Pedestrian attribute recognition algorithm based on multi-label adversarial domain adaptation
-
摘要:
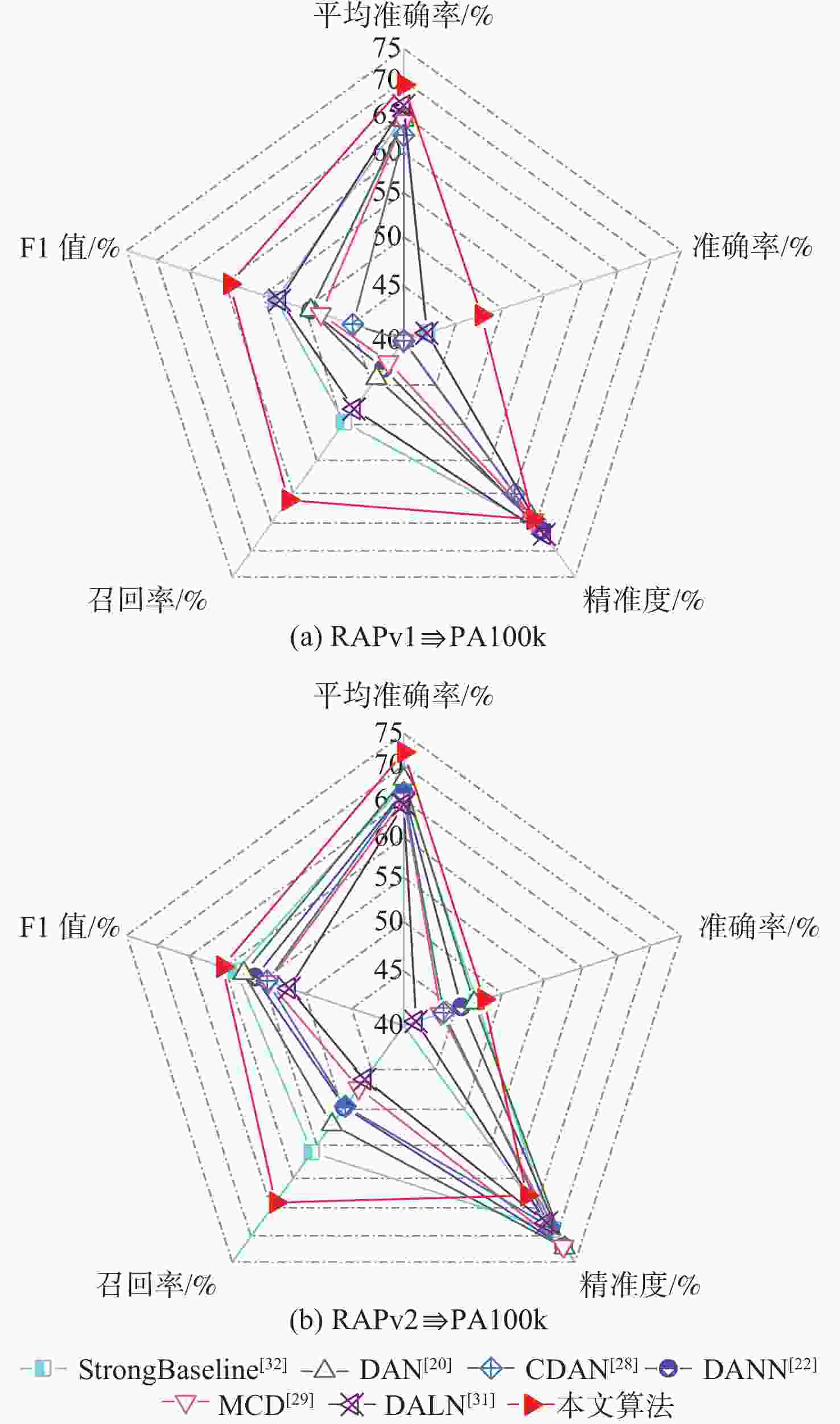
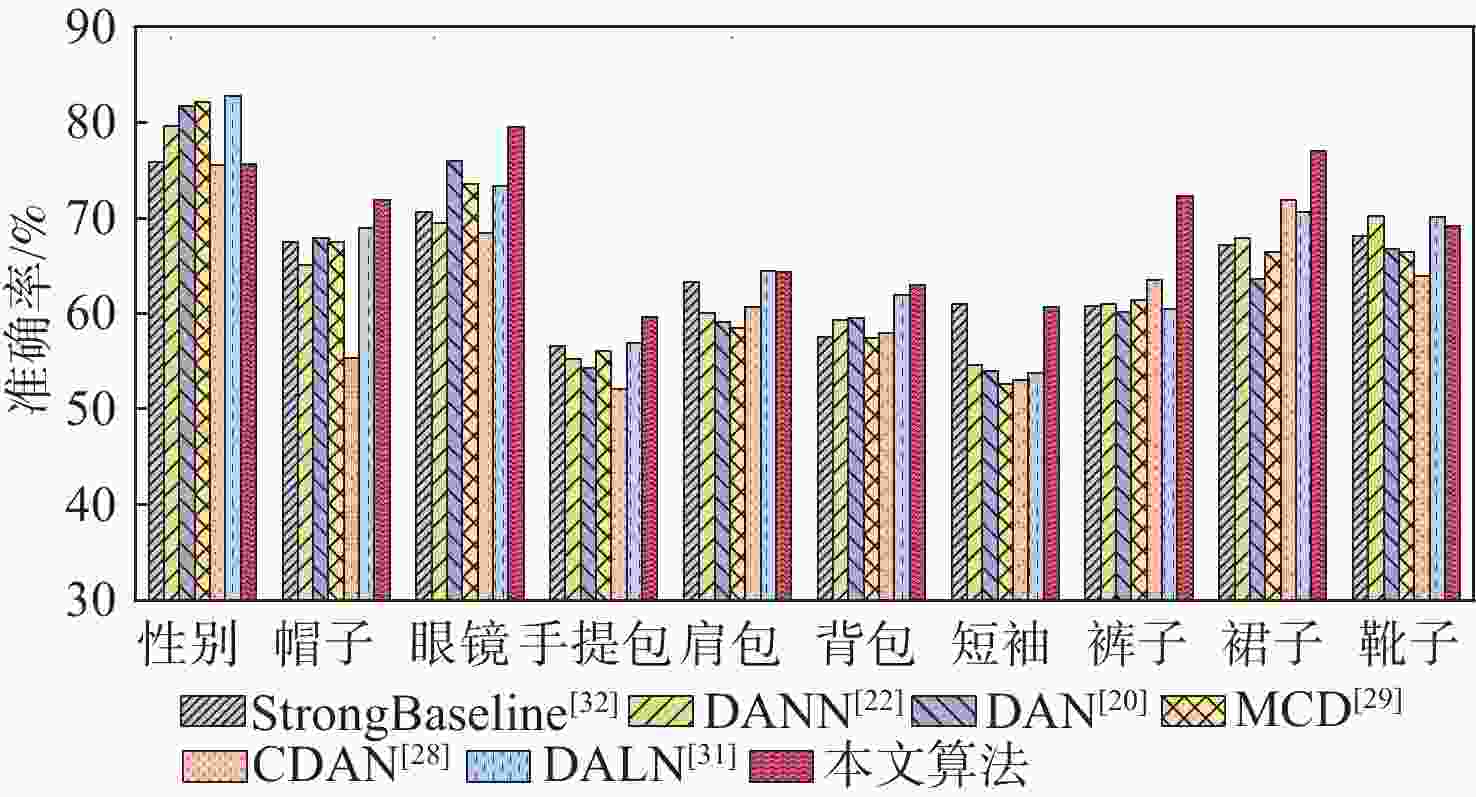
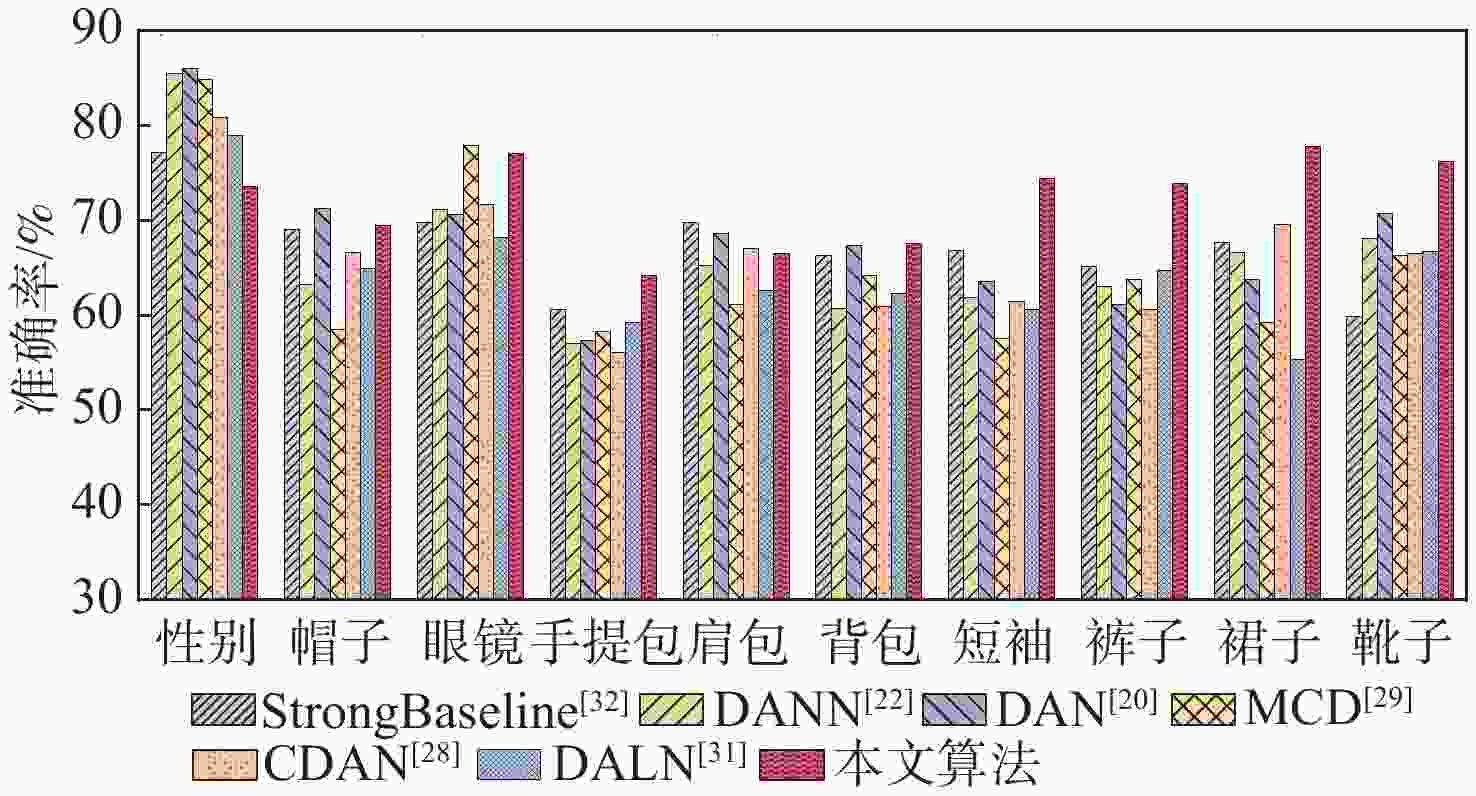
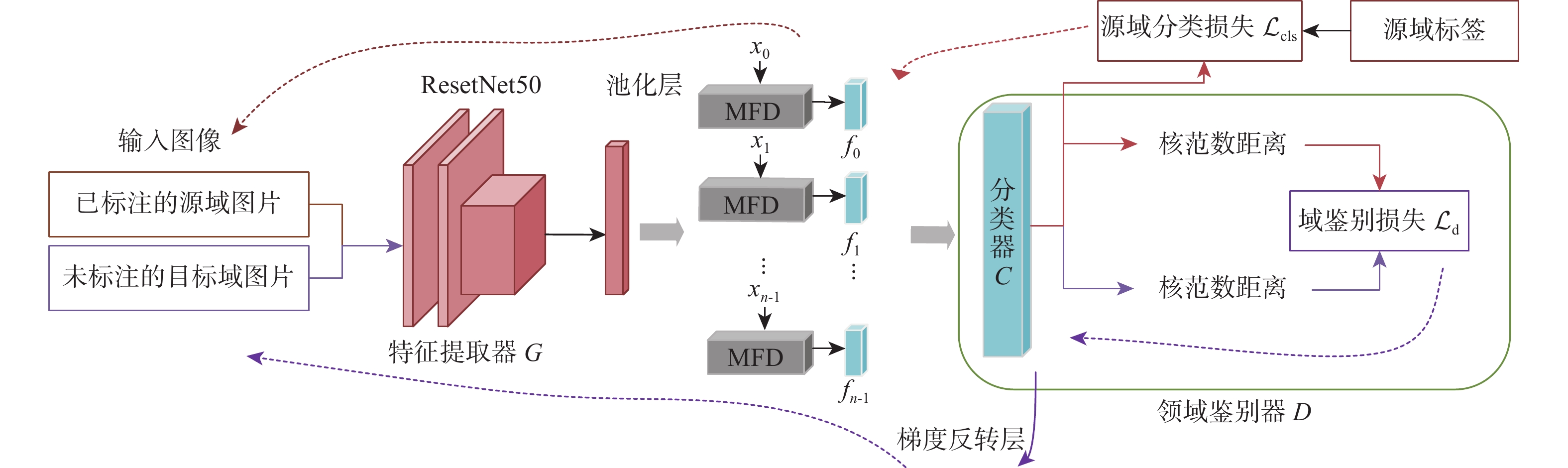
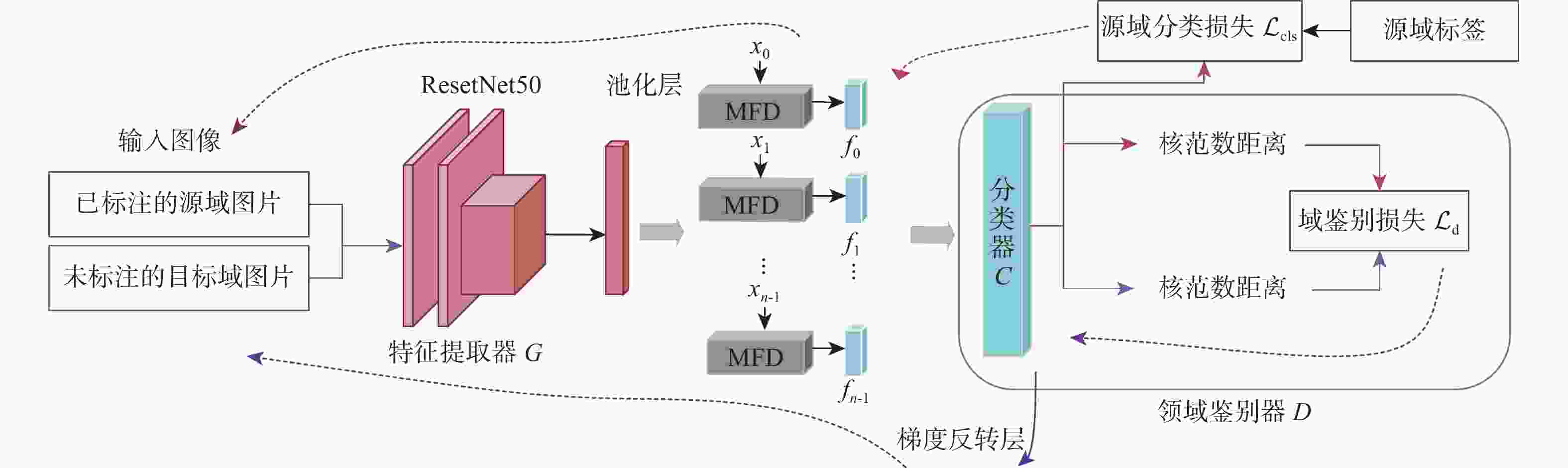
针对无监督领域自适应算法通常局限于单标签学习问题,难以适配针对行人属性的多标签分类任务,提出一种多标签对抗领域自适应的行人属性识别算法。为适应行人属性多标签领域迁移任务,基于多标签特征分离模块,利用特定类别语义对主干网络提取的深度特征进行属性分离,有效提取特定属性的表征信息。针对不同领域属性特征分布差异较大的难点,提出基于分类器复用的多标签领域鉴别模块,同时实现多标签领域对齐和多标签分类,有效利用预测的鉴别信息捕获特征分布的多模式结构。实验结果表明:所提算法对比基准模型有明显提升,在平均准确率、准确率、召回率和F1指标上分别提升了4.49%、5.5%、11.44%和5.89%;所提算法为多标签领域自适应学习提供了新思路。
Abstract:Current unsupervised domain adaption algorithms usually consider only single-label learning, failing to adapt to multi-label classification tasks in pedestrian attribute recognition. To address this issue, a multi-label adversarial domain adaptation algorithm was proposed for pedestrian attribute recognition. First, to adapt to the domain transfer task of multiple attribute labels, a multi-label feature disentanglement module was employed to effectively disentangle attributes of deep features extracted from the backbone network with specific attributes based on category-specific semantics. Secondly, to reduce the gap of attribute feature distributions in different domains, a multi-label domain discrimination module based on classifier reuse was proposed to achieve both multi-attribute domain alignment and multi-label classification, which effectively exploited the predicted discrimination information to capture the multi-mode structures of feature distribution. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves superior results than the baseline model, with improvements of 4.49%, 5.5%, 11.44% and 5.89% on mean accuracy, accuracy, recall and F1 values, respectively. The proposed algorithm provides a new insight for multi-label domain adaptation learning.
-
表 1 实验软硬件环境
Table 1. Experimental hardware and software environment
实验环境 配置 CPU Intel Xeon E5-2680 v4 GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX 1080Ti 操作系统 Ubuntu 18.04.2 深度学习框架 Pytorch 1.9 计算机语言 Python 3.8 表 2 模型参数设置
Table 2. Model parameters setting
参数 数值 图片预处理大小 256×192 批处理大小 64 学习率 0.01 动量大小 0.9 训练轮次 30 表 3 在RAPv1$ \Rrightarrow $PA100k上的消融实验
Table 3. Ablation experiments on RAPv1$ \Rrightarrow $PA100k
算法 EmA/% EAcc/% EPrec/% ERec/% EF1/% ResNet50 64.85 42.22 65.75 49.71 53.44 ResNet50+MFD 65.32 43.04 67.17 51.93 54.99 ResNet50+MFD+DA 65.83 39.41 63.43 45.86 50.01 ResNet50+MDD 66.34 42.14 66.95 47.99 52.99 本文算法 69.34 47.72 64.33 61.15 59.33 表 4 在RAPv2$ \Rrightarrow $PA100k上的消融实验
Table 4. Ablation experiments on RAPv2$ \Rrightarrow $PA100k
算法 EmA/% EAcc/% EPrec/% ERec/% EF1/% ResNet50 67.19 47.24 68.93 56.01 58.47 ResNet50+MFD 68.82 47.92 73.15 55.28 59.57 ResNet50+MFD+DA 67.74 44.51 66.22 53.26 55.66 ResNet50+MDD 64.34 41.14 67.56 46.15 51.88 本文算法 72.04 47.99 62.85 64.01 60.33 -
[1] WANG X, ZHENG S F, YANG R, et al. Pedestrian attribute recognition: a survey[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 121: 108220. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108220 [2] WILSON G, COOK D J. A survey of unsupervised deep domain adaptation[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2020, 11(5): 1-46. [3] STACKE K, EILERTSEN G, UNGER J, et al. Measuring domain shift for deep learning in histopathology[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2021, 25(2): 325-336. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3032060 [4] YU H X, ZHENG W S, WU A, et al. Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2148-2157. [5] WANG D, ZHANG S. Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10978-10987. [6] LI D W, CHEN X T, HUANG K Q. Multi-attribute learning for pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios[C]//Proceedings of 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 111-115. [7] SARFRAZ M S, SCHUMANN A, WANG Y, et al. Deep view-sensitive pedestrian attribute inference in an end-to-end model[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. London: BMVA Press, 2017, 134: 1-13. [8] YU K, LENG B, ZHANG Z, et al. Weakly-supervised learning of mid-level features for pedestrian attribute recognition and localization[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. London: BMVA Press, 2017: 1-11. [9] LIU P, LIU X, YAN J, et al. Localization guided learning for pedestrian attribute recognition[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. London: BMVA Press, 2018: 142-152. [10] LI D, CHEN X, ZHANG Z, et al. Pose guided deep model for pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-6. [11] WU M D, HUANG D, GUO Y F, et al. Distraction-aware feature learning for human attribute recognition via coarse-to-fine attention mechanism[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2020: 12394-12401. [12] ZHANG J, REN P, LI J. Deep template matching for pedestrian attribute recognition with the auxiliary supervision of attribute-wise keypoints[EB/OL]. (2020-11-13)[2020-05-26]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2011.06798. [13] LIU X, ZHAO H, TIAN M, et al. Hydraplus-net: attentive deep features for pedestrian analysis[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 350-359. [14] GUO H, ZHENG K, FAN X, et al. Visual attention consistency under image transforms for multi-label image classification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 729-739. [15] JI Z, HE E, WANG H, et al. Image-attribute reciprocally guided attention network for pedestrian attribute recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2019, 120: 89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.01.010 [16] TAN Z, YANG Y, WAN J, et al. Attention-based pedestrian attribute analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(12): 6126-6140. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2919199 [17] ZHAO H, TIAN M, SUN S, et al. Spindle net: person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1077-1085. [18] LI Q, ZHAO X, HE R, et al. Visual-semantic graph reasoning for pedestrian attribute recognition[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2019, 33(1): 8634-8641. [19] WU J, LIU H, JIANG J, et al. Person attribute recognition by sequence contextual relation learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(10): 3398-3412. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2982962 [20] LONG M, CAO Y, WANG J, et al. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 97-105. [21] LONG M, ZHU H, WANG J, et al. Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2208-2217. [22] GANIN Y, LEMPITSKY V. Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015, 9908: 1180-1189. [23] GHIFARY M, KLEIJN W B, ZHANG M, et al. Deep reconstruction-classification networks for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 597-613. [24] BOUSMALIS K, TRIGEORGIS G, SILBERMAN N, et al. Domain separation networks[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016, 29: 343-351. [25] TZENG E, HOFFMAN J, SAENKO K, et al. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 7167-7176. [26] PEI Z, CAO Z, LONG M, et al. Multi-adversarial domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2018, 32(1): 3934-3941. [27] HOFFMAN J, TZENG E, PARK T, et al. Cycada: cycle-consistent adversarial domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1989-1998. [28] LONG M, CAO Z, WANG J, et al. Conditional adversarial domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018, 31: 1-11. [29] SAITO K, WATANABE K, USHIKU Y, et al. Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 3723-3732. [30] CHEN T, XU M, HUI X, et al. Learning semantic-specific graph representation for multi-label image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 522-531. [31] CHEN L, CHEN H, WEI Z, et al. Reusing the task-specific classifier as a discriminator: discriminator-free adversarial domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 7181-7190. [32] JIA J, HUANG H, YANG W, et al. Rethinking of pedestrian attribute recognition: realistic datasets with efficient method[EB/OL]. (2020-05-25)[2020-05-26]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.11909. [33] LI D, ZHANG Z, CHEN X, et al. A richly annotated pedestrian dataset for person retrieval in real surveillance scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(4): 1575-1590. -






 下载:
下载: