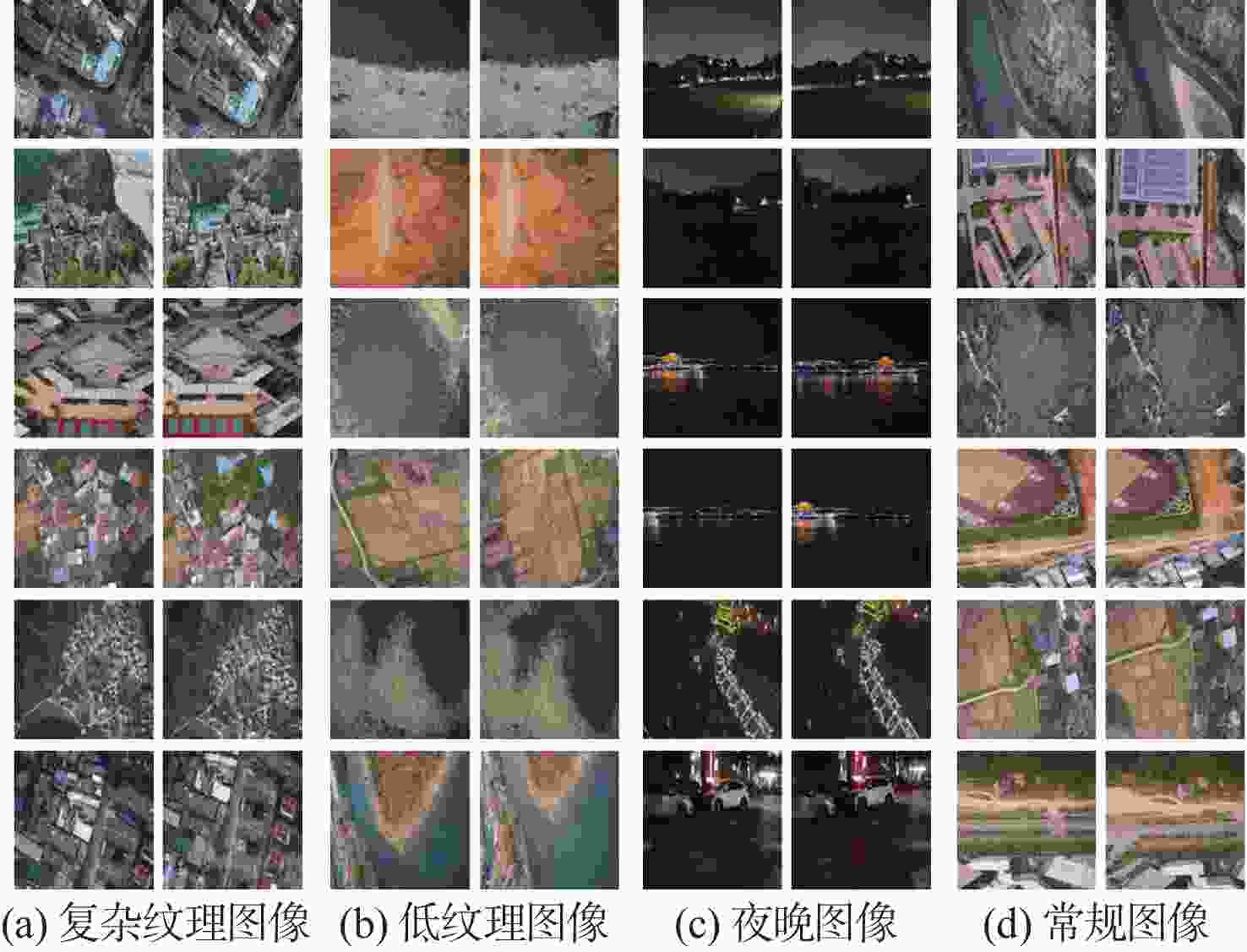
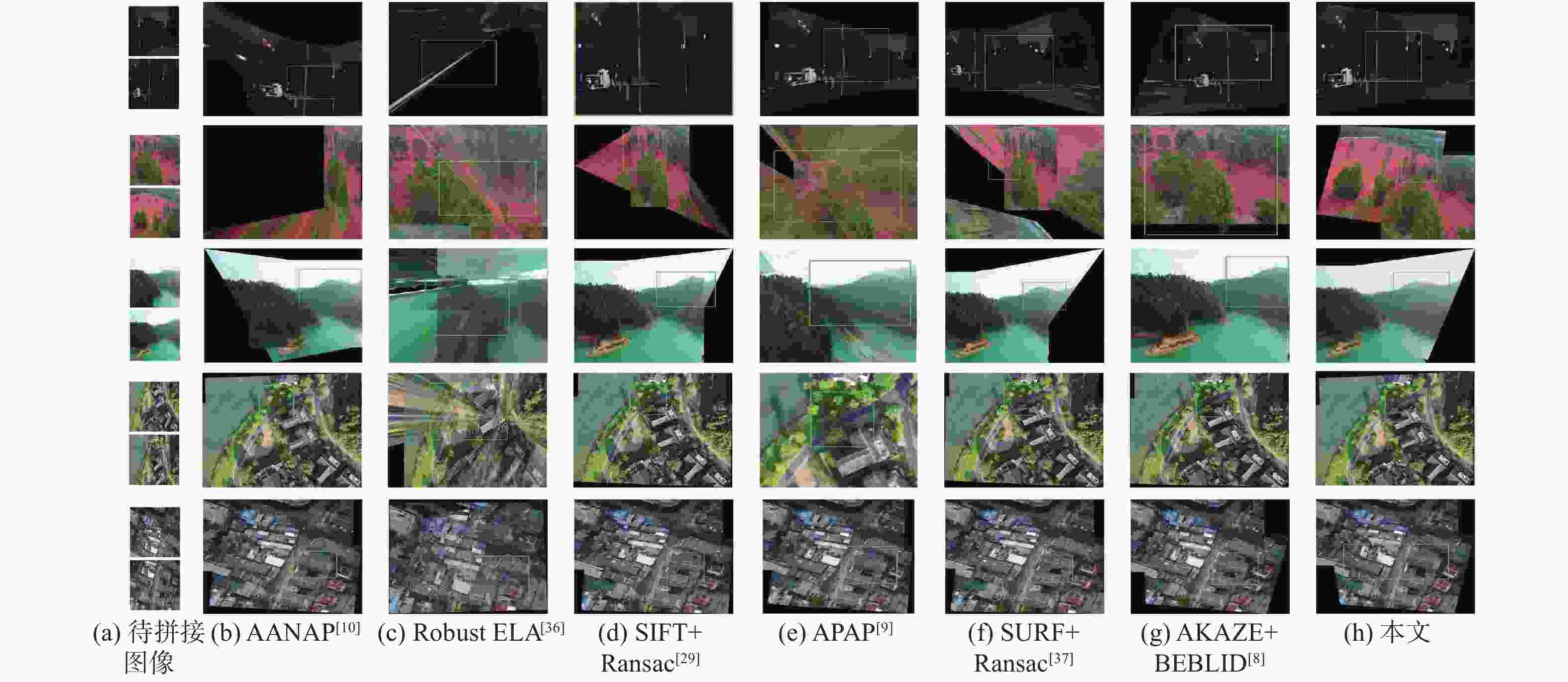
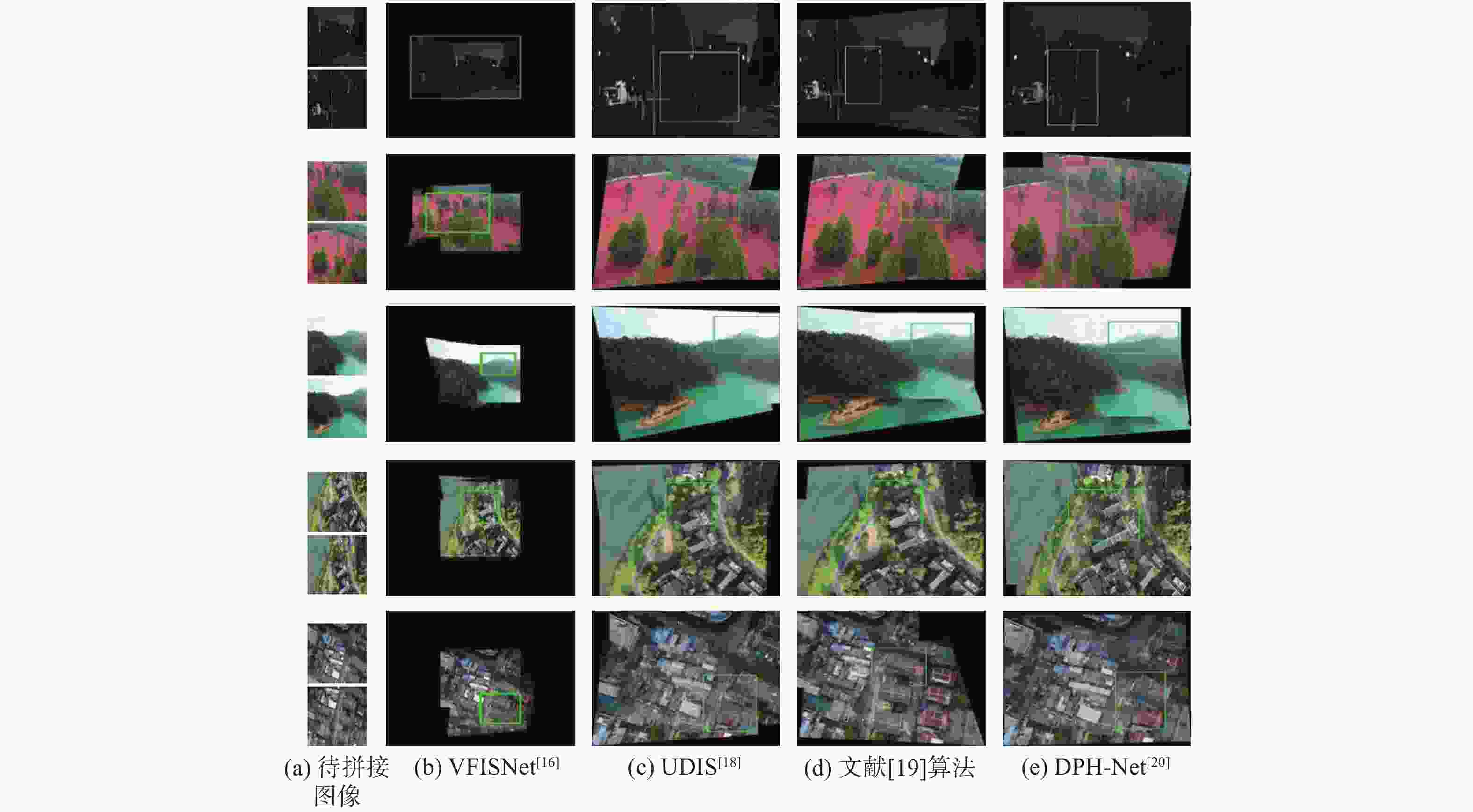
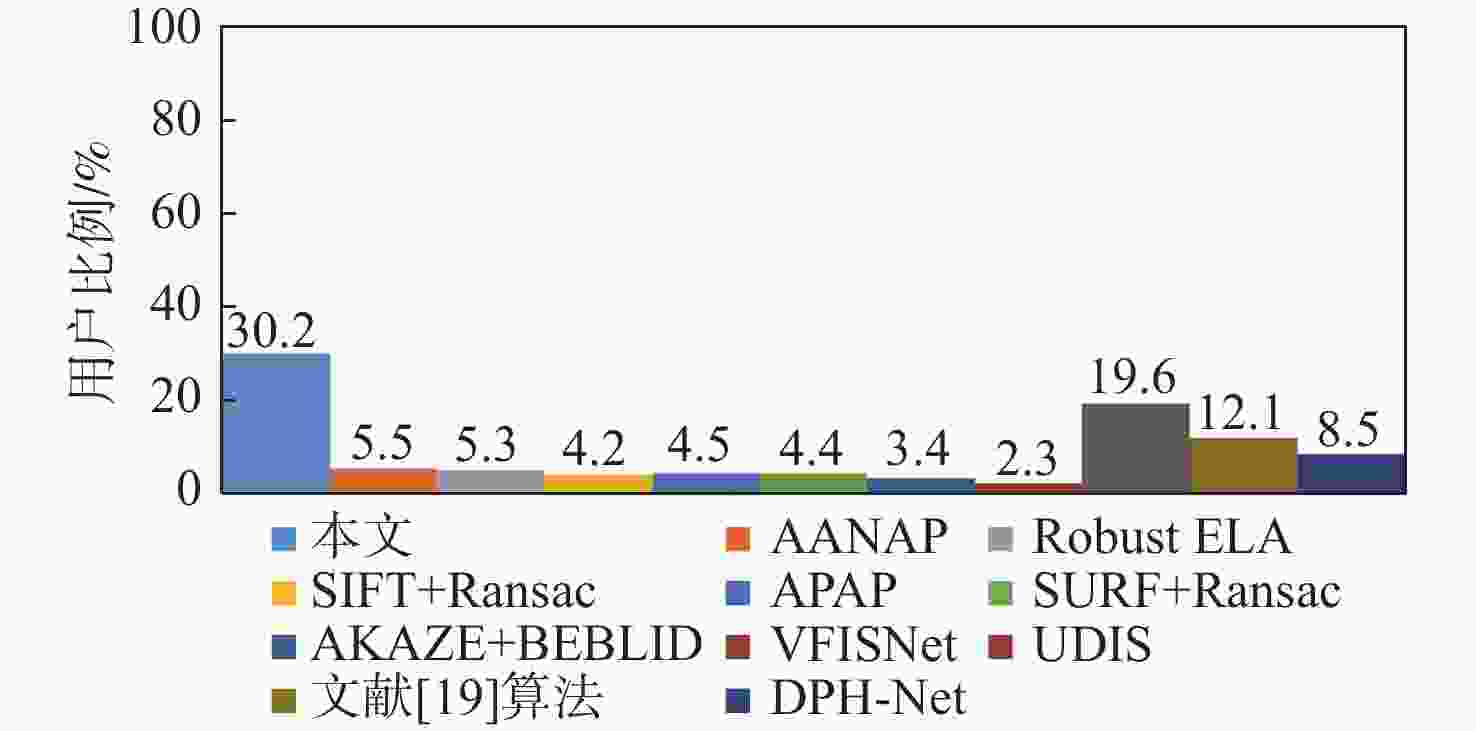
-
摘要:
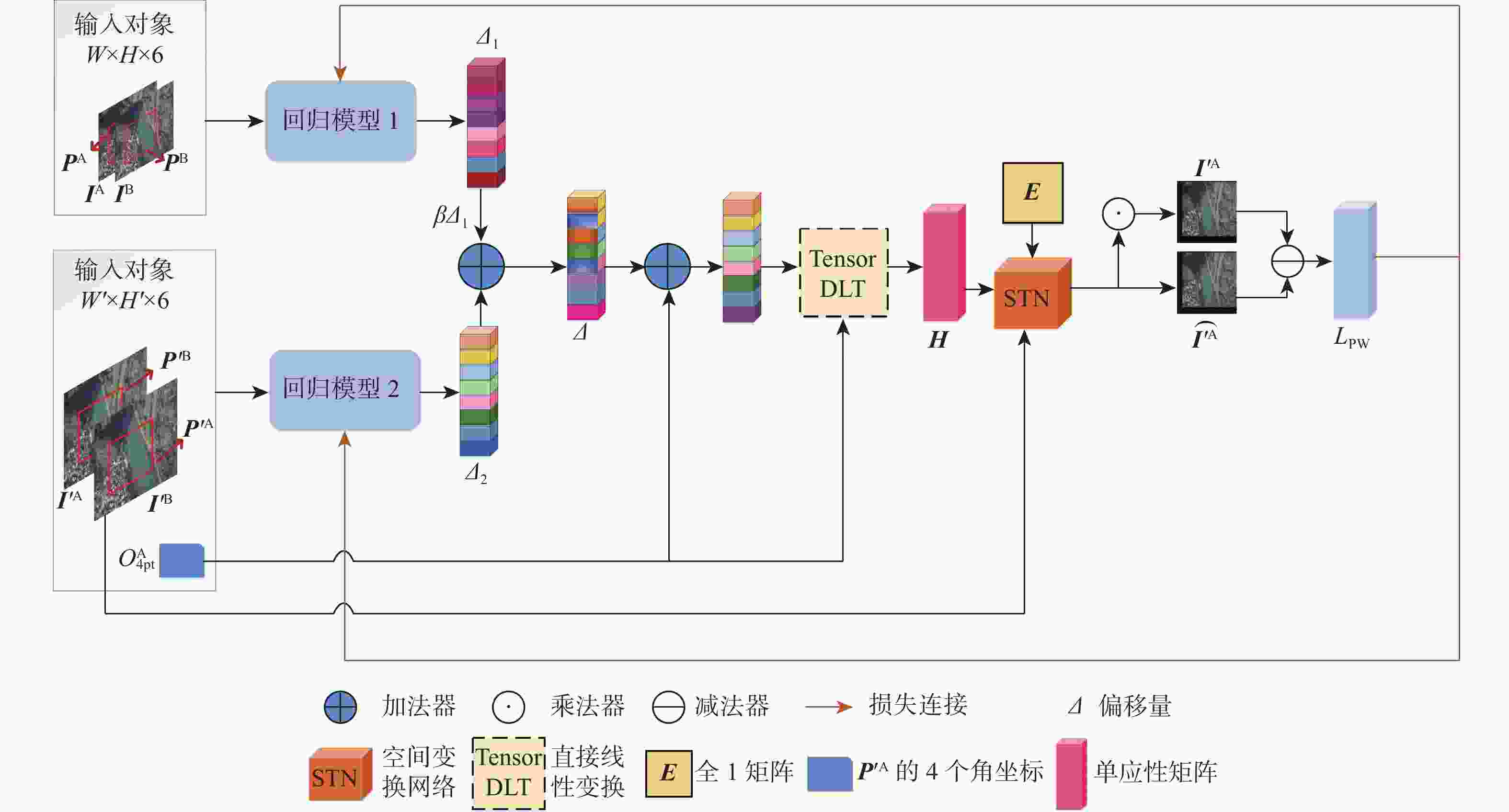
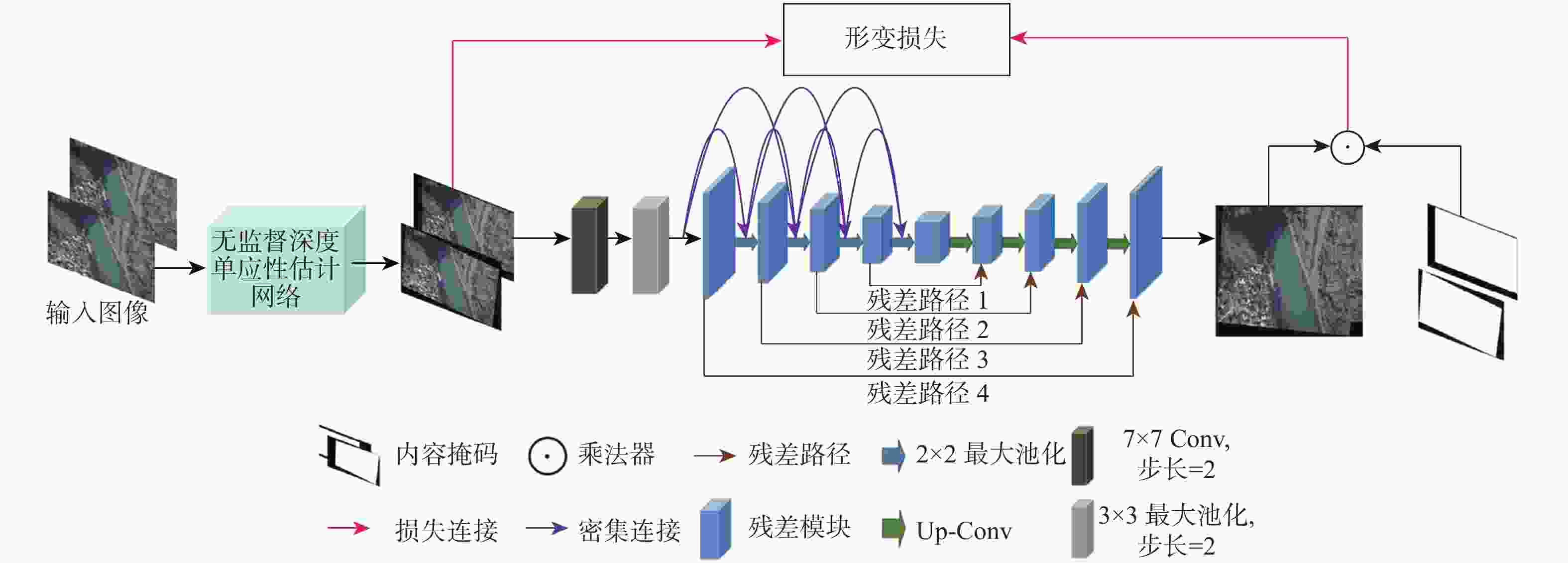
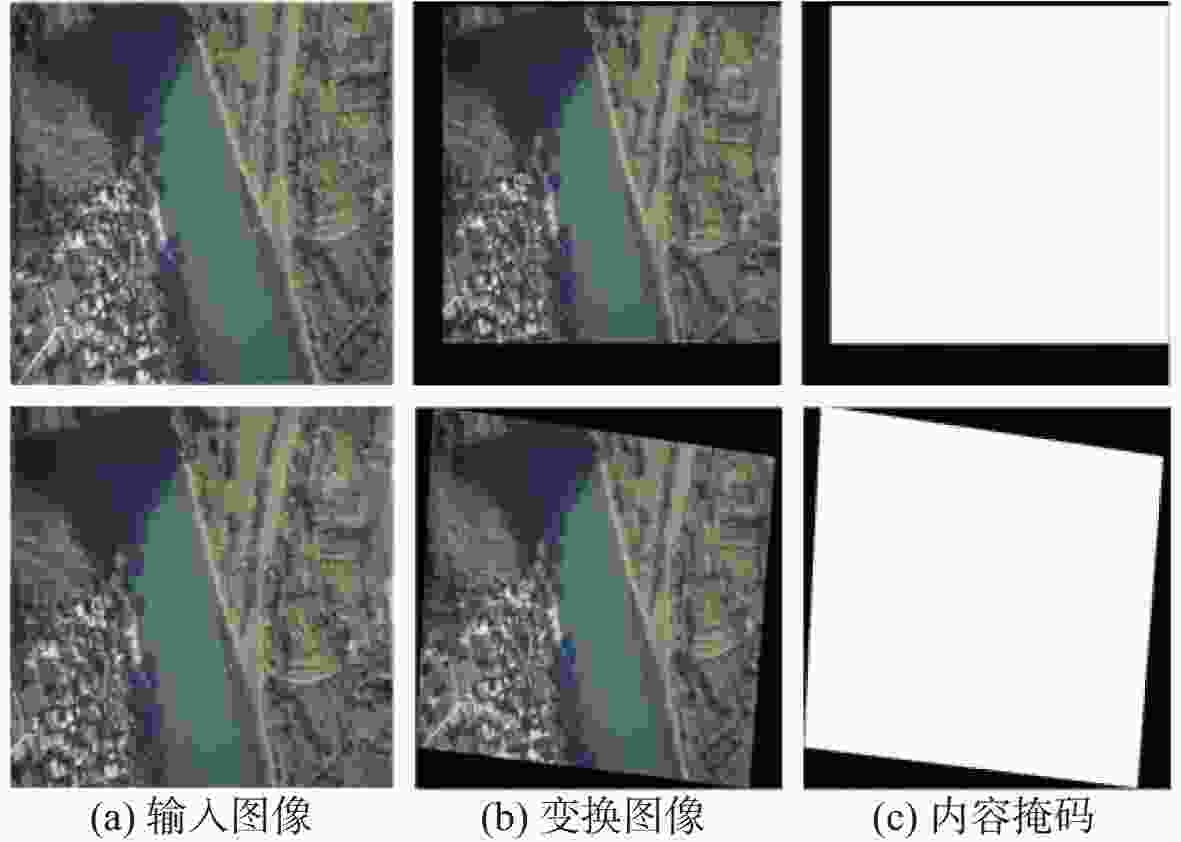
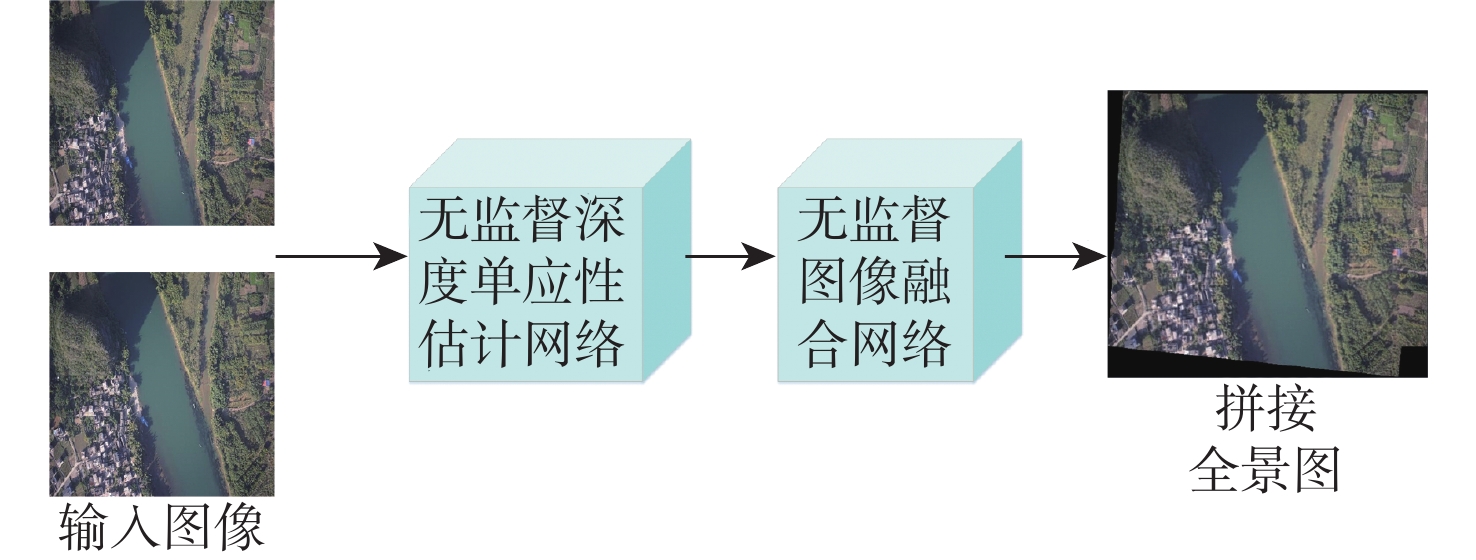
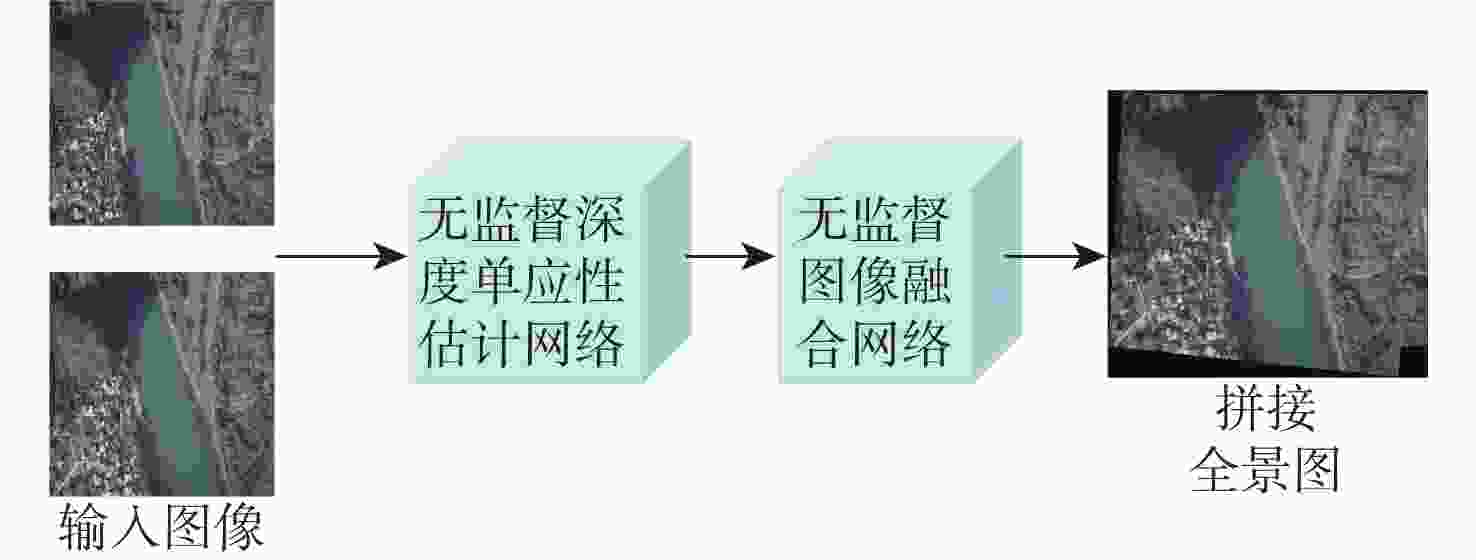
传统的图像拼接算法过度依赖特征的准确定位或分布,导致在复杂的航拍场景下鲁棒性差。因此,提出了一个完整的无监督深度学习航拍图像拼接框架,其由无监督深度单应性估计网络和无监督图像融合网络组成。无监督深度单应性估计网络旨在通过学习参考图像和目标图像之间的单应性变换,为后续的拼接工作提供准确的对齐信息;无监督图像融合网络用于学习航拍图像拼接的变形规则,生成最终的拼接结果。为了训练所提学习框架,提供了一个用于无监督航拍图像拼接的真实数据集,比较了尺度不变特征变换(SIFT)+Ransac、加速非线型扩散特征检测与匹配(AKAZE)+增强型高效二进制局部图像描述符(BEBLID)、基于BRIEF算法的快速二值特征向量(ORB)+Ransac和基于深度学习的图像拼接算法,实验结果表明,结构相似性指数(SSIM)提高了39.94%,峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了36.55%,均方根误差(RMSE)降低了66.09%。此外,所提算法在真实的航拍场景下相较于现有的基于深度学习和传统的图像拼接算法具有更好的视觉拼接效果和鲁棒性。
Abstract:Traditional image stitching approaches predominantly depend on accurate feature localization and distribution, which leads to suboptimal robustness in intricate aerial photography contexts. Consequently, a comprehensive unsupervised deep learning framework for aerial image stitching was devised, encompassing an unsupervised deep homography estimation network and an unsupervised image fusion network. First, the deep homography estimation network was employed to provide precise alignment data for subsequent stitching by ascertaining the homographic transformation between reference and target images. Subsequently, the image fusion network was utilized to learn deformation patterns of aerial image stitching, generating the final stitched output. Additionally, a real dataset for unsupervised aerial image stitching was introduced to facilitate the training of the learning framework. Comparative analysis was conducted on the suggested unmanned aerial vehicle aerial image dataset, incorporating scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) + Ransac, accelerated-nonlinear diffusion-based feature detection and matching (AKAZE) + boosted efficient binary local image descriptor (BEBLID), oriented brief (ORB) + Ransac, and deep-learning-based image stitching algorithms. Experiments show that the value of structural similarity (SSIM) is increased by 39.94%; the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is increased by 36.55%, and the root mean square error (RMSE) is reduced by 66.09%. Moreover, the proposed method demonstrates superior visual stitching performance and robustness in authentic aerial scenarios compared to existing deep-learning-based and traditional image stitching methods.
-
Key words:
- aerial image /
- deep homography estimation /
- image stitching /
- unsupervised /
- image fusion
-
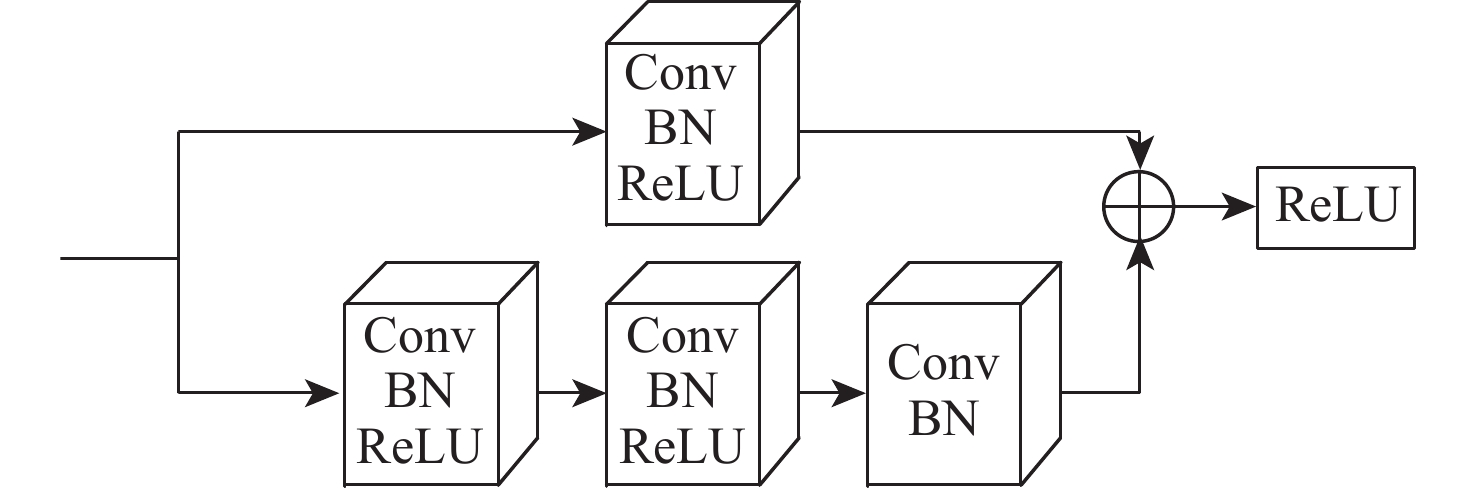
表 1 网络各层参数及特征图大小
Table 1. Parameters of each layer of network and feature map size
层名称 层操作 特征图大小/像素 Con1_x 7×7, 64, 步长=2 256×256 最大池化 3×3, 步长=2 128×128 Con2_x $\left[ \begin{gathered} 3 \times 3,64 \\ 3 \times 3,64 \\ \end{gathered} \right] \times 3$ 128×128 Con3_x $\left[ \begin{gathered} 3 \times 3,128 \\ 3 \times 3,128 \\ \end{gathered} \right] \times 4$ 64×64 Con4_x $\left[ \begin{gathered} 3 \times 3,256 \\ 3 \times 3,256 \\ \end{gathered} \right] \times 6$ 32×32 Con5_x $\left[ \begin{gathered} 3 \times 3,512 \\ 3 \times 3,512 \\ \end{gathered} \right] \times 3$ 16×16 平均池化 2×2, 步长=2 8×8 全连接层 8个偏移量 1×1 表 2 不同算法的单应性比较
Table 2. Homography estimation results of different methods
算法 平均PSNR/dB 平均SSIM 平均RMSE 传统单应性估计 X3×3 14.2336 0.2434 16.7963 SIFT+Ransac[29] 23.8325 0.7485 7.2675 AKAZE+BEBLID[8] 22.1323 0.6241 7.4103 ORB+Ransac[30] 21.6325 0.5986 8.8875 深度单应性估计(有监督) DHN[31] 19.9563 0.6131 5.2236 文献[19]算法 23.9723 0.7543 4.9216 DPH-Net[20] 22.8356 0.7412 6.6235 深度单应性估计(无监督) UDHN[32] 21.8526 0.6721 5.1203 UDIS[18] 25.0521 0.8023 4.2651 本文 27.2513 0.8377 3.0136 表 3 不同算法的图像拼接时间比较
Table 3. Comparison of image stitching time of different methods
s 表 4 消融研究框架
Table 4. Ablation research framework
框架 单分支 双分支 编解码网络 编解码网络+
密集连接编解码网络+
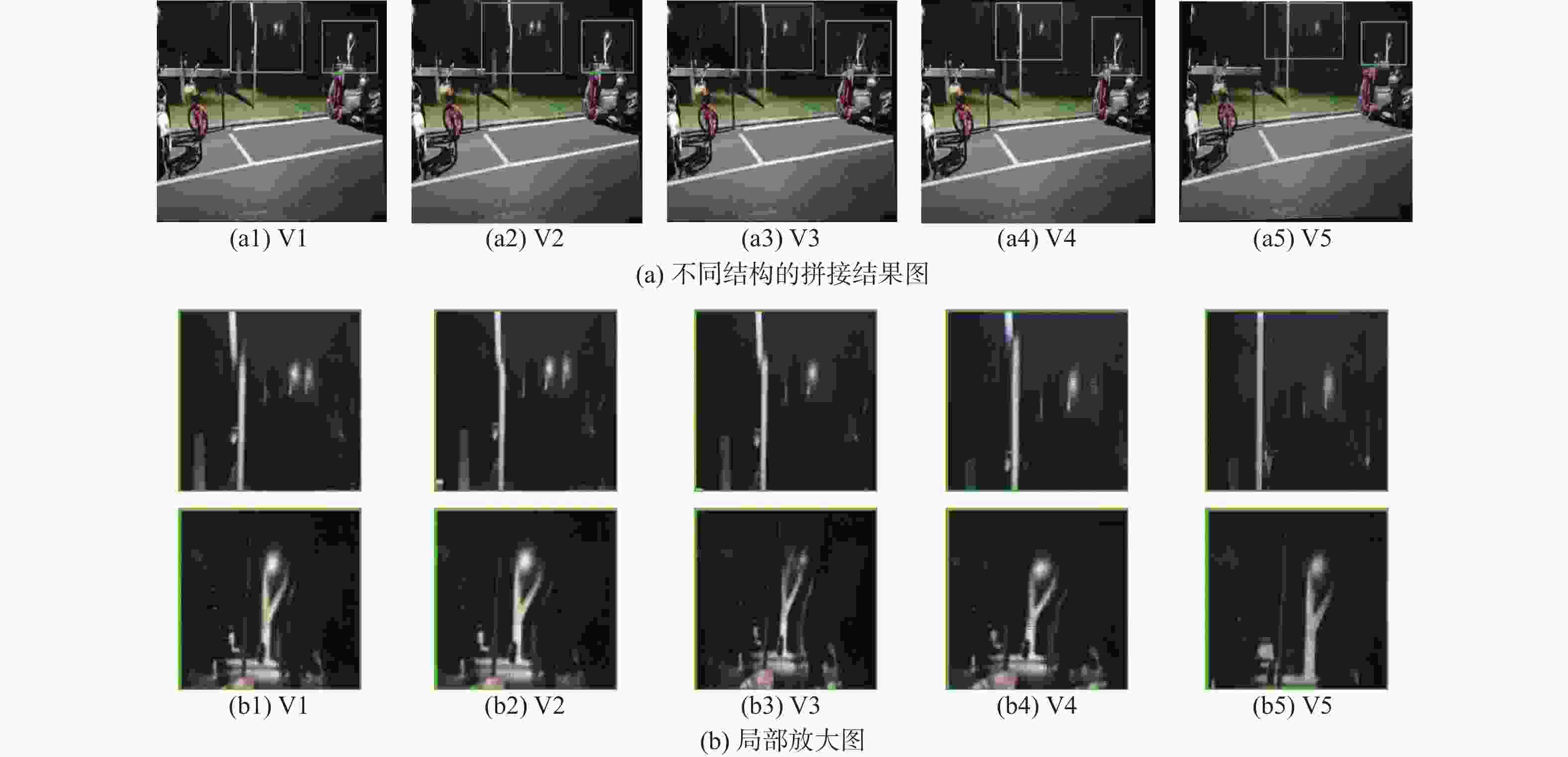
残差路径V1 √ √ V2 √ √ V3 √ √ V4 √ √ V5 √ √ √ -
[1] 蒲良, 张学军. 基于深度学习的无人机视觉目标检测与跟踪[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2022, 48(5): 872-880.PU L, ZHANG X J. Deep learning based UAV vision object detection and tracking[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(5): 872-880(in Chinese). [2] YANG C, LIU X, ZHOU H, et al. Towards accurate image stitching for drone-based wind turbine blade inspection[J]. Renewable Energy, 2023, 203: 267-279. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.12.063 [3] XIE W H. Research on target extraction system of UAV remote sensing image based on artificial intelligence[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Communication Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 1-5. [4] CHEN J, LI Z X, PENG C L, et al. UAV image stitching based on optimal seam and half-projective warp[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1068. doi: 10.3390/rs14051068 [5] JONG T K, BONG D B L. An effective feature detection approach for image stitching of near-uniform scenes[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2023, 110: 116872. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2022.116872 [6] ZHANG J D, XIU Y. Image stitching based on human visual system and SIFT algorithm[J]. The Visual Computer, 2024, 40(1): 427-439. doi: 10.1007/s00371-023-02791-4 [7] 宋飞, 杨扬, 杨昆, 等. 基于双特征的丘陵山区耕地低空遥感图像配准算法[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2018, 44(9): 1952-1963.SONG F, YANG Y, YANG K, et al. Low-altitude remote sensing image registration algorithm based on dual-feature for arable land in hills and mountains[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(9): 1952-1963(in Chinese). [8] 宗慧琳, 袁希平, 甘淑, 等. 改进AKAZE算法的泥石流区无人机影像特征匹配[J]. 测绘通报, 2023(2): 91-96.ZONG H L, YUAN X P, GAN S, et al. An improved AKAZE algorithm for UAV image feature matching in debris flow area[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2023(2): 91-96(in Chinese). [9] ZARAGOZA J, CHIN T J, BROWN M S, et al. As-projective-as-possible image stitching with moving DLT[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2339-2346. [10] LIN C C, PANKANTI S U, RAMAMURTHY K N, et al. Adaptive as-natural-as-possible image stitching[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1155-1163. [11] CHANG C H, SATO Y, CHUANG Y Y. Shape-preserving half-projective warps for image stitching[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 3254-3261. [12] CHEN Y S, CHUANG Y Y. Natural image stitching with the global similarity prior[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 186-201. [13] 梁镇锋, 夏海英. 一种面向无人机航拍图像的快速拼接算法[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(3): 41-52.LIANG Z F, XIA H Y. A fast stitching algorithm for UAV aerial images[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 41(3): 41-52(in Chinese). [14] HOANG V D, TRAN D P, NHU N G, et al. Deep feature extraction for panoramic image stitching[C]//Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 141-151. [15] YAN M, YIN Q, GUO P. Image stitching with single-hidden layer feedforward neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4162-4169. [16] NIE L, LIN C Y, LIAO K, et al. A view-free image stitching network based on global homography[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2020, 73: 102950. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2020.102950 [17] NIE L, LIN C Y, LIAO K, et al. Learning edge-preserved image stitching from large-baseline deep homography[EB/OL]. (2020-12-11)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2012.06194. [18] NIE L, LIN C Y, LIAO K, et al. Unsupervised deep image stitching: reconstructing stitched features to images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 6184-6197. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3092828 [19] ZHU F Z, LI J C, ZHU B, et al. UAV remote sensing image stitching via improved VGG16 Siamese feature extraction network[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 229: 120525. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120525 [20] HUANG C W, PAN X, CHENG J C, et al. Deep image registration with depth-aware homography estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 6-10. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3238274 [21] 马腾宇, 李孜, 刘日升, 等. 基于无监督学习的多模态可变形配准[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2021, 47(3): 658-664.MA T Y, LI Z, LIU R S, et al. Multimodal deformable registration based on unsupervised learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(3): 658-664(in Chinese). [22] IANDOLA F N, HAN S, MOSKEWICZ M W, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size[EB/OL]. (2016-11-04)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07360. [23] HARTLEY R, ZISSERMAN A. Multiple view geometry in computer vision[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [24] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Spatial Transformer networks[C]//Proceedings of the 21th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2015: 2017-2025. [25] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [26] ZHAO H, GALLO O, FROSIO I, et al. Loss functions for image restoration with neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(1): 47-57. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2644865 [27] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, LI F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 694-711. [28] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [29] BROWN M, LOWE D G. Automatic panoramic image stitching using invariant features[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2007, 74(1): 59-73. doi: 10.1007/s11263-006-0002-3 [30] RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 2564-2571. [31] DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, RABINOVICH A. Deep image homography estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 5668-5676. [32] NGUYEN T, CHEN S W, SHIVAKUMAR S S, et al. Unsupervised deep homography: a fast and robust homography estimation model[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(3): 2346-2353. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2809549 [33] WINKLER S, MOHANDAS P. The evolution of video quality measurement: from PSNR to hybrid metrics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2008, 54(3): 660-668. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2008.2000733 [34] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [35] HODSON T O. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): when to use them or not[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2022, 15(14): 5481-5487. doi: 10.5194/gmd-15-5481-2022 [36] LI J, WANG Z M, LAI S M, et al. Parallax-tolerant image stitching based on robust elastic warping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(7): 1672-1687. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2777461 [37] BAY H, TUYTELAARS T, VAN GOOL L. SURF: speeded up robust features[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 404-417. -






 下载:
下载: