Continual learning method based on differential feature distillation for multimodal network
-
摘要:
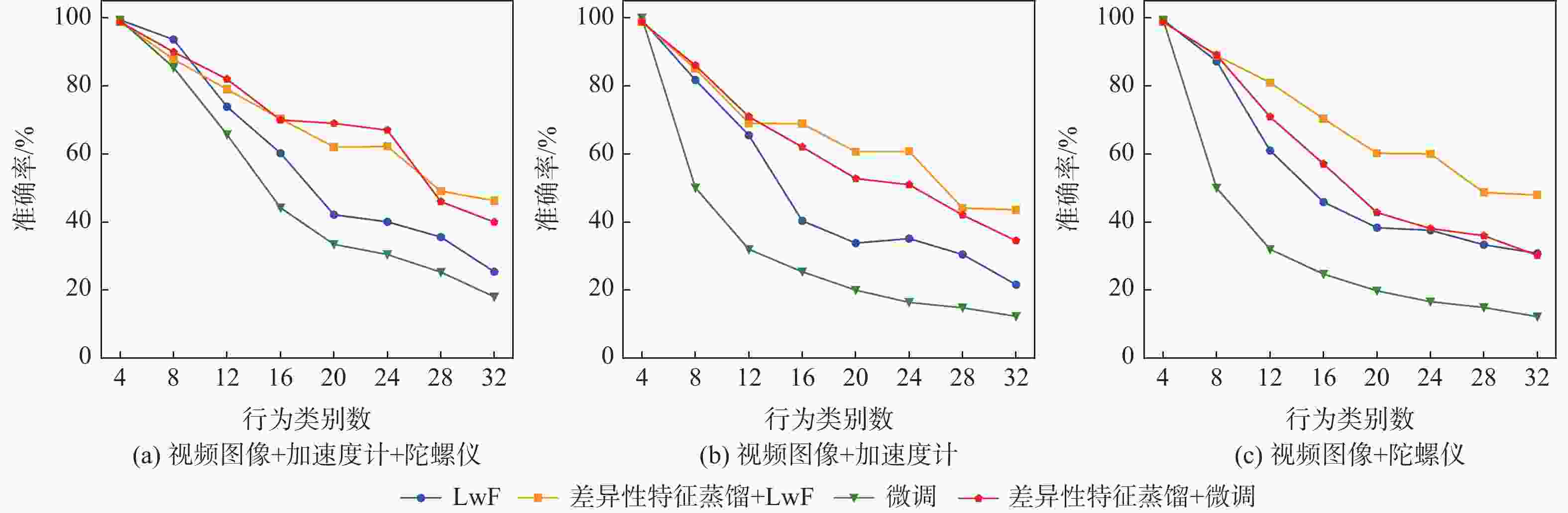
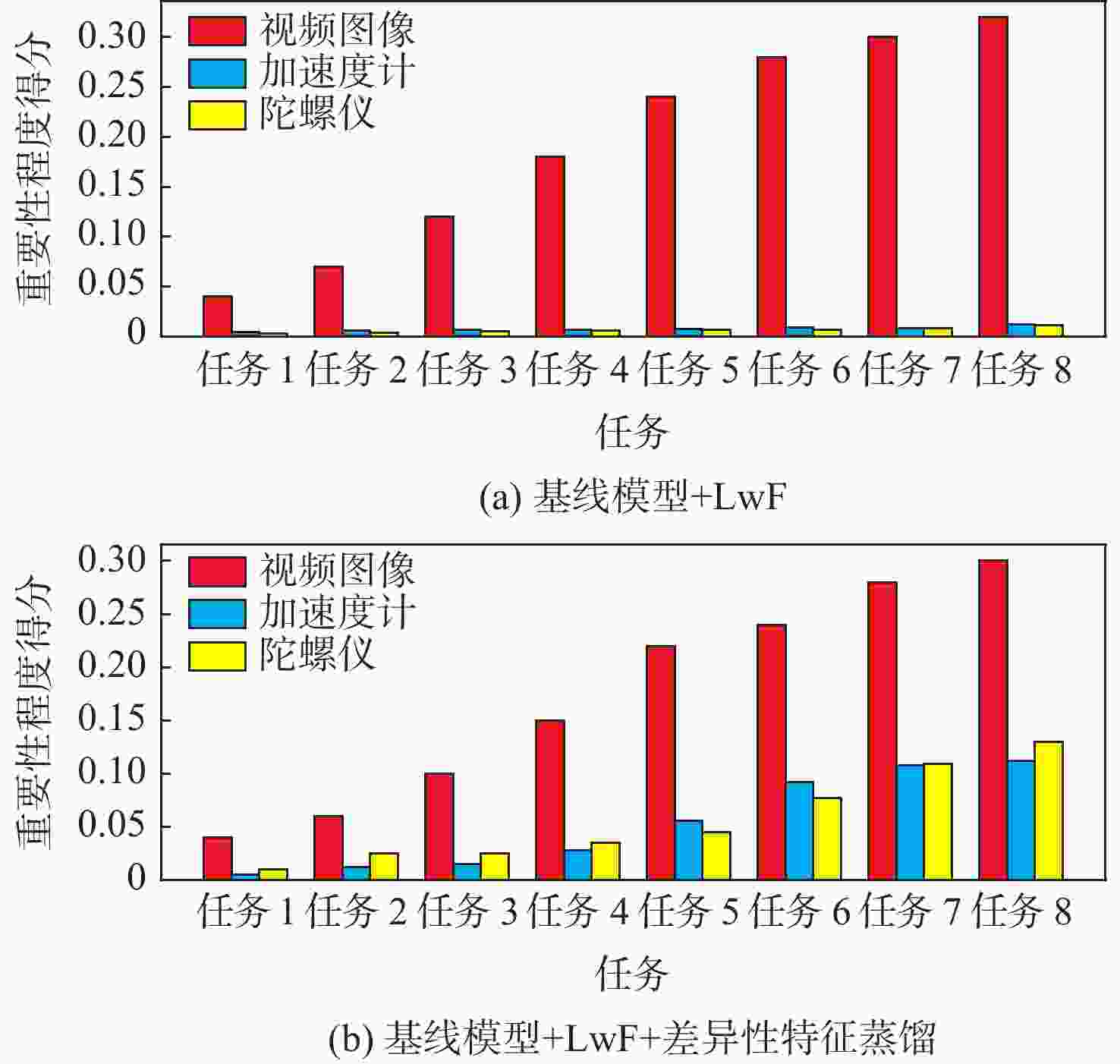
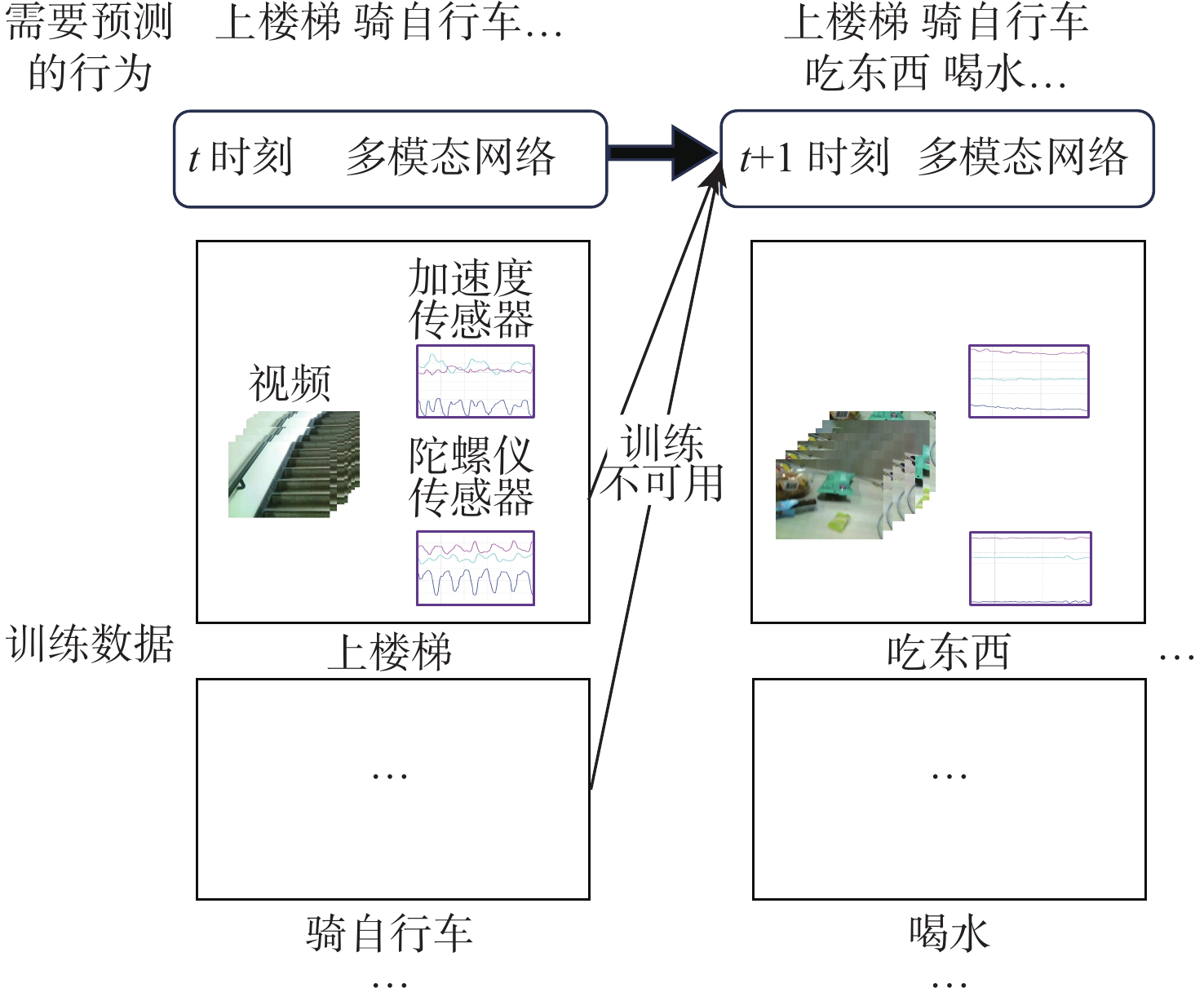
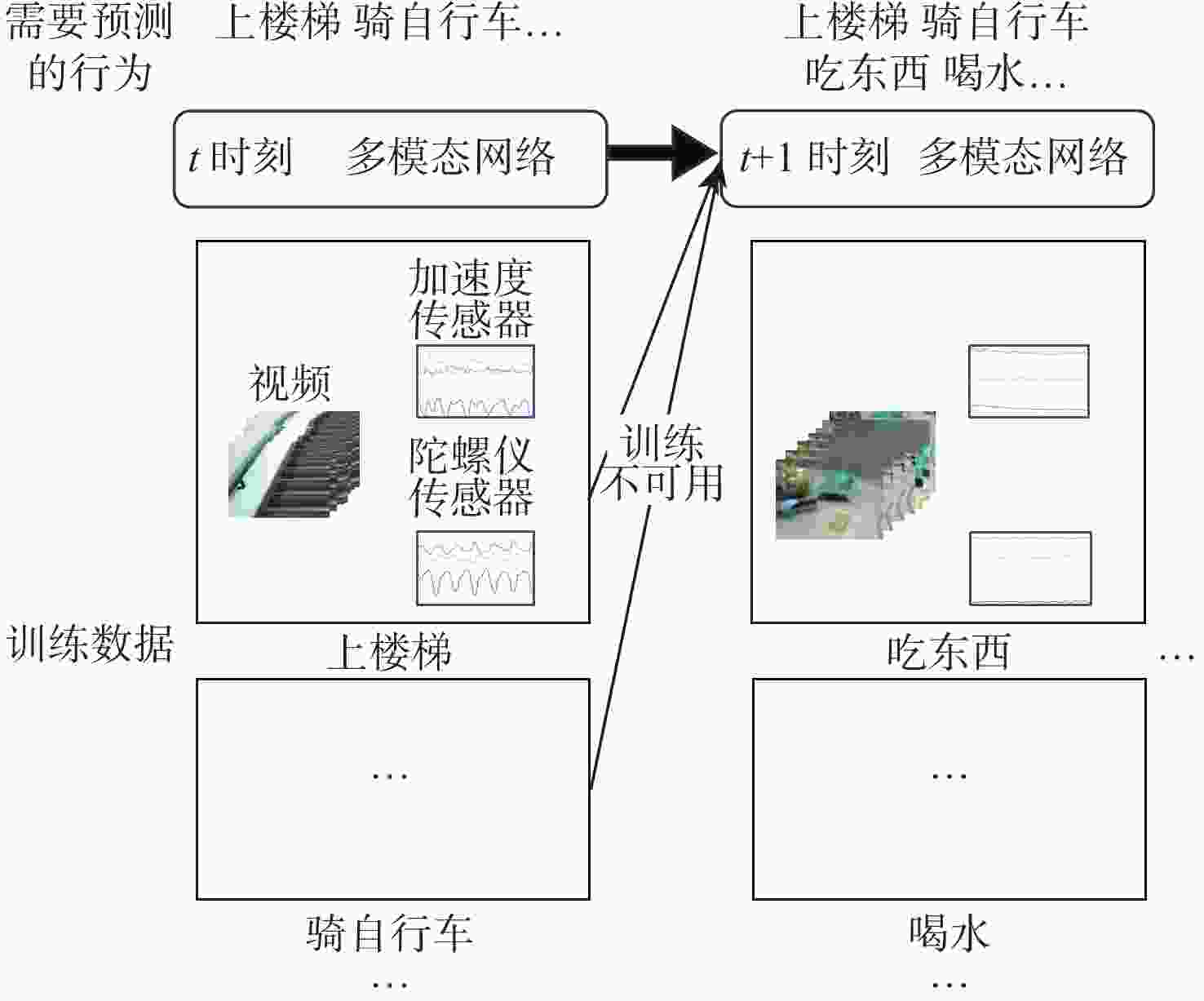
近年来连续学习成为一个新的研究热点,但在多模态架构的连续学习任务中,数据不能被完全利用,导致了严重的灾难性遗忘和学习受阻问题。因此,提出了基于特征蒸馏的多模态连续学习方法。该方法重点考虑不同模态在任务表现方面的差异性,选择较多或较少地保留模态旧知识,以激发各模态从整体角度挖掘具有判别性特征的潜力。在多模态行为识别数据集UESTC-MMEA-CL上的实验验证了所提方法的有效性。在进行到第8个任务时,所提方法的平均准确率在微调基础上提升了22.0%,在不遗忘学习(LwF)的基础上提升了20.1%。与经典的知识蒸馏方法相比,提出的差异性特征蒸馏方法显著提高了传感器模态的利用率,从而更显著地缓解了多模态网络的灾难性遗忘问题。
Abstract:Continual learning has become a new research hotspot in recent years. However, in the continual learning of multimodal architecture, the data are generally not fully utilized, resulting in catastrophic forgetting and learning obstruction. To address these issues, a multimodal continual learning method based on feature distillation was proposed. By focusing on differences in task performance between different modalities, this method chose to retain more or less old knowledge of the modality, so as to stimulate each modality’s potential in exploring discriminative features from an overall perspective. Experiments on the multimodal behavior recognition dataset UESTC-MMEA-CL validated the effectiveness of this method. When approaching the eighth task, the proposed method achieved an improved accuracy by an average of 22.0% and 20.1% based on fine-tuning and learning without forgetting (LwF), respectively. Compared with the classic knowledge distillation method, the proposed method better utilized sensor modalities, thereby significantly alleviating the catastrophic forgetting issue of multimodal networks.
-
Key words:
- machine learning /
- continual learning /
- multimodality /
- behavior recognition /
- feature distillation
-
表 1 网络参数设置
Table 1. Network parameter setting
表 2 消融对比
Table 2. Ablation comparison
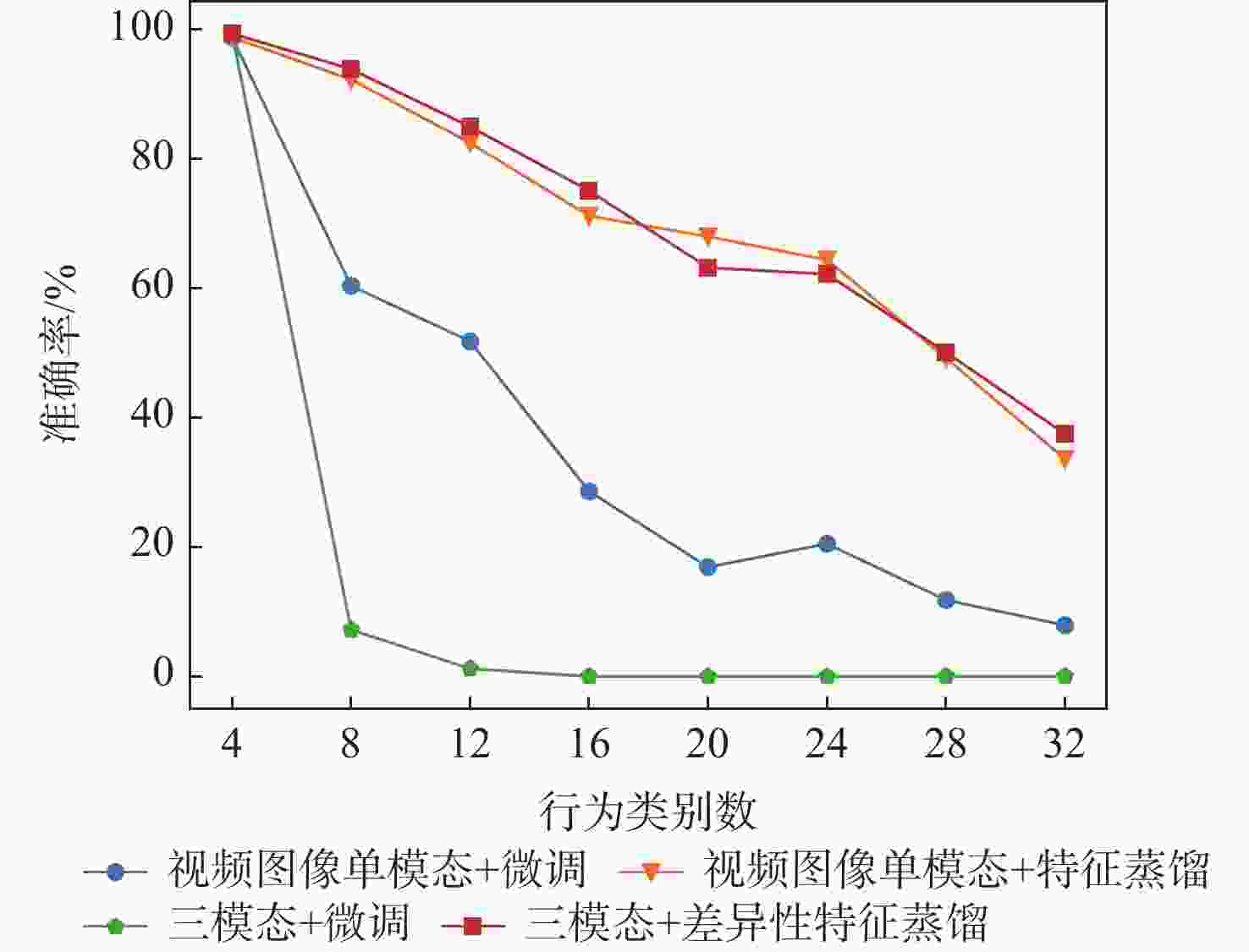
模型+连续学习策略 平均准确率/% 8×4 4×8 视频图像单模态+LwF 29.3 53.2 三模态+LwF 25.8 39.0 三模态+LwF+特征蒸馏 30.6 52.5 三模态+LwF+差异性特征蒸馏 46.3 58.9 注:“8×4”代表将全32个行为类别分成8个任务,每个任务中有4个类别;“4×8”代表将全32个行为类别分成4个任务,每个任务中有8个类别。 表 3 融合方法对比
Table 3. Fusion method comparison
表 4 去偏系数的有效性(三模态)
Table 4. Effectiveness of debiasing coefficient (triple modalities)
累加方式 准确率/% 任务1 任务2 任务3 任务4 直接累加 98.3 82.5 62.2 53.0 去偏累加 98.3 82.5 68.2(+6.0) 58.9(+5.9) 注:括号内数值为相对于“直接累加”的准确率相对增益。 -
[1] XU L F, WU Q B, PAN L L, et al. Towards continual egocentric activity recognition: a multi-modal egocentric activity dataset for continual learning[EB/OL]. (2023-01-26)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10931v1. [2] KAZAKOS E, NAGRANI A, ZISSERMAN A, et al. EPIC-fusion: audio-visual temporal binding for egocentric action recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5491-5500. [3] DAMEN D M, DOUGHTY H, FARINELLA G M, et al. Rescaling egocentric vision: collection, pipeline and challenges for EPIC-KITCHENS-100[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(1): 33-55. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01531-2 [4] SPRIGGS E H, DE LA TORRE F, HEBERT M. Temporal segmentation and activity classification from first-person sensing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 17-24. [5] CHEN C, JAFARI R, KEHTARNAVAZ N. UTD-MHAD: a multimodal dataset for human action recognition utilizing a depth camera and a wearable inertial sensor[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 168-172. [6] SONG S B, CHANDRASEKHAR V, MANDAL B, et al. Multimodal multi-stream deep learning for egocentric activity recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 378-385. [7] NAKAMURA K, YEUNG S, ALAHI A, et al. Jointly learning energy expenditures and activities using egocentric multimodal signals[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6817-6826. [8] KIRKPATRICK J, PASCANU R, RABINOWITZ N, et al. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(13): 3521-3526. [9] LIU X L, MASANA M, HERRANZ L, et al. Rotate your networks: better weight consolidation and less catastrophic forgetting[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 2262-2268. [10] ZENKE F, POOLE B, GANGULI S. Continual learning through synaptic intelligence[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney: PMLR, 2017, 70: 3987-3995. [11] LI Z Z, HOIEM D. Learning without forgetting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(12): 2935-2947. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2773081 [12] REBUFFI S A, KOLESNIKOV A, SPERL G, et al. iCaRL: incremental classifier and representation learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5533-5542. [13] DOUILLARD A, CORD M, OLLION C, et al. PODNet: pooled outputs distillation for small-tasks incremental learning[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 86-102. [14] KANG M, PARK J, HAN B. Class-incremental learning by knowledge distillation with adaptive feature consolidation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 16050-16059. [15] YAN S P, XIE J W, HE X M. DER: dynamically expandable representation for class incremental learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, IEEE Press, 2021: 3013-3022. [16] ZHOU D W, WANG Q W, YE H J, et al. A model or 603 exemplars: towards memory-efficient class-incremental learning[C]//Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations. Kigali: ICLR, 2023. [17] WANG F Y, ZHOU D W, YE H J, et al. FOSTER: feature boosting and compression for class-incremental learning[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2022: 398-414. [18] ZHU K, ZHAI W, CAO Y, et al. Self-sustaining representation expansion for non-exemplar class-incremental learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 9286-9295. [19] IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: PMLR, 2015, 37: 448-456. [20] ORDÓÑEZ F J, ROGGEN D. Deep convolutional and LSTM recurrent neural networks for multimodal wearable activity recognition[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(1): 115. doi: 10.3390/s16010115 [21] QIAN N. On the momentum term in gradient descent learning algorithms[J]. Neural Networks, 1999, 12(1): 145-151. doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(98)00116-6 [22] BROUSMICHE M, ROUAT J, DUPONT S. Multi-level attention fusion network for audio-visual event recognition[EB/OL]. (2021-06-12)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.06736v1. [23] SHI Z S, LIANG J, LI Q Q, et al. Multi-modal multi-action video recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13658-13667. -






 下载:
下载: