B W, COLLINS M D, ZHU Y K, et al. Panoptic-DeepLab: a simple, strong, and fast baseline for bottom-up panoptic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 12472-12482. [21] ZOU Q, DU X Z, LIU Y Z, et al. Dynamic path planning and motion control of microrobotic swarms for mobile target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(4): 2454-2468. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2022.3207289 [22] MAHFOUDI M N, TURLETTI T, PARMENTELAT T, et al. ORION: orientation estimation using commodity Wi-Fi[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1233-1238. [23] CHRISTIE G, ABUJDER R R R M, FOSTER K, et al. Learning geocentric object pose in oblique monocular images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 14500-14508. [24] TANG H Y, LIU J N, ZHAO M, et al. Progressive layered extraction (PLE): a novel multi-task learning (MTL) model for personalized recommendations[C]//Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems. New York: ACM, 2020: 269-278. [25] LIU X D, HE P C, CHEN W Z, et al. Multi-task deep neural networks for natural language understanding[C]//Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 4487-4496. [26] WU P, GUO R Z, TONG X Z, et al. Link-RGBD: cross-guided feature fusion network for RGBD semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(24): 24161-24175. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3218601 [27] ZHANG Y, XIONG C Y, LIU J J, et al. Spatial information-guided adaptive context-aware network for efficient RGB-D semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(19): 23512-23521. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3304637 [28] HUANG L, GUO H. Research on multi-task learning method based on causal features[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision and Machine Learning. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 924-927. [29] BEYER L, HERMANS A, LEIBE B. Biternion Nets: continuous head pose regression from discrete training labels[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 9358: 157-168. [30] SILBERMAN N, HOIEM D, KOHLI P, et al. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 746-760. [31] SEICHTER D, FISCHEDICK S B, KÖHLER M, et al. Efficient multi-task RGB-D scene analysis for indoor environments[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1-10. [32] SONG S R, LICHTENBERG S P, XIAO J X. SUN RGB-D: a RGB-D scene understanding benchmark suite[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 567-576. -






 下载:
下载: