Edge-intelligent transmission optimization of emergency surveillance video based on IcD-FDRL
-
摘要:
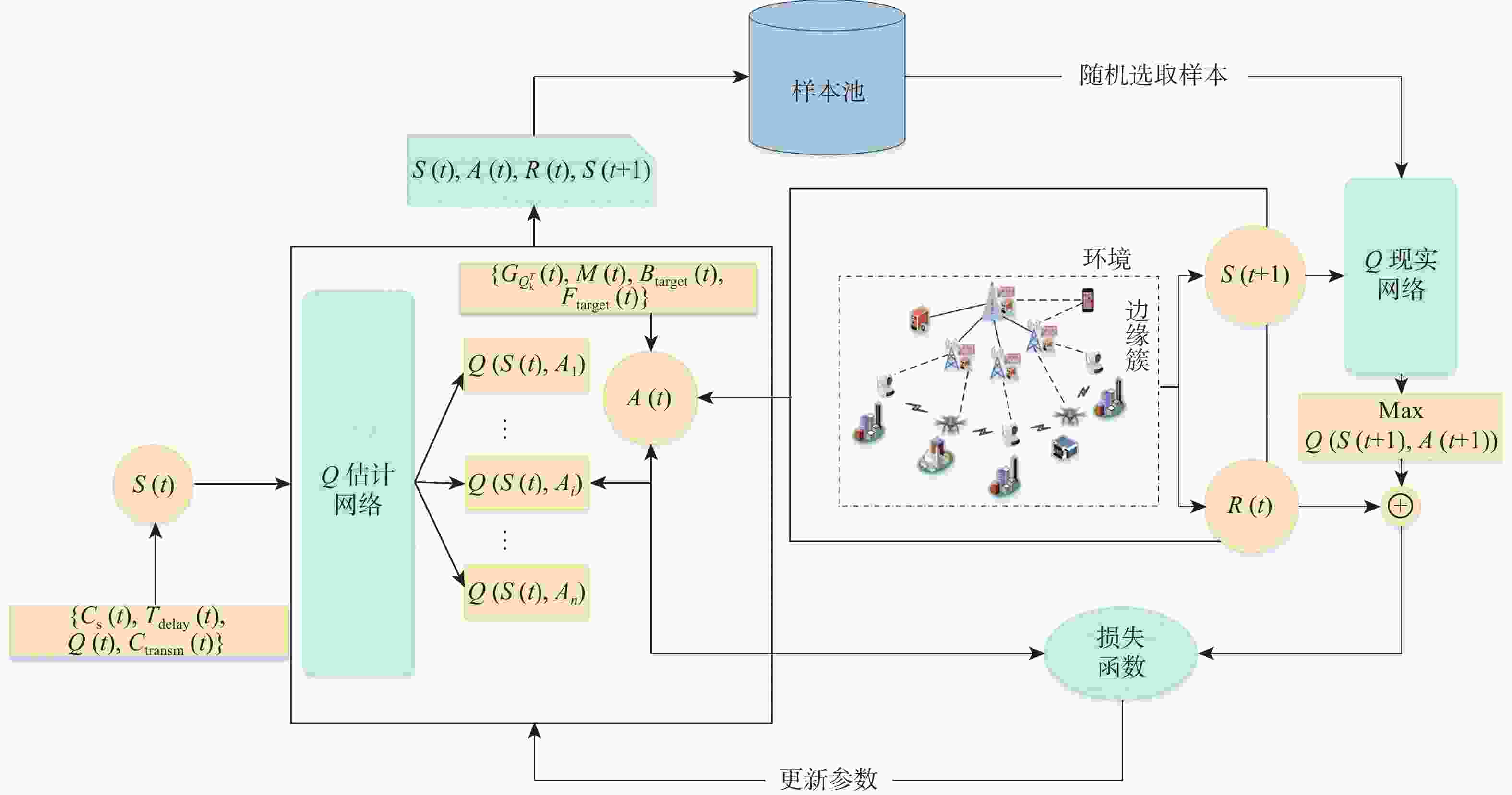
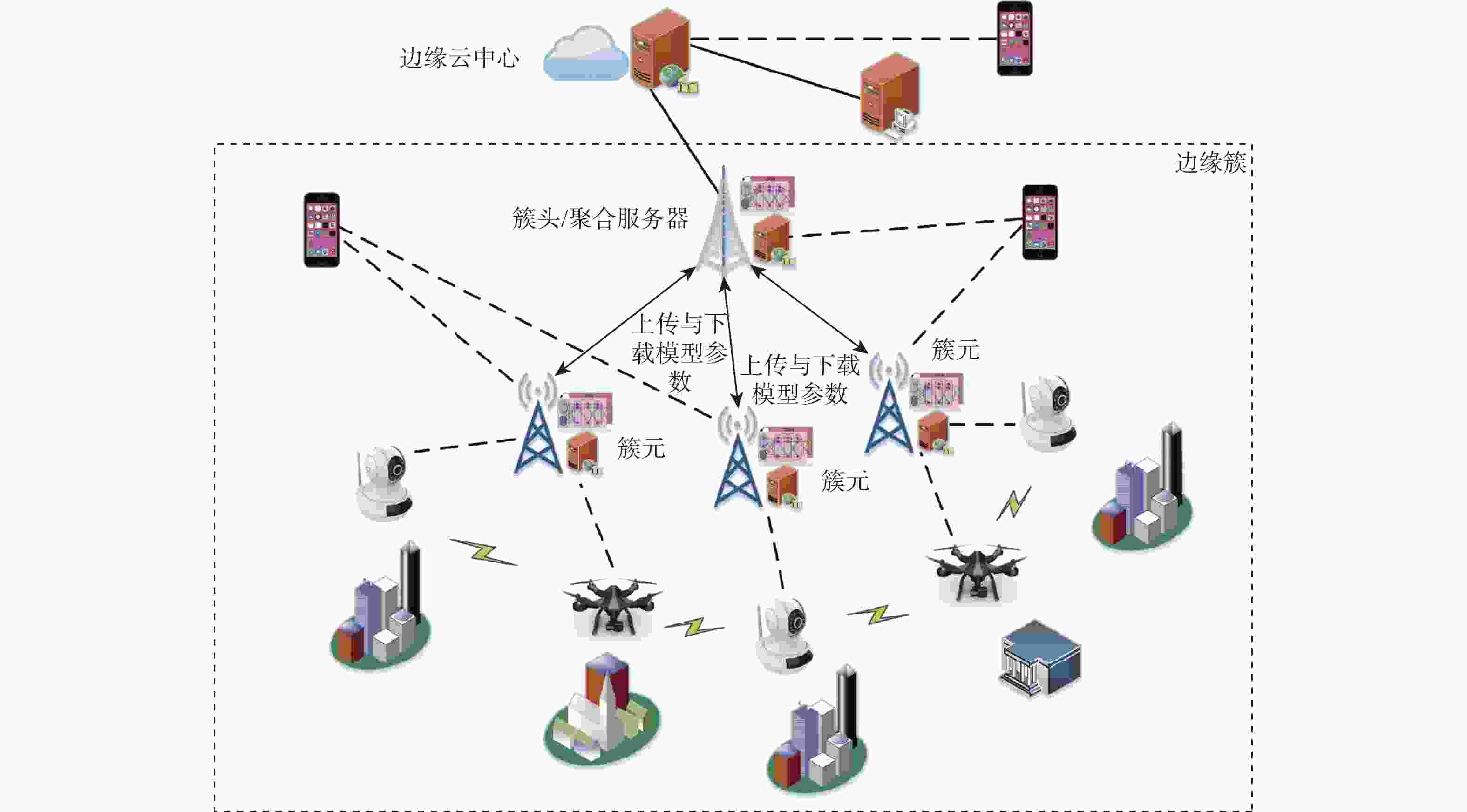
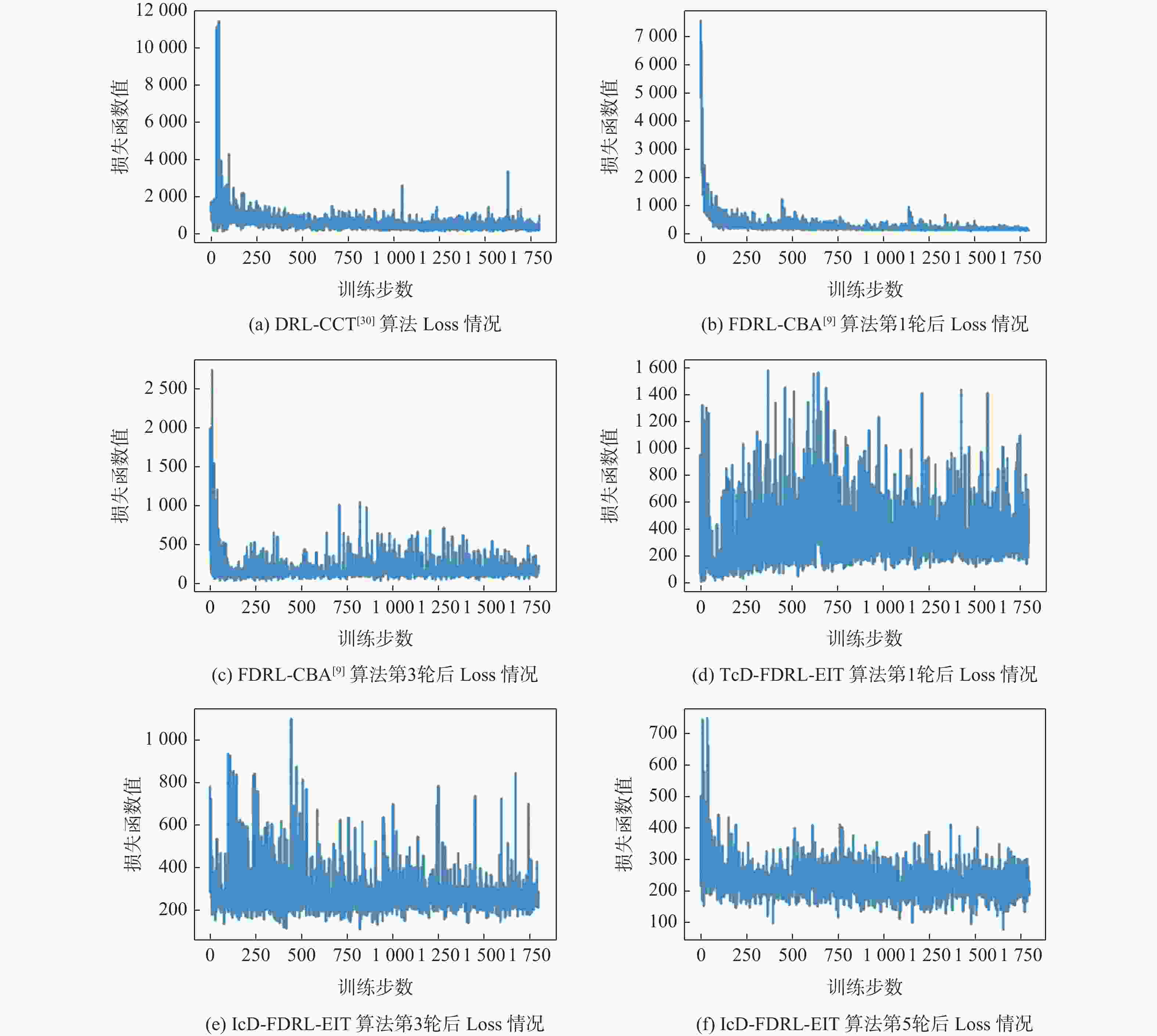
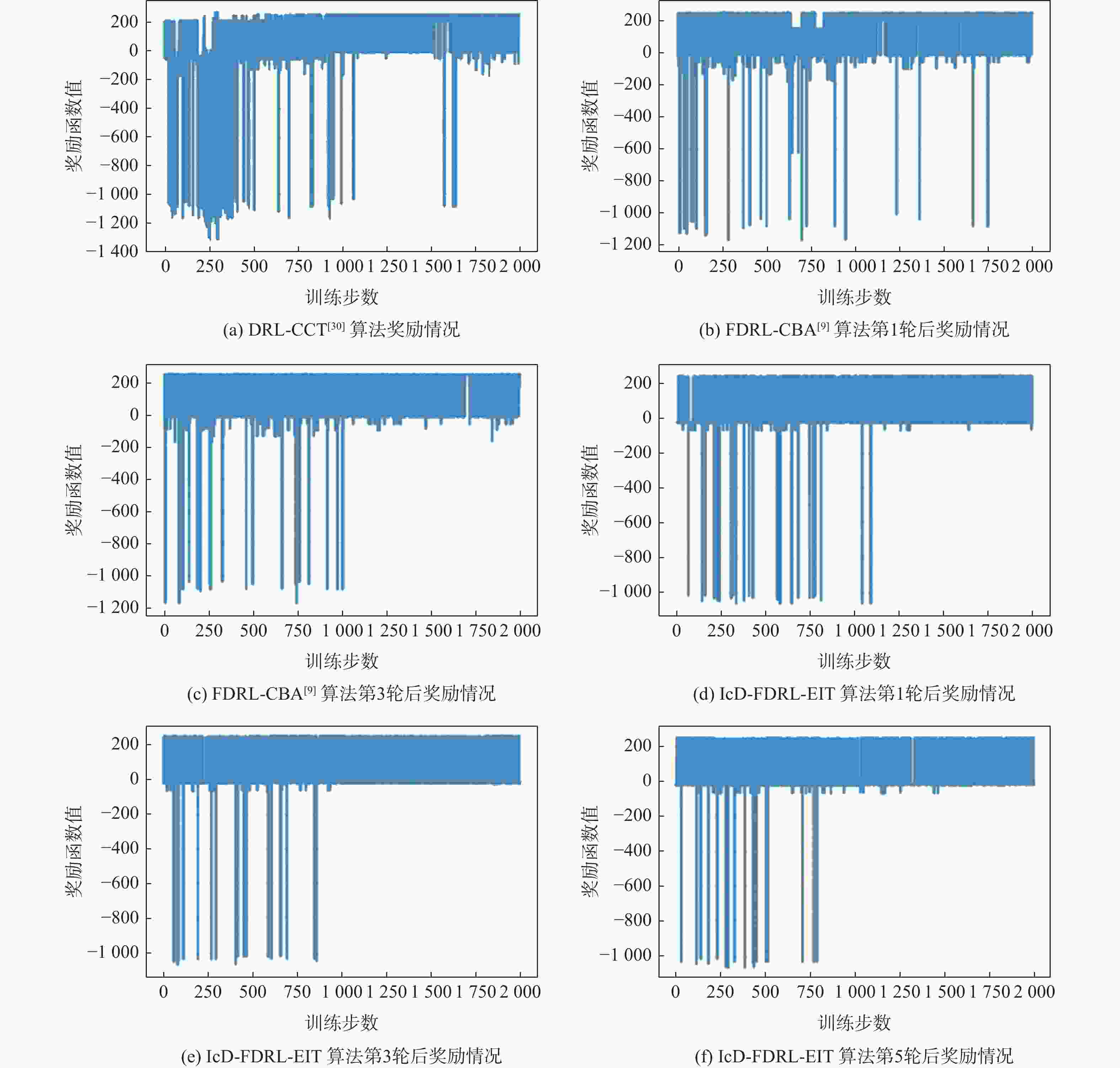
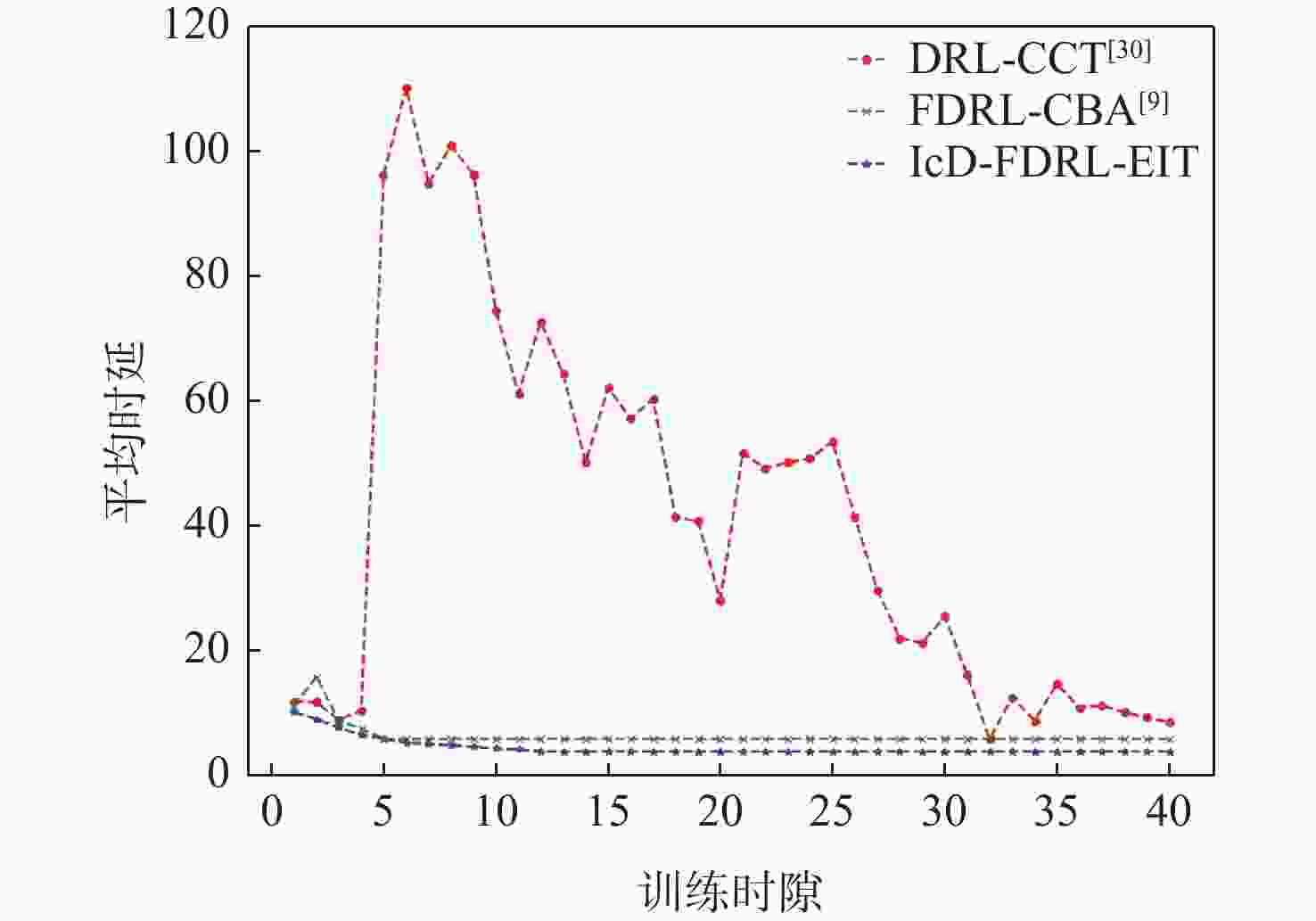
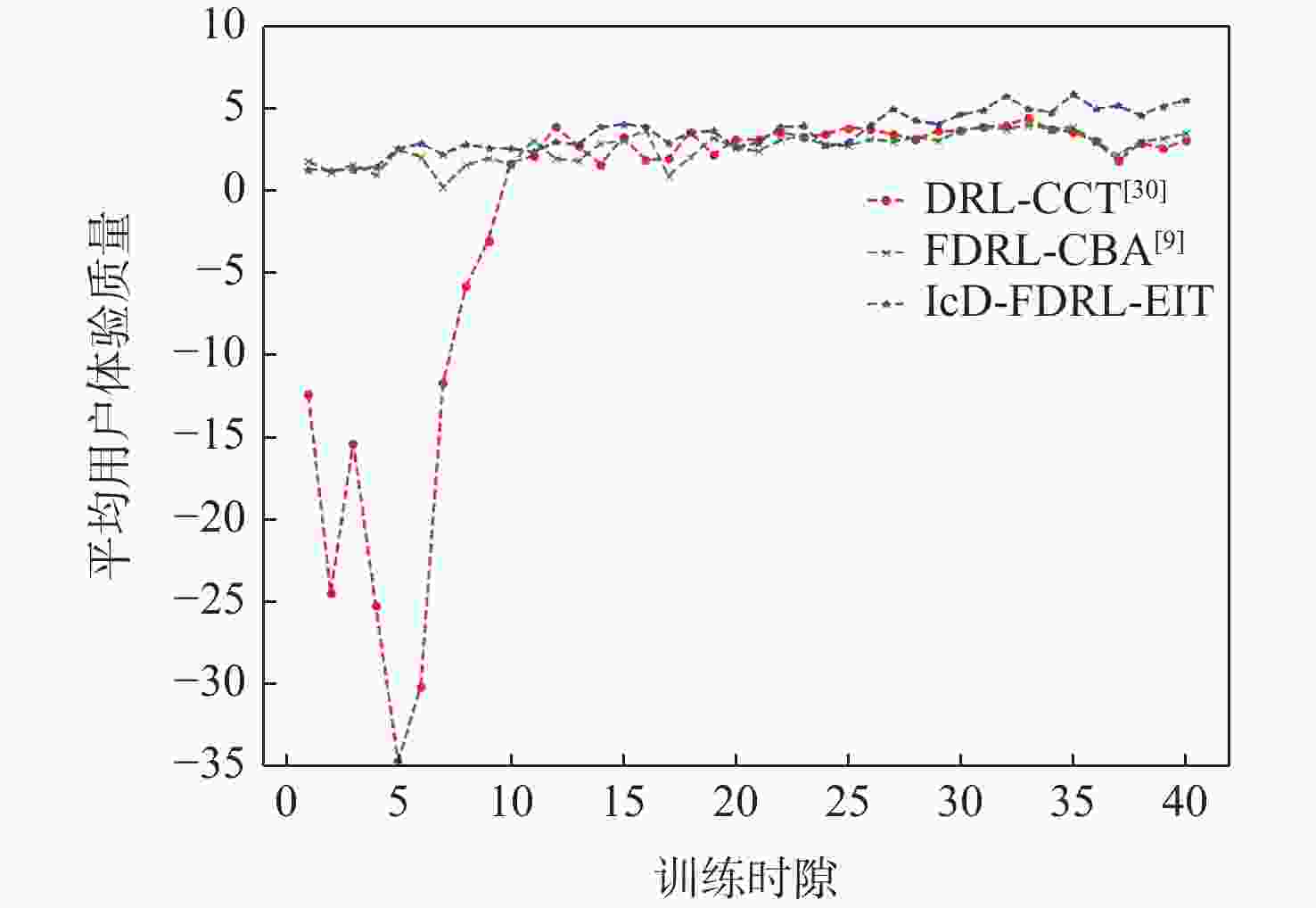
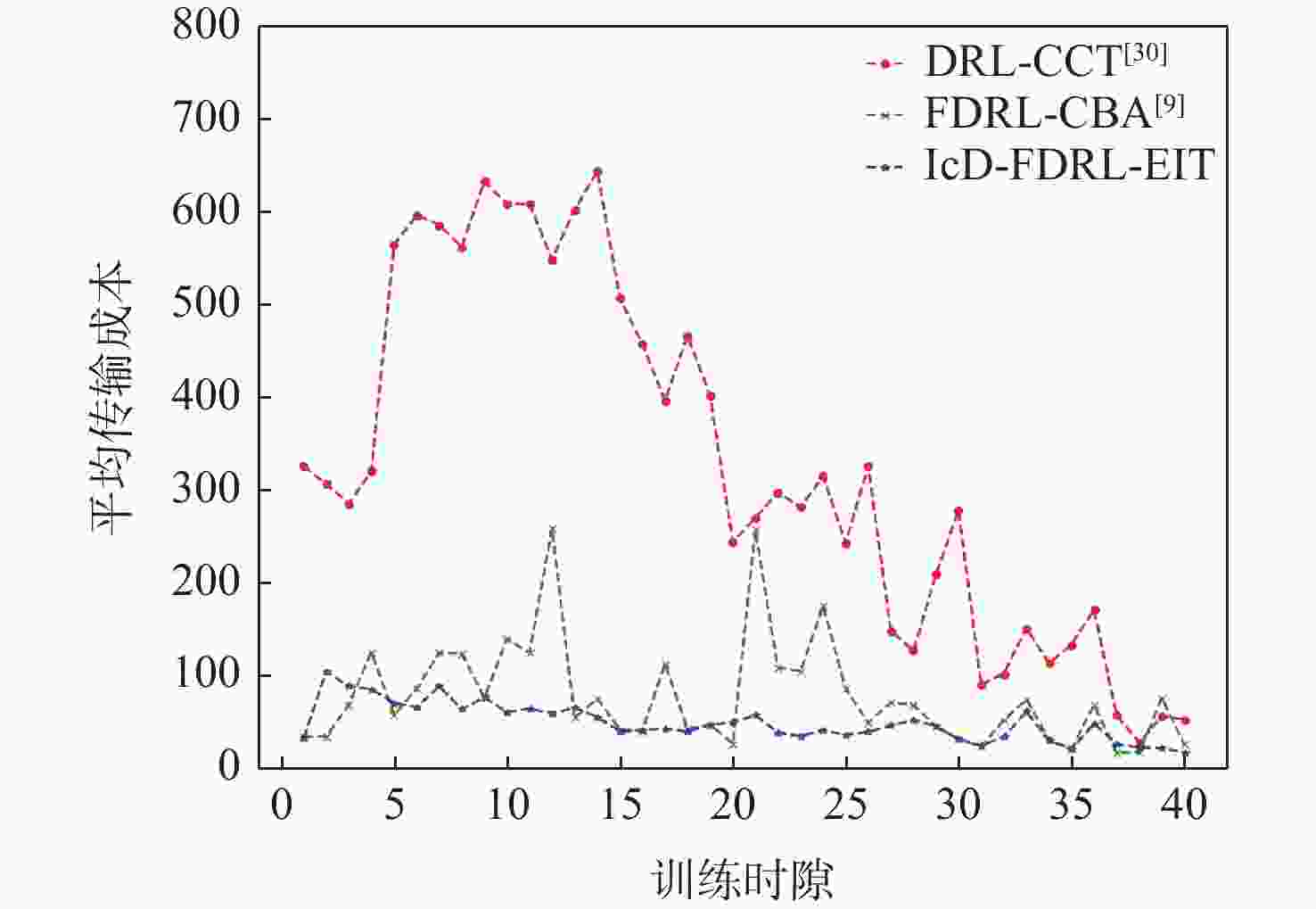
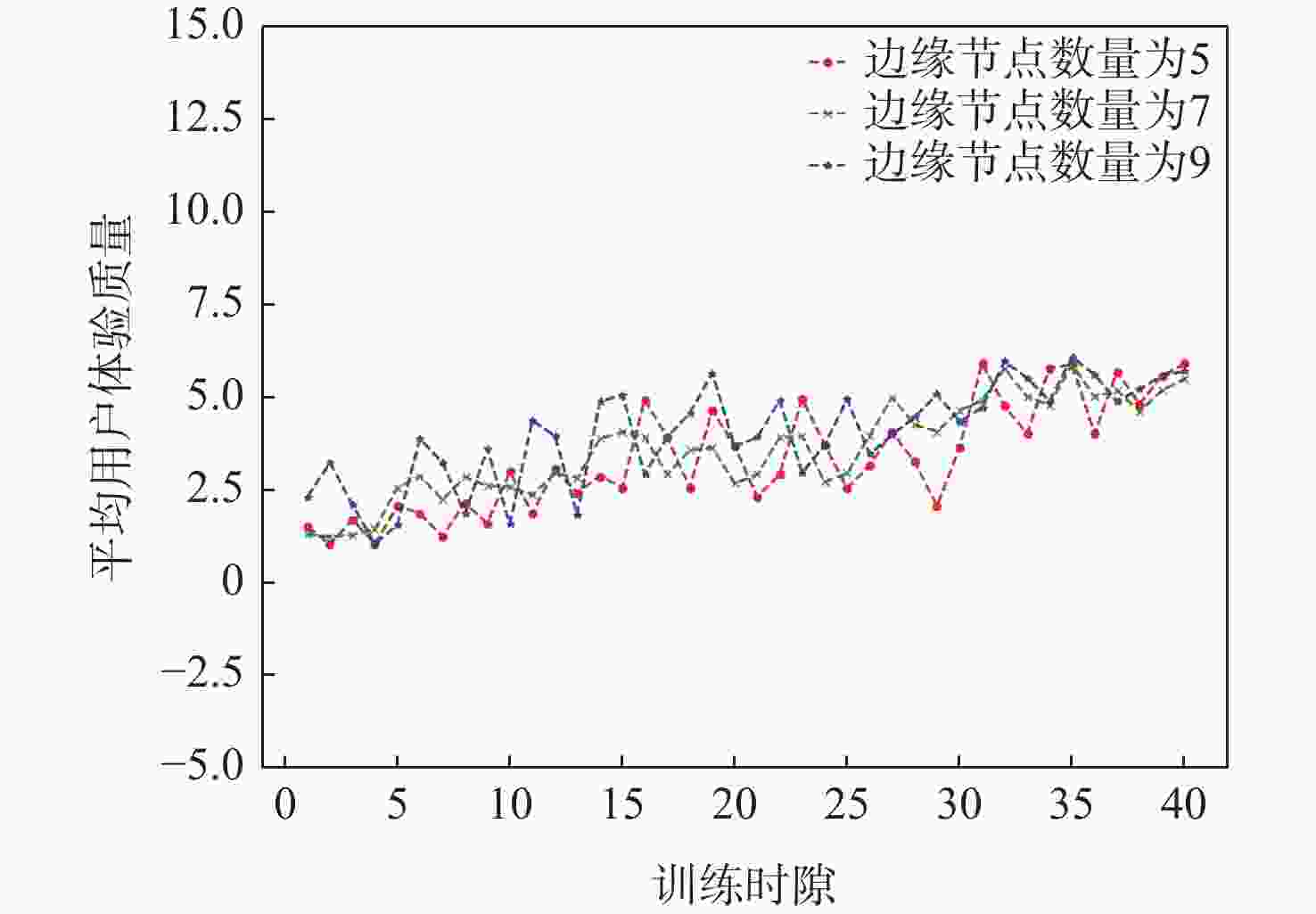
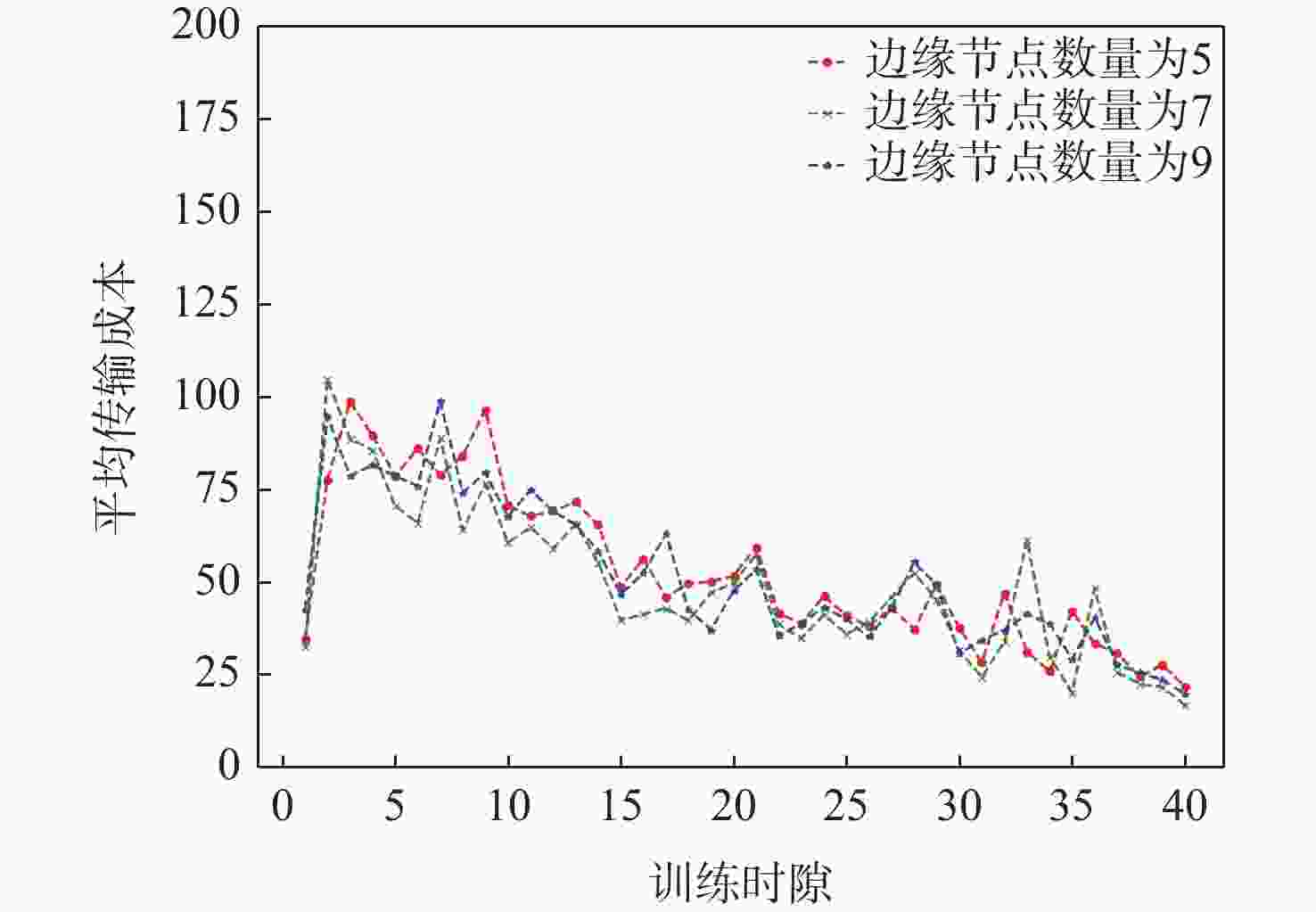
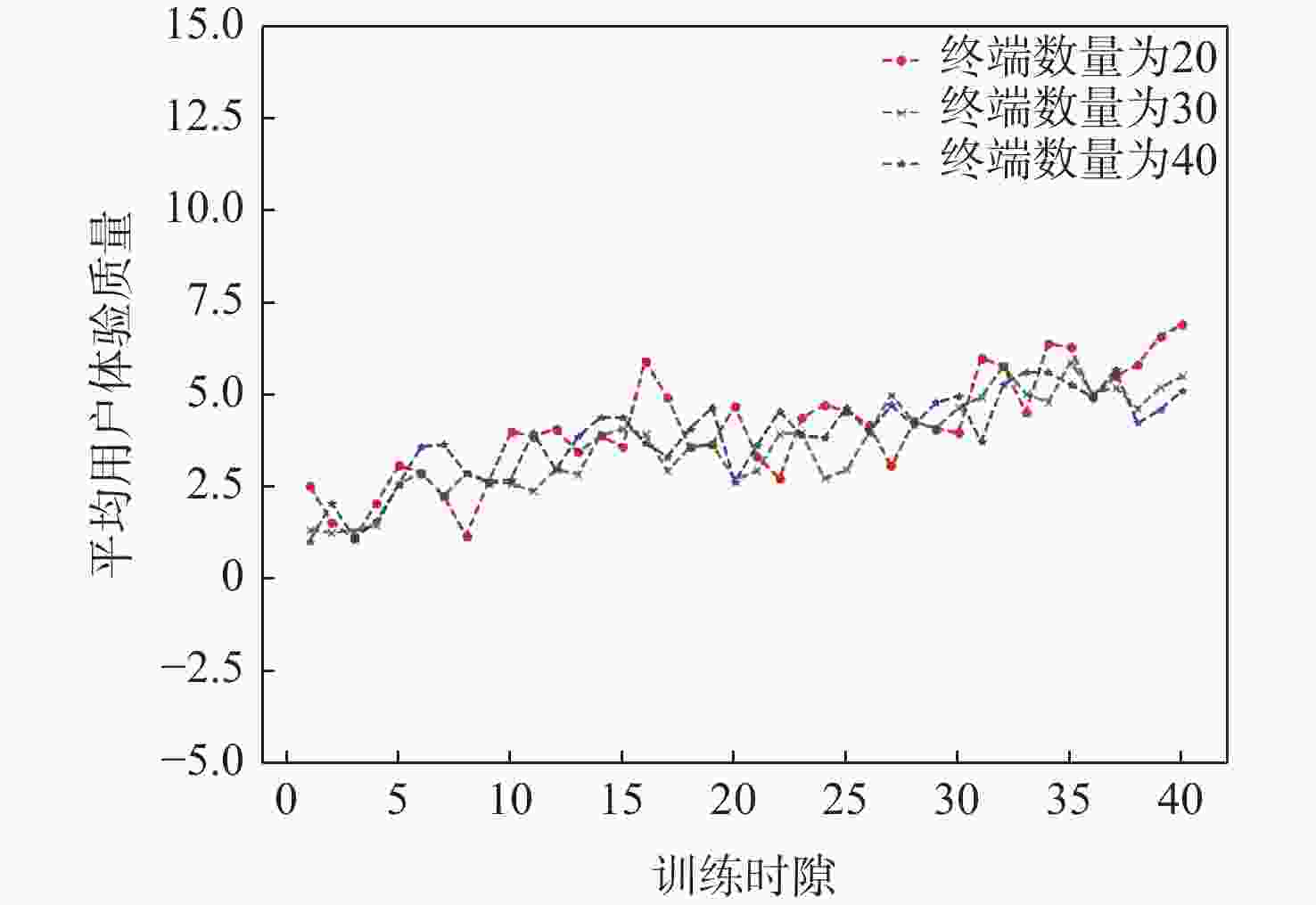
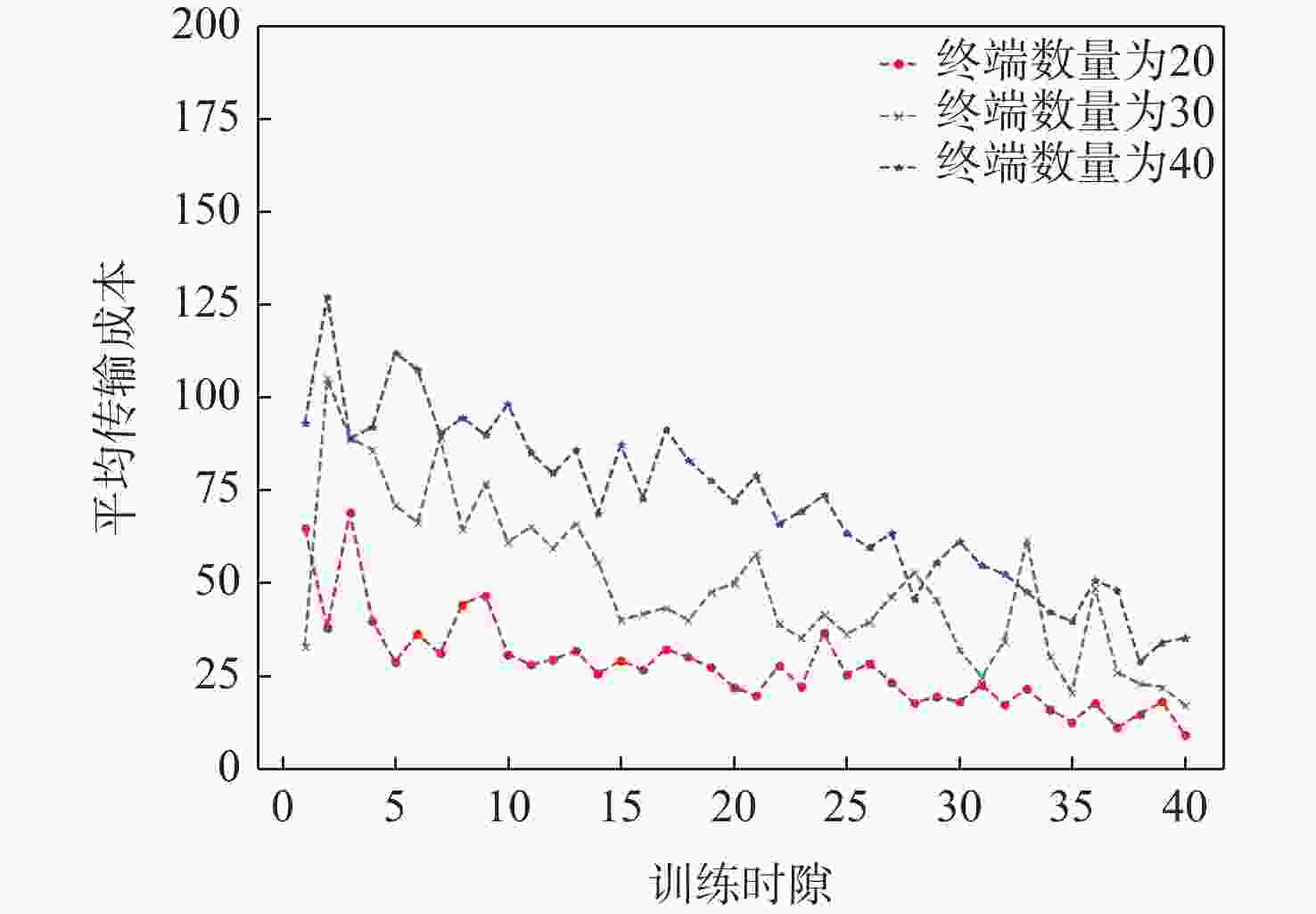
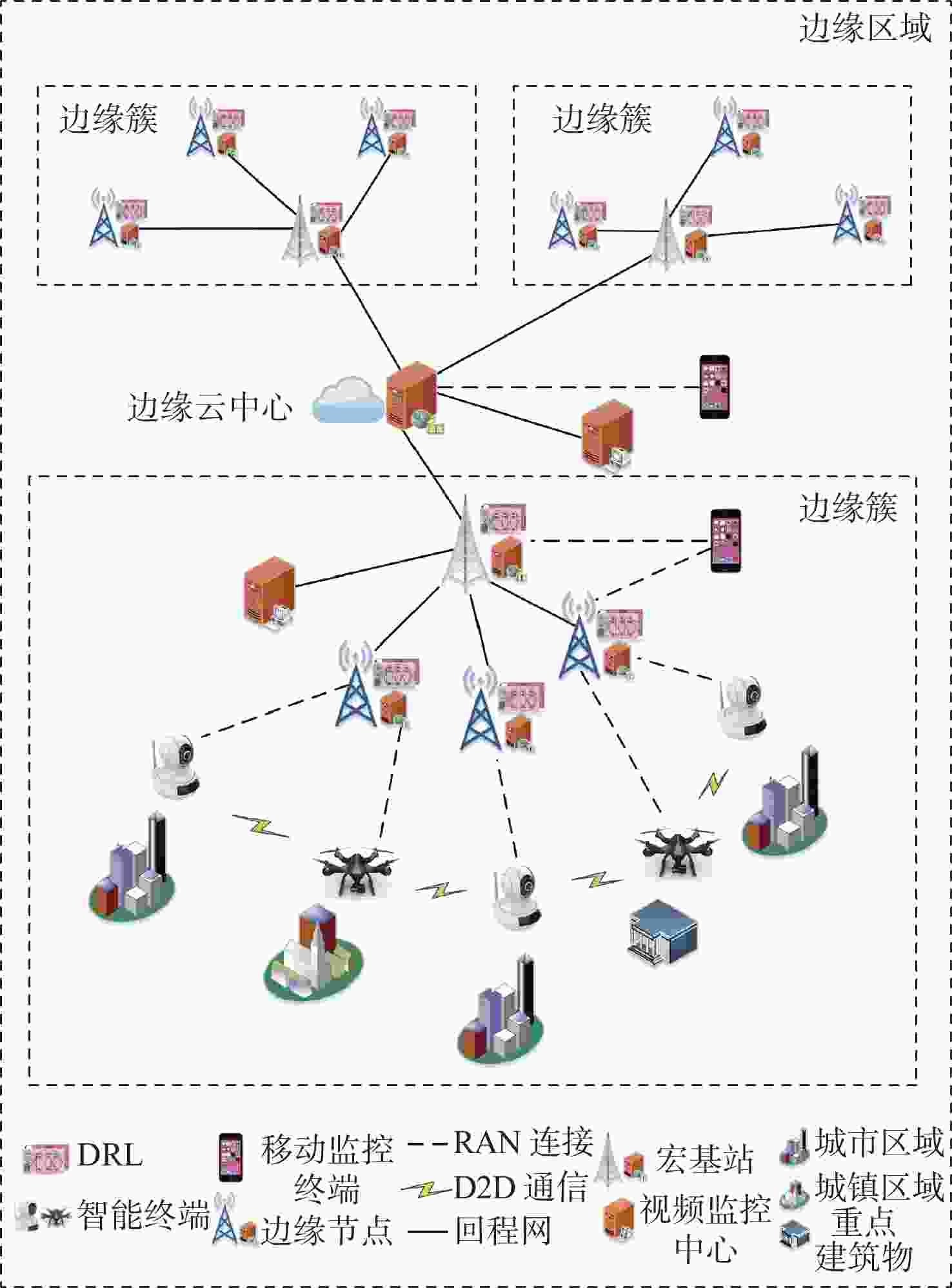
应急监控视频传输作为提升突发事件监测、公共安全事件处理、灾后重建等情况下应急工作处理能力的关键技术手段,逐渐成为国家智慧应急体系建设重点支持的专业领域和研究方向。随着5G技术、决策型人工智能技术的不断发展,为实现自适应的高质量应急监控视频传输,针对局部区域内公共安全和应急救援监控,建立一种应急监控视频边缘智能传输架构,设计了应急监控视频重要性度量方法,提出簇内动态联邦深度强化学习(IcD-FDRL)算法,并实现了基于簇内动态联邦深度强化学习的应急监控视频边缘智能传输优化,以打破监控数据孤岛,提升算法学习效率,实现重要应急监控视频的低时延、低成本、高质量和优先传输。通过仿真实验进行了对比分析,验证了所提模型和算法的有效性。
Abstract:Emergency surveillance video transmission is a key technical means to improve emergency handling capability under circumstances such as emergency monitoring, public security incident handling, and post-disaster reconstruction. It has gradually become a key focus of research and development in the construction of the national smart emergency system. With the continuous development of 5G technology and decision-making artificial intelligence technology in recent years, an edge-intelligent transmission architecture for emergency surveillance video was established, aimed at public safety and emergency rescue monitoring in local areas. This model seeks to achieve adaptive and high-quality transmission of emergency surveillance video. Furthermore, the importance measurement method of emergency surveillance video was designed, and an intra-clustered dynamic federated deep reinforcement learning algorithm was proposed. The proposed optimization method based on intra-clustered dynamic federated deeps reinforcement learning (IcD-FDRL) enhances the edge-intelligent transmission of emergency surveillance video, breaks monitoring data silos, improves algorithm learning efficiency, and realizes low-delay, low-cost, high-quality, and priority transmission of important emergency surveillance video. Finally, a simulation experiment was performed and its results were compared, verifying the effectiveness of the proposed model and algorithms.
-
表 1 实验中主要参数设置
Table 1. Setting of main parameters in experiments
参数 取值 参数 取值 $ \alpha $ 0.4 $ {\omega _5} $ 0.1 $ \beta $ 0.3 $ {\omega _6} $ 0.1 $ \delta $ 0.3 Nc 7 $ \rho $ 7 K 10 学习率 0.01 $ {N_{{\text{user}}}} $ 30 $ {\mu _1} $ 1 $ \{ N_{{\text{cpu}}}^b\} $ $ \left\{ {2,4,6,8} \right\} $ $ {\mu _2} $ 0 $ {{D}}/{\mathrm{s}} $ 10 $ {\omega _1} $ 1.2 $ \gamma $ 0.9 $ {\omega _2} $ 1.2 $ \varepsilon $ 0.9 $ {\omega _3} $ 1.0 $ \psi $ 600 $ {\omega _4} $ 1.0 $ \lambda $ 0.65 -
[1] 张铮, 李政华. 中国特色应急管理制度体系构建: 现实基础、存在问题与发展策略[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38(1): 138-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2022.01.010ZHANG Z, LI Z H. Emergency management system construction with Chinese characteristics: realistic foundation, existing problems and development strategy[J]. Journal of Management World, 2022, 38(1): 138-144(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2022.01.010 [2] 刘鲲. 智能视频监控中事件理解的关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2021.LIU K. Research on key technologies of event understanding in intelligent video surveillance[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021(in Chinese). [3] 黄韬, 刘江, 汪硕, 等. 未来网络技术与发展趋势综述[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(1): 130-150. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021006HUANG T, LIU J, WANG S, et al. Survey of the future network technology and trend[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(1): 130-150(in Chinese). doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021006 [4] 伏玉笋, 杨根科. 人工智能在移动通信中的应用: 挑战与实践[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(9): 190-201.FU Y S, YANG G K. Application of artificial intelligence in mobile communication: challenge and practice[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(9): 190-201(in Chinese). [5] 梁应敞, 谭俊杰, NIYATO D. 智能无线通信技术研究概况[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(7): 1-17. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020145LIANG Y C, TAN J J, NIYATO D. Overview on intelligent wireless communication technology[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(7): 1-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020145 [6] LI Y. A suvey on edge intelligent video surveillance with deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Network Intelligence, 2022, 7(1): 70-83. [7] WANG X F, LI R B, WANG C Y, et al. Attention-weighted federated deep reinforcement learning for device-to-device assisted heterogeneous collaborative edge caching[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(1): 154-169. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3036946 [8] LEI M, LI Q, GE X H, et al. Partially collaborative edge caching based on federated deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(1): 1389-1394. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3206876 [9] LI Y. Federated deep reinforcement learning-based caching and bitrate adaptation for VR panoramic video in clustered MEC networks[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(23): 3968. doi: 10.3390/electronics11233968 [10] WEI Y K, ZHOU S P, LENG S P, et al. Federated learning empowered end-edge-cloud cooperation for 5G HetNet security[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(2): 88-94. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.2000340 [11] QUINTANA-RAMIREZ I, SEQUEIRA L, RUIZ-MAS J. An edge-cloud approach for video surveillance in public transport vehicles[J]. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 2021, 19(10): 1763-1771. doi: 10.1109/TLA.2021.9477277 [12] YAN K P, SHAN H G, SUN T X, et al. Reinforcement learning-based mobile edge computing and transmission scheduling for video surveillance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2022, 10(2): 1142-1156. [13] KE R M, ZHUANG Y F, PU Z Y, et al. A smart, efficient, and reliable parking surveillance system with edge artificial intelligence on IoT devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(8): 4962-4974. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2984197 [14] MING Z X, CHEN J S, CUI L Z, et al. Edge-based video surveillance with graph-assisted reinforcement learning in smart construction[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(12): 9249-9265. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3090513 [15] HOU B, ZHANG J X. Real-time surveillance video salient object detection using collaborative cloud-edge deep reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-8. [16] KIM D, KIM K, PARK S. Automatic PTZ camera control based on deep-Q network in video surveillance system[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-3. [17] 施巍松, 张星洲, 王一帆, 等. 边缘计算: 现状与展望[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(1): 69-89. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20180760SHI W S, ZHANG X Z, WANG Y F, et al. Edge computing: state-of-the-art and future directions[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(1): 69-89(in Chinese). doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20180760 [18] 赵梓铭, 刘芳, 蔡志平, 等. 边缘计算: 平台、应用与挑战[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2018, 55(2): 327-337. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170228ZHAO Z M, LIU F, CAI Z P, et al. Edge computing: platforms, applications and challenges[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(2): 327-337(in Chinese). doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170228 [19] 施巍松, 孙辉, 曹杰, 等. 边缘计算: 万物互联时代新型计算模型[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2017, 54(5): 907-924. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2017.20160941SHI W S, SUN H, CAO J, et al. Edge computing: an emerging computing model for the Internet of everything era[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2017, 54(5): 907-924(in Chinese). doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2017.20160941 [20] HU Y C, PATEL M, SABELLA D, et al. Mobile edge computing-a key technology towards 5G[J]. European Telecommunications Standards Institute, 2015: 1-16. [21] TALEB T, SAMDANIS K, MADA B, et al. On multi-access edge computing: a survey of the emerging 5G network edge cloud architecture and orchestration[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1657-1681. [22] 吴冀衍, 程渤, 南国顺, 等. 面向异构无线网移动视频传输的联合信源信道编码方式[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(2): 439-454.WU J Y, CHENG B, NAN G S, et al. A novel joint source-channel coding scheme for mobile video delivery in heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(2): 439-454(in Chinese). [23] SAHA N, ZANGOOEI M, GOLKARIFARD M, et al. Deep reinforcement learning approaches to network slice scaling and placement: a survey[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2023, 61(2): 82-87. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.006.2200534 [24] CHIEN W C, WENG H Y, LAI C F. Q-learning based collaborative cache allocation in mobile edge computing[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 102: 603-610. [25] WANG S, ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. A survey on mobile edge networks: convergence of computing, caching and communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 6757-6779. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2685434 [26] 李佳, 谢人超, 贾庆民, 等. 面向视频流的MEC缓存转码联合优化研究[J]. 电信科学, 2018, 34(8): 76-86.LI J, XIE R C, JIA Q M, et al. A survey on joint optimization of MEC caching and transcoding for video streaming[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2018, 34(8): 76-86(in Chinese). [27] MANIOTIS P, THOMOS N. Viewport-aware deep reinforcement learning approach for 360° video caching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 24: 386-399. [28] ZHONG C, GURSOY M C, VELIPASALAR S. Deep reinforcement learning-based edge caching in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(1): 48-61. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.2968326 [29] PANG Z Y, SUN L F, HUANG T C, et al. Towards QoS-aware cloud live transcoding: a deep reinforcement learning approach[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 670-675. [30] WAN Z, LI Y. Deep reinforcement learning-based collaborative video caching and transcoding in clustered and intelligent edge B5G networks[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2020, 2020(1): 6684293. [31] AN B, SUN S, WANG R D. Deep reinforcement learning for quantitative trading: challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2022, 37(2): 23-26. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2022.3165994 [32] HE X M, WANG K, HUANG H W, et al. Green resource allocation based on deep reinforcement learning in content-centric IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2020, 8(3): 781-796. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2018.2805718 [33] MENG F, CHEN P, WU L N, et al. Power allocation in multi-user cellular networks: deep reinforcement learning approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6255-6267. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3001736 [34] PARK S, KIM J, KWON D, et al. Joint offloading and streaming in mobile edges: a deep reinforcement learning approach[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE VTS Asia Pacific Wireless Communications Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-4. [35] ZHANG H, WU W J, WANG C Y, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based offloading decision optimization in mobile edge computing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-7. [36] HE Y, ZHAO N, YIN H X. Integrated networking, caching, and computing for connected vehicles: a deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(1): 44-55. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2760281 [37] WANG F X, ZHANG C, WANG F, et al. Intelligent edge-assisted crowdcast with deep reinforcement learning for personalized QoE[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 910-918. [38] CHEN M H, PONEC M, SENGUPTA S, et al. Utility maximization in peer-to-peer systems with applications to video conferencing[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2012, 20(6): 1681-1694. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2012.2201166 [39] SUTTON R S, BARTO A G. Reinforcement learning: an introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018. [40] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 -






 下载:
下载: