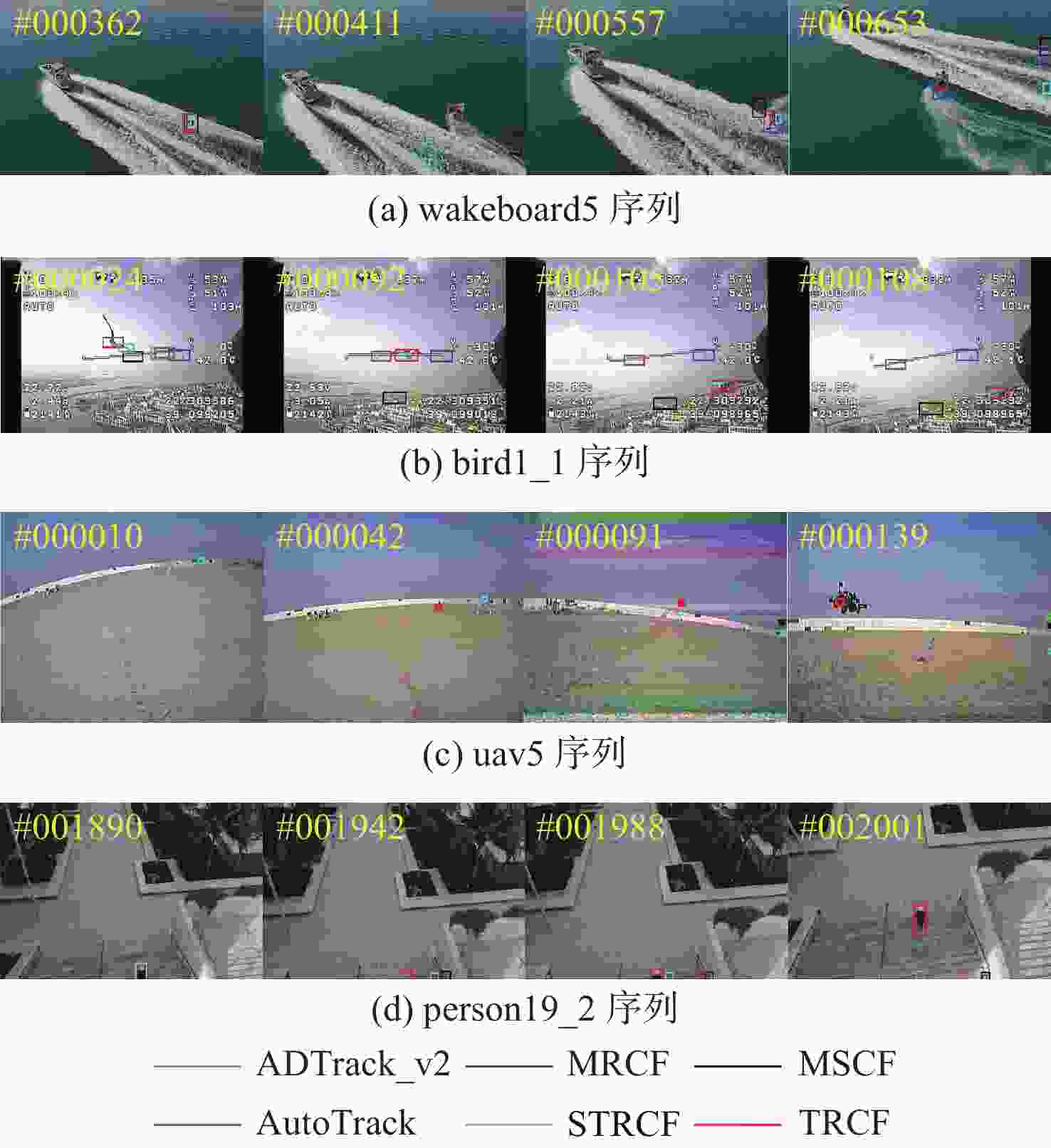
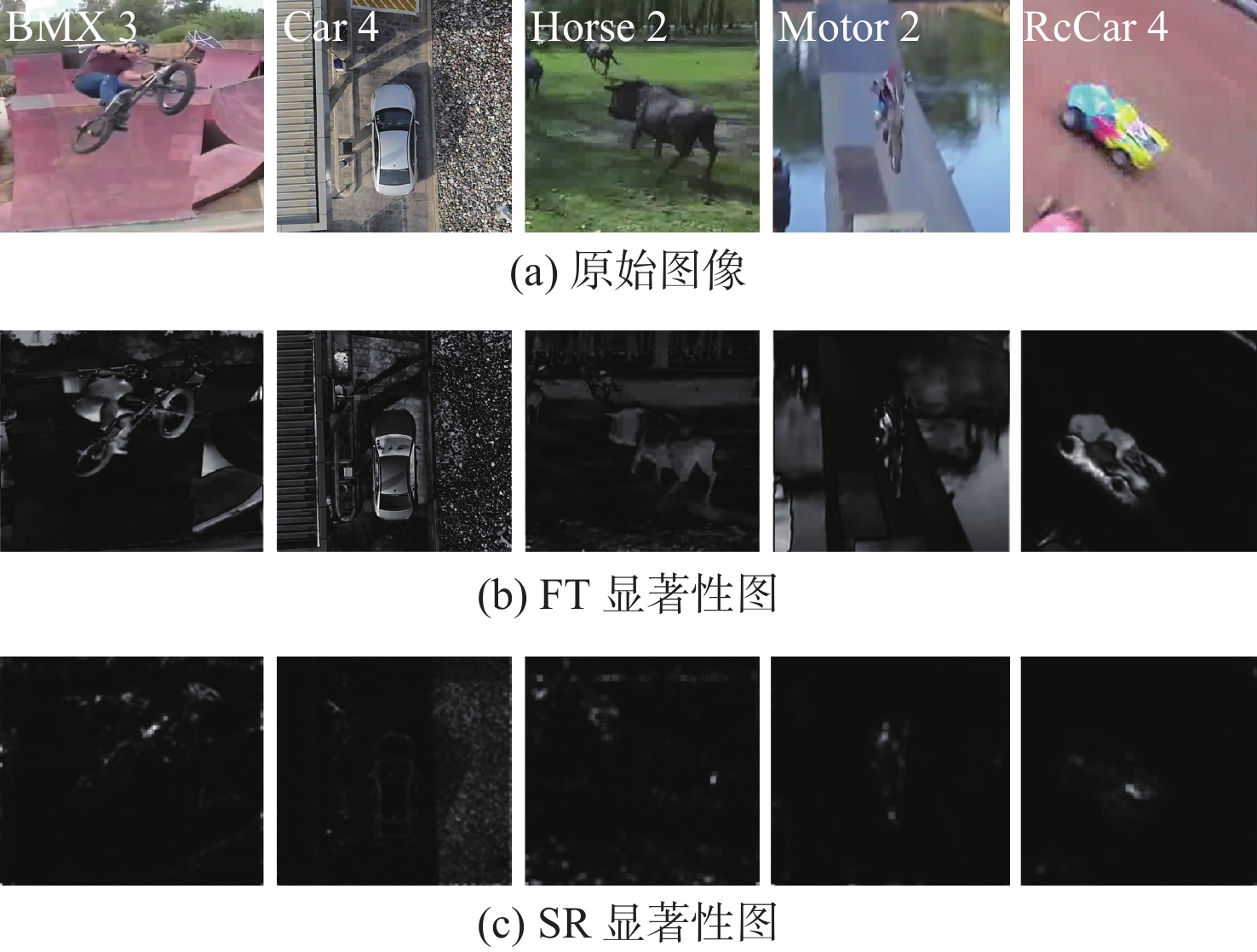
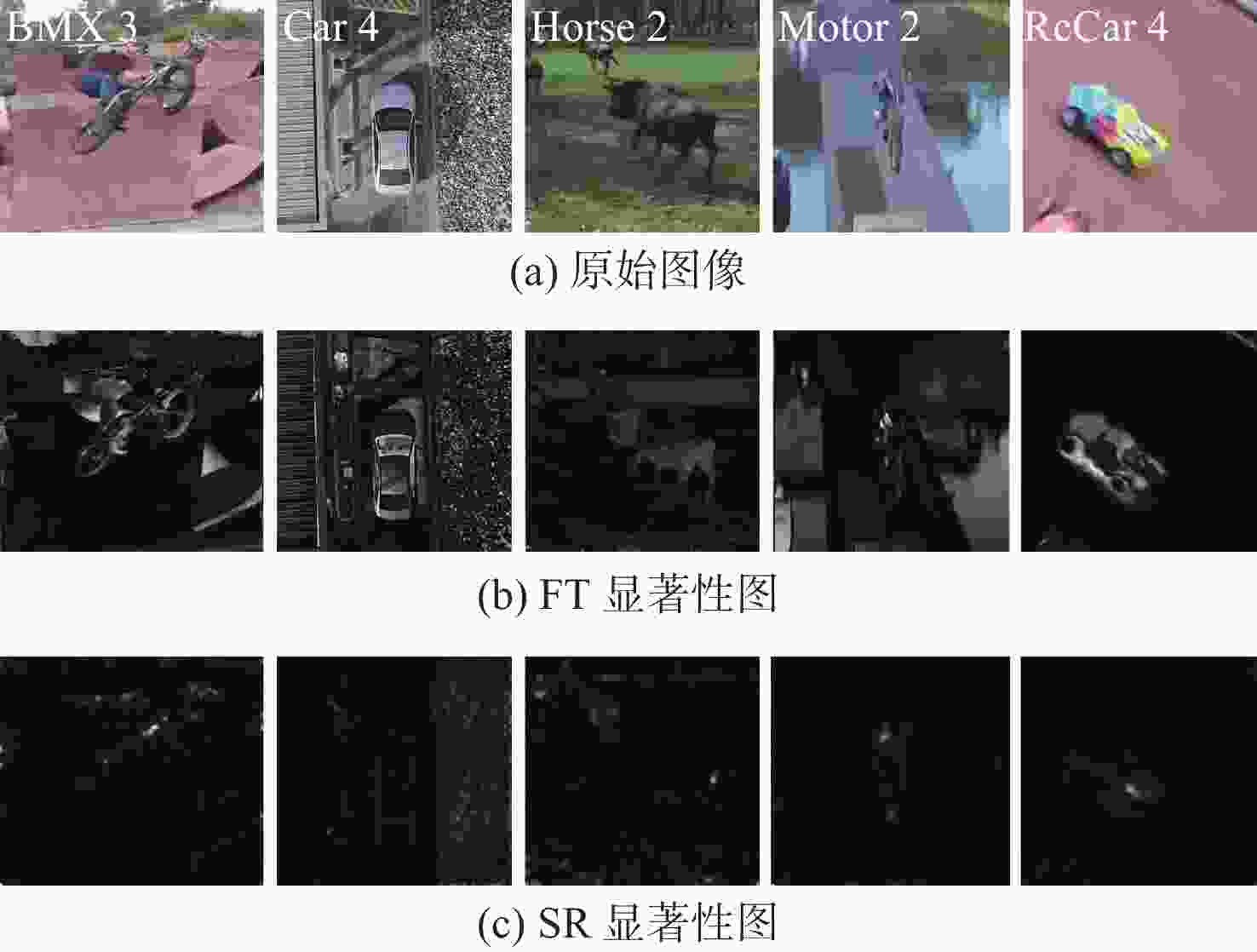
Saliency-aware triple-regularized correlation filter algorithm for UAV object tracking
-
摘要:
无人机(UAV)场景中的目标跟踪在很多现实任务中得到广泛应用。与一般场景中的目标跟踪任务不同,UAV目标跟踪更易受到复杂环境干扰和算力的限制。基于此,提出了一种显著性感知三重正则化相关滤波(TRCF)UAV目标跟踪算法。采用高效的显著性目标检测算法动态生成对偶空间正则化器来抑制边界效应,惩罚不相关的背景噪声系数。引入时间正则化应对目标因外观变化而导致的滤波器退化问题,提供更鲁棒的外观模型。此外,引入轻量型的深度网络CF-VGG来提取目标的深度特征,并与手工特征线性融合描述目标的语义信息,提高跟踪精度。在5个公开的UAV基准数据集上进行了充分实验,结果表明:所提算法在5个数据集上的整体性能均有不同程度提升,证明了算法的有效性和鲁棒性,且算法的实时跟踪速度约为21帧/s,能够胜任UAV的目标跟踪任务。
Abstract:Object tracking in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) scenarios has been widely applied in many real-world tasks. Different from general object tracking, UAV object tracking is more easily affected by complex environmental interferences and computational limitations. In this paper, a saliency-aware triple-regularized correlation filter (TRCF) for UAV object tracking was proposed. An efficient saliency detection algorithm was used to dynamically generate a dual-spatial regularizer to suppress boundary effects and apply a penalty to irrelevant background noise coefficients. Temporal regularization was introduced to address the filter degradation problem caused by appearance variation, providing a more robust appearance model. In addition, a lightweight deep network CF-VGG was employed to extract deep features, which were linearly fused with hand-crafted features to describe the object’s semantic information with improved tracking accuracy. Experiments were conducted on five publicly available UAV benchmark datasets. Results show that compared to the baseline methods, the proposed method demonstrates improvements on the five datasets, proving its effectiveness and robustness. The method also shows a real-time tracking speed of about 21 frames per second, making it suitable for UAV object-tracking tasks.
-
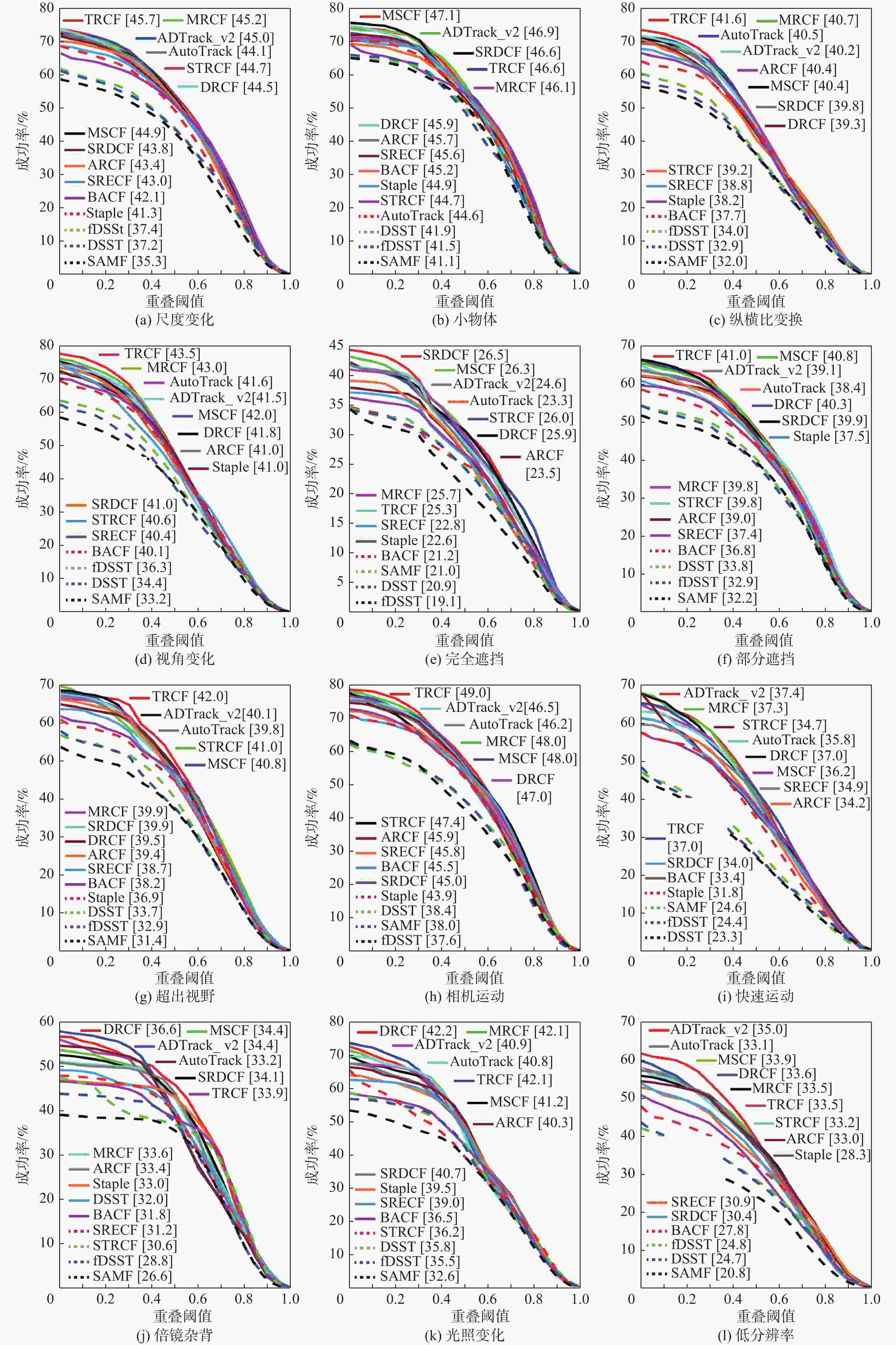
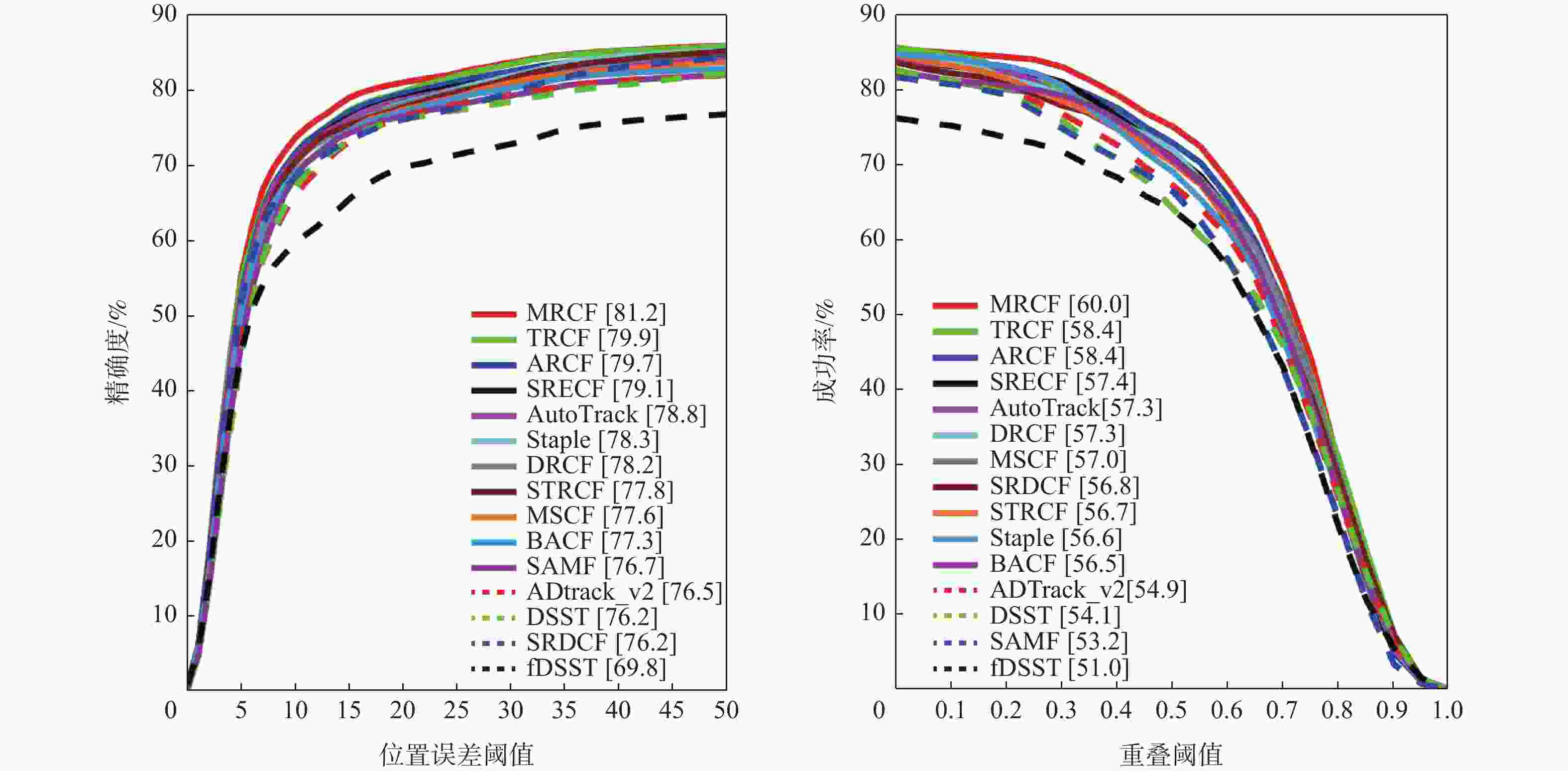
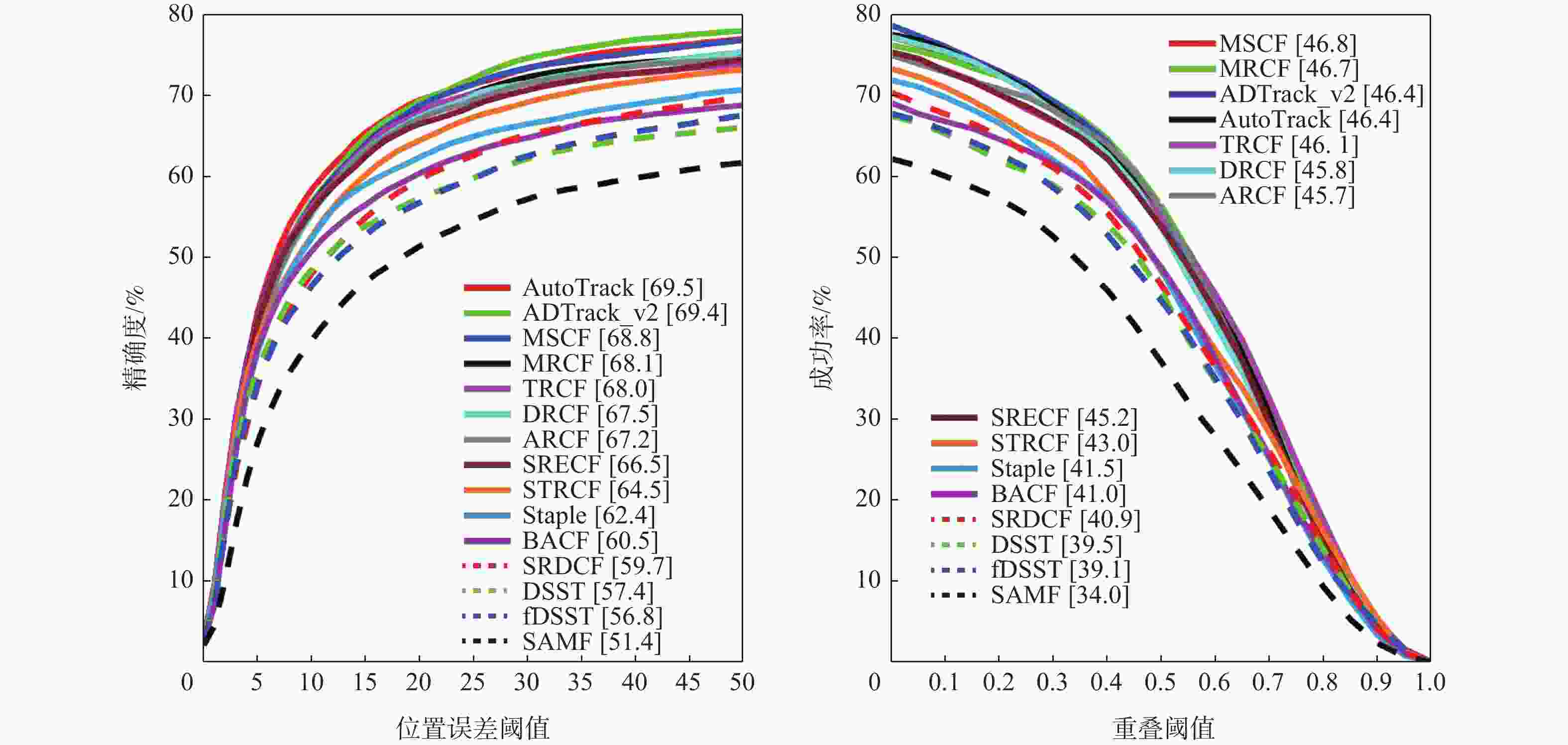
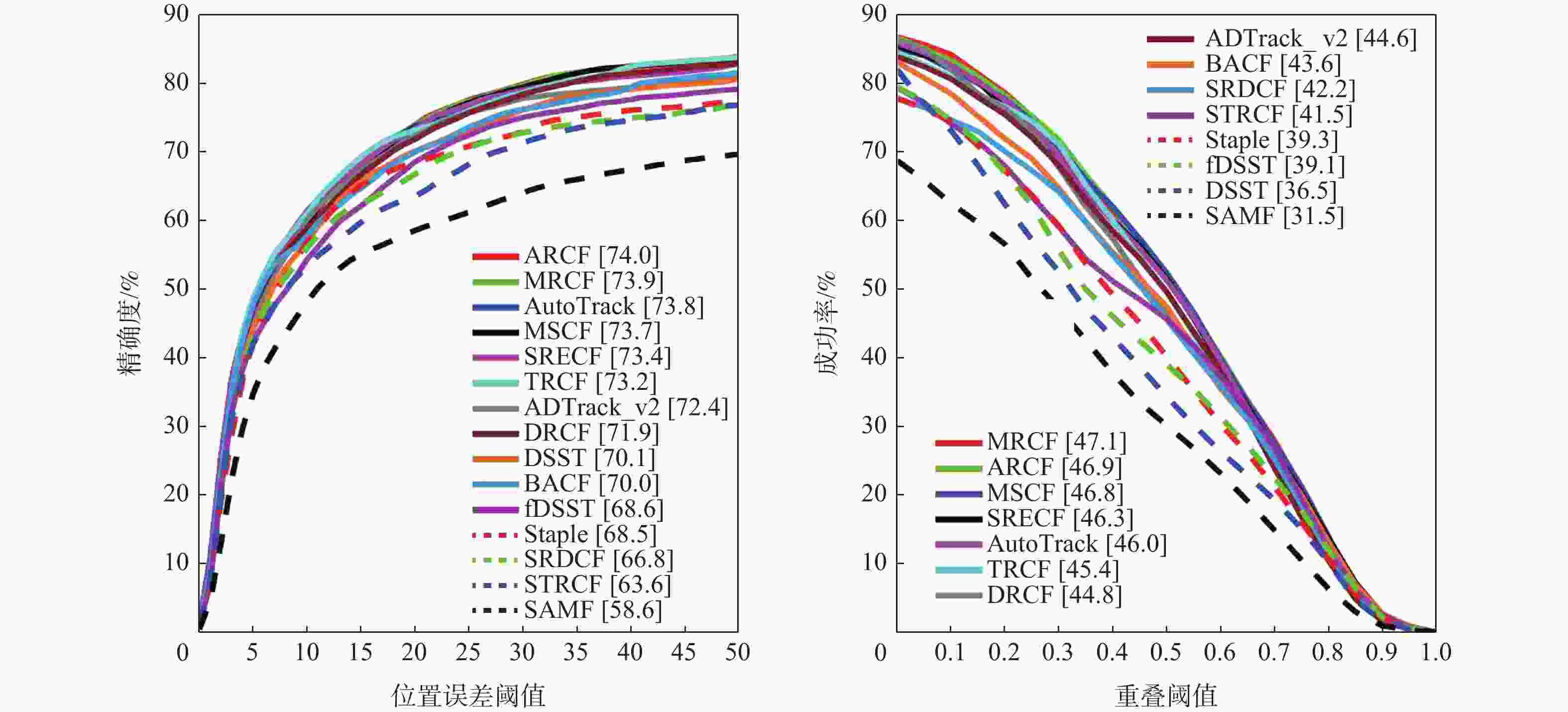
表 1 本文算法与基准算法的性能比较
Table 1. Comparisons between the proposed method and baseline method
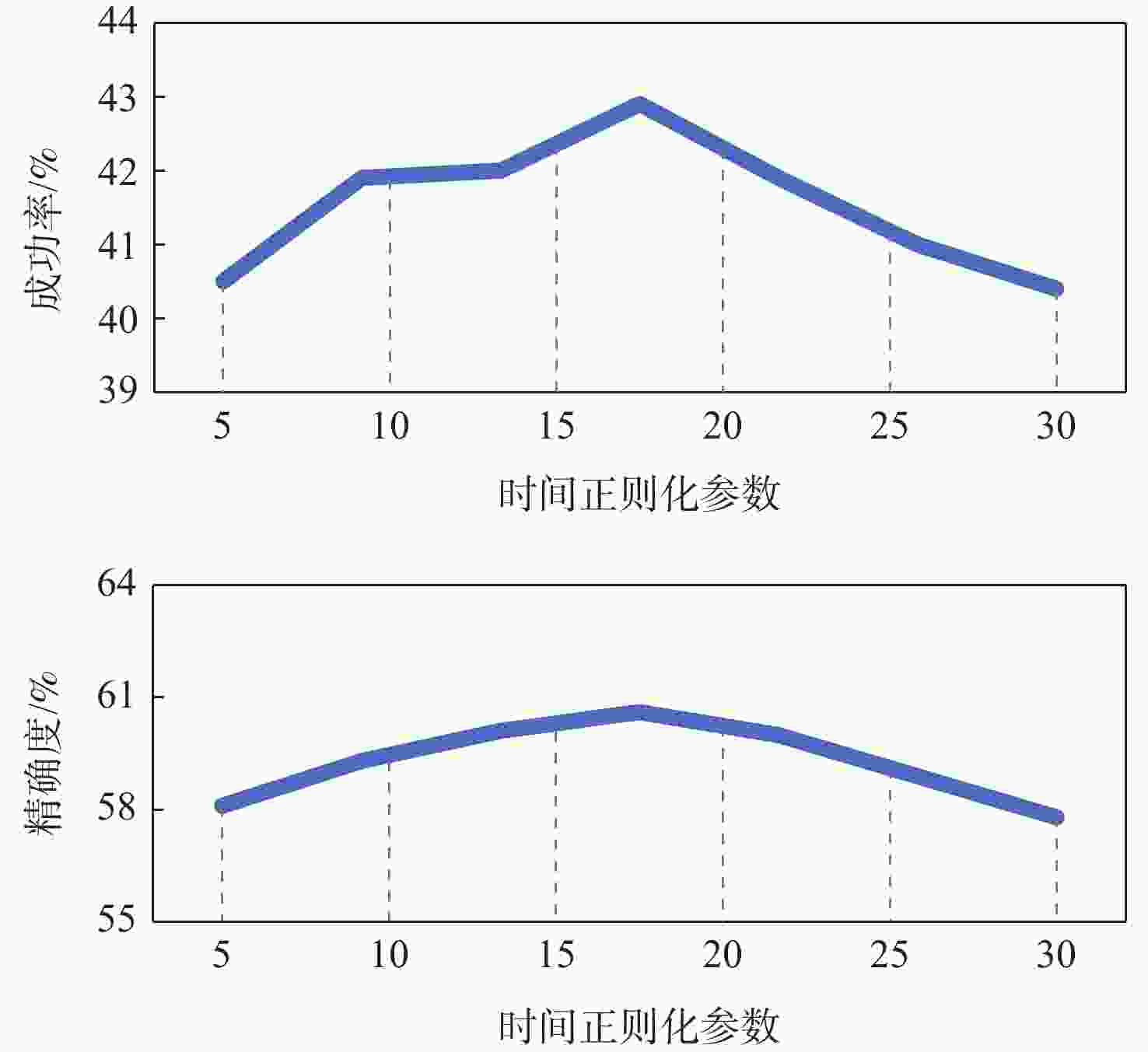
% 表 2 消融实验结果对比
Table 2. Ablation study results
% 基准数据集 精确度 成功率 DRCF DRCF+
TrDRCF+
FTDRCF+
CF-VGGDRCF+
CF-VGG+
TrDRCF+
CF-VGG+
FT+TrDRCF DRCF+
TrDRCF+
FTDRCF+
CF-VGGDRCF+
CF-VGG+
TrDRCF+
CF-VGG+
FT +TrUAV123[21] 69.6 66.3 67.9 70.1 69.8 70.3 47.9 46.4 47.7 48.3 48.4 48.8 UAVDT[24] 71.9 71.0 73.2 70.2 73.3 73.2 44.8 44.3 46.0 44.7 45.4 45.4 VisDrone-SOT2018[22] 78.2 80.6 78.3 76.2 79.9 79.9 57.3 57.6 56.8 55.6 58.5 58.4 注:粗体表示与基准算法相比性能增强;Base+FT、Base+CF-VGG、Base+Tr、Base+CF-VGG+Tr分别表示在基准算法中加入FT显著性目标检测模块、轻量级深度特征、时间正则化、同时加入轻量级深度特征和时间正则化;Base+CF-VGG+FT+Tr为加入所有模块的TRCF目标跟踪算法。 表 3 各算法在UAV数据集上的帧率比较
Table 3. FPS comparison of different algorithms on UAV datasets
帧/s 算法 帧率 平均值 UAVDT VisDrone-SOT2018 UAV123 MRCF 46.9316 33.3641 35.0628 38.4528 MSCF 28.691 24.8189 23.3937 25.6345 BACF 58.749 37.0889 39.5027 45.1135 DSST 140.946 61.7457 84.6391 95.7769 fDSST 201.1066 146.093 164.2684 170.489 SAMF 14.722 7.5533 9.9559 10.7437 SRDCF 15.5058 8.0745 10.2923 11.2909 STRCF 28.712 20.9129 21.2095 23.6115 AutoTrack 35.2138 41.8124 40.8652 39.2971 ARCF 22.1567 21.1463 22.44 21.9143 DRCF 38.3627 30.208 31.9774 33.5160 TRCF 24.1157 16.7908 23.0223 21.3096 注:粗体、斜体、下划线分别表示第1、第2、第3名。 表 4 消融实验帧率对比
Table 4. FPS results of ablation study
帧/s 模块 帧率 平均值 VisDrone-SOT2018 UAV123 UAVDT DRCF 30.208 39.0783 38.3627 35.883 DRCF+Tr 27.464 7 33.7011 41.4456 34.2038 DRCF+FT 25.2424 30.7487 38.7303 31.5738 DRCF+CF-VGG 19.6298 23.0575 29.1539 23.9471 DRCF+CF-VGG+FT+Tr 16.7908 23.0223 24.1157 21.3096 -
[1] TAHIR A, BÖLING J, HAGHBAYAN M H, et al. Swarms of unmanned aerial vehicles: a survey[J]. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2019, 16: 100106. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2019.100106 [2] YUAN C, LIU Z X, ZHANG Y M. Aerial images-based forest fire detection for firefighting using optical remote sensing techniques and unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2017, 88(2): 635-654. [3] KANELLAKIS C, NIKOLAKOPOULOS G. Survey on computer vision for UAVs: current developments and trends[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2017, 87(1): 141-168. [4] JIAO L C, WANG D, BAI Y D, et al. Deep learning in visual tracking: a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(9): 5497-5516. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3136907 [5] FU C H, LI B W, DING F Q, et al. Correlation filters for unmanned aerial vehicle-based aerial tracking: a review and experimental evaluation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2022, 10(1): 125-160. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2021.3072992 [6] BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 2544-2550. [7] DANELLJAN M, KHAN F S, FELSBERG M, et al. Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1090-1097. [8] MA C, HUANG J B, YANG X K, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3074-3082. [9] DANELLJAN M, ROBINSON A, SHAHBAZ KHAN F, et al. Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 472-488. [10] DANELLJAN M, BHAT G, KHAN F S, et al. ECO: efficient convolution operators for tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6931-6939. [11] BHAT G, JOHNANDER J, DANELLJAN M, et al. Unveiling the power of deep tracking[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer , 2018: 493-509. [12] GALOOGAHI H K, SIM T, LUCEY S. Correlation filters with limited boundaries[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4630-4638. [13] GALOOGAHI H K, FAGG A, LUCEY S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1144-1152. [14] YUAN Y, CHEN Y M, JING Y Q, et al. FRATCF: feature-residue real-time UAV tracking based on automatic spatio-temporal regularization correlation filter[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1-6. [15] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4310-4318. [16] LUKEŽIC A, VOJÍR T, ZAJC L C, et al. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4847-4856. [17] 王法胜, 尹双双, 贺冰, 等. 引入高斯掩膜的相关滤波目标跟踪算法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2023, 28(10): 3092-3106. doi: 10.11834/jig.220856WANG F S, YIN S S, HE B, et al. A Gaussian mask-based correlation filter tracking algorithm[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2023, 28(10): 3092-3106(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.220856 [18] LIN F L, FU C H, HE Y J, et al. ReCF: exploiting response reasoning for correlation filters in real-time UAV tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 10469-10480. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3094654 [19] HAN R Z, FENG W, WANG S. Fast learning of spatially regularized and content aware correlation filter for visual tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7128-7140. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2998978 [20] LI Y M, FU C H, HUANG Z Y, et al. Intermittent contextual learning for keyfilter-aware UAV object tracking using deep convolutional feature[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 23: 810-822. [21] MUELLER M, SMITH N, GHANEM B. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 445-461. [22] WEN L Y, ZHU P F, DU D W, et al. VisDrone-SOT2018: the vision meets drone single-object tracking challenge results[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 469-495. [23] FU C H, CAO Z A, LI Y M, et al. Onboard real-time aerial tracking with efficient Siamese anchor proposal network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5606913. [24] DU D W, QI Y K, YU H Y, et al. The unmanned aerial vehicle benchmark: object detection and tracking[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 375-391. [25] WANG Y B, WANG F S, WANG C, et al. Learning saliency-aware correlation filters for visual tracking[J]. The Computer Journal, 2022, 65(7): 1846-1859. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxab026 [26] ZHU G B, WANG J Q, WU Y, et al. MC-HOG correlation tracking with saliency proposal[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2016, 30(1): 3690-3696. [27] FU C H, XU J T, LIN F L, et al. Object saliency-aware dual regularized correlation filter for real-time aerial tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(12): 8940-8951. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2992301 [28] HOU X D, ZHANG L Q. Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 1-8. [29] ACHANTA R, HEMAMI S, ESTRADA F, et al. Frequency-tuned salient region detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 1597-1604. [30] WANG N, ZHOU W G, SONG Y B, et al. Real-time correlation tracking via joint model compression and transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 6123-6135. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2989544 [31] CHATFIELD K, SIMONYAN K, VEDALDI A, et al. Return of the devil in the details: delving deep into convolutional nets[C]//Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham: BMVA Press, 2014: 1-11. [32] HINTON G, VINYALS O, DEAN J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network[C]//Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 10387-10396. [33] ROMERO A, BALLAS N, KAHOU S E, et al. FitNets: hints for thin deep nets[EB/OL].(2015-03-27)[2023-06-01]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6550. [34] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham: BMVA Press, 2014: 1-11. [35] LI F, TIAN C, ZUO W M, et al. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4904-4913. [36] WU Y, LIM J, YANG M H. Online object tracking: a benchmark[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2411-2418. [37] LI Y M, FU C H, DING F Q, et al. AutoTrack: towards high-performance visual tracking for UAV with automatic spatio-temporal regularization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11920-11929. [38] LI B W, FU C H, DING F Q, et al. All-day object tracking for unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(8): 4515-4529. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3162892 [39] YE J J, FU C H, LIN F L, et al. Multi-regularized correlation filter for UAV tracking and self-localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(6): 6004-6014. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3088366 [40] ZHENG G Z, FU C H, YE J J, et al. Mutation sensitive correlation filter for real-time UAV tracking with adaptive hybrid label[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 503-509. [41] DAI K N, WANG D, LU H C, et al. Visual tracking via adaptive spatially-regularized correlation filters[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4665-4674. [42] FU C H, JIN J, DING F Q, et al. Spatial reliability enhanced correlation filter: an efficient approach for real-time UAV tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 26: 4123-4137. [43] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, GOLODETZ S, et al. Staple: complementary learners for real-time tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1401-1409. [44] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Discriminative scale space tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1561-1575. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2609928 [45] LI Y, ZHU J. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 254-265. -






 下载:
下载: