Optimal dynamic response exploration for SIMO Buck converter based on differential evolution algorithm
-
摘要:
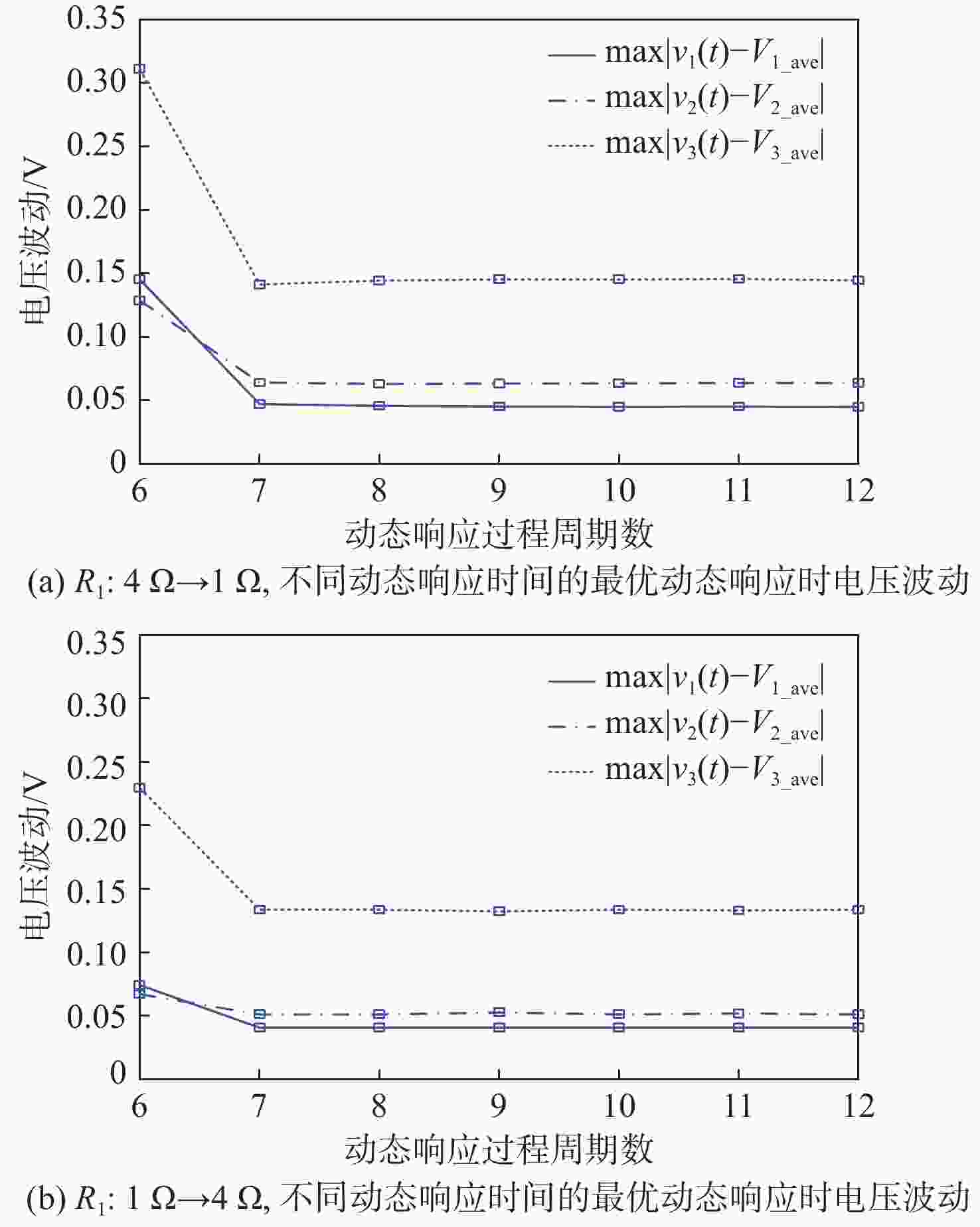
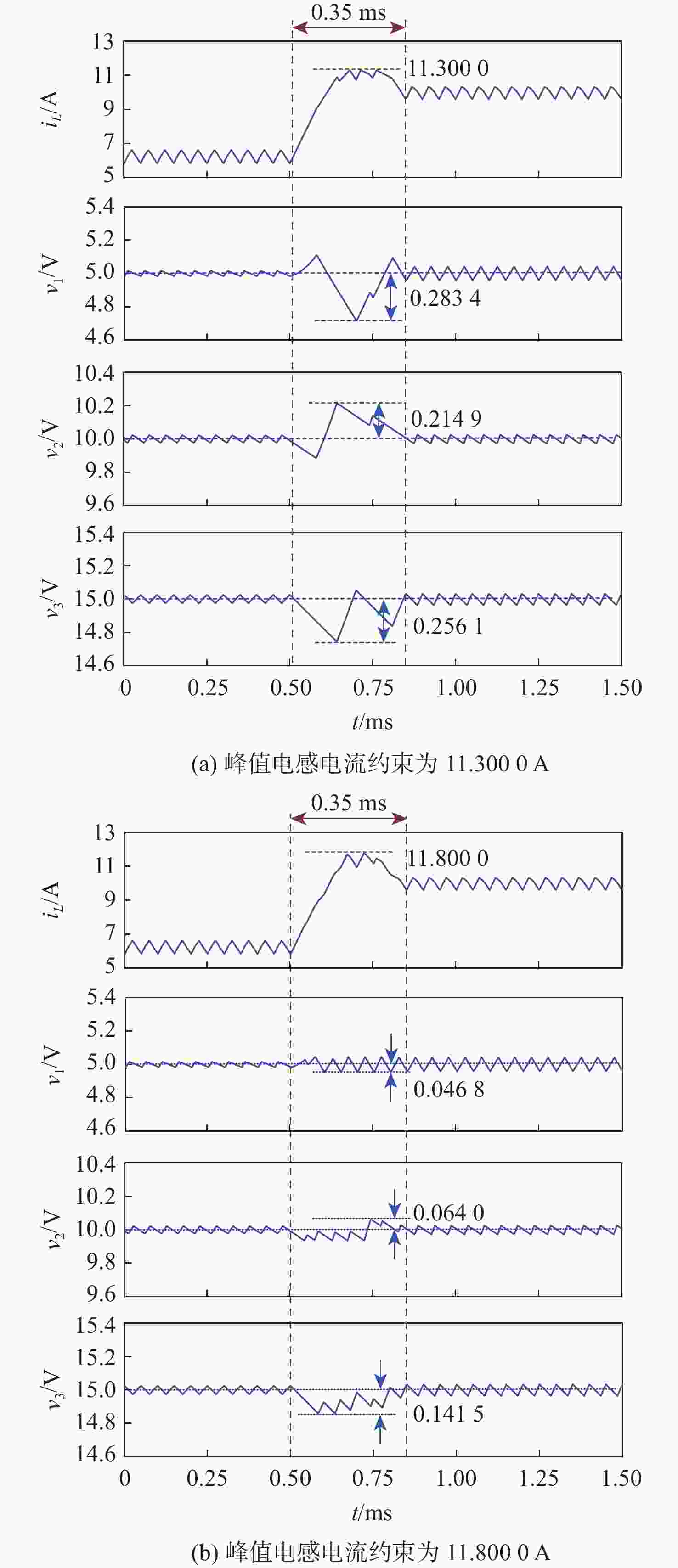
随着单电感多输出(SIMO)直流变换器的广泛应用,其动态响应问题备受关注。为探究SIMO Buck变换器最优动态响应的理论极限,根据变换器工作原理建立数学模型,利用改进的差分进化(DE)算法进行搜索求解。所提方法可以搜索求解出不同目标下的变换器最优动态响应要求,如最优的自调节或交叉调节,还可以获得不同约束下的最优动态响应,如不同的动态响应时间、峰值电感电流。基于启发式DE算法的最优动态响应理论极限搜索,有助于全面了解SIMO直流变换器的动态性能,并指导控制器设计以优化动态响应过程。
-
关键词:
- 单电感多输出直流变换器 /
- 动态响应 /
- 差分进化算法 /
- 自调节 /
- 交叉调节
Abstract:With the widespread application of single-inductor multiple-output (SIMO) DC-DC converters, their dynamic response has much concern for domestic and foreign researchers. To explore the theoretical limit of the optimal dynamic response for the SIMO Buck converter, this paper first establishes a corresponding mathematical model according to the working principle of the converter, and then an improved differential evolution (DE) algorithm is employed to search out the solution. In addition, the suggested approach can investigate the best dynamic response with various goals, including the best self-regulation or cross-regulation. It is also possible to know the optimal dynamic response with different constraints, such as different dynamic response times and peak inductor currents. In order to completely recognize the dynamic performance of SIMO DC-DC converters, the theoretical limit exploration of optimal dynamic response based on the heuristic DE intelligent algorithm is useful. Ideally, this will direct the controller design in order to obtain an optimized dynamic response.
-
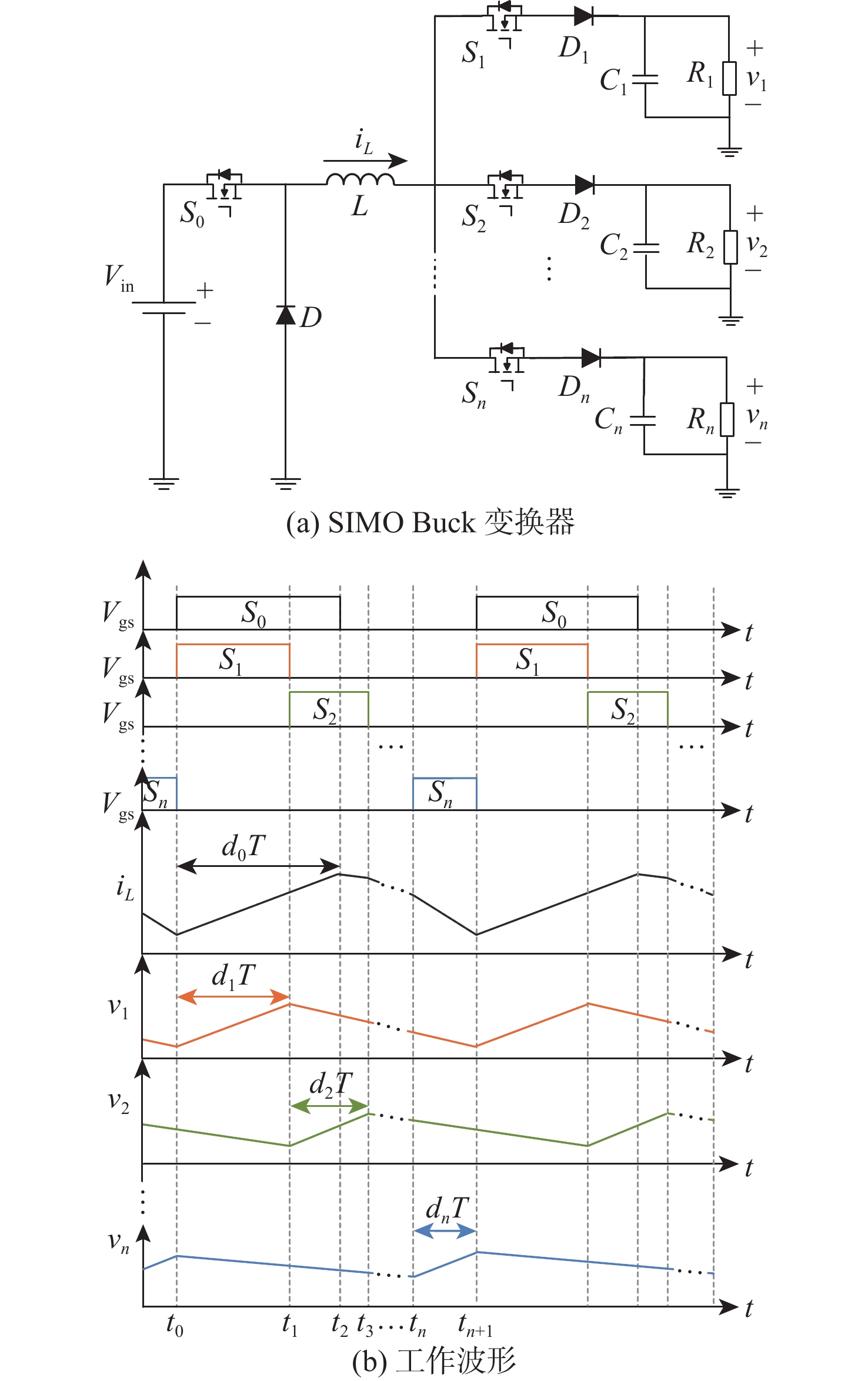
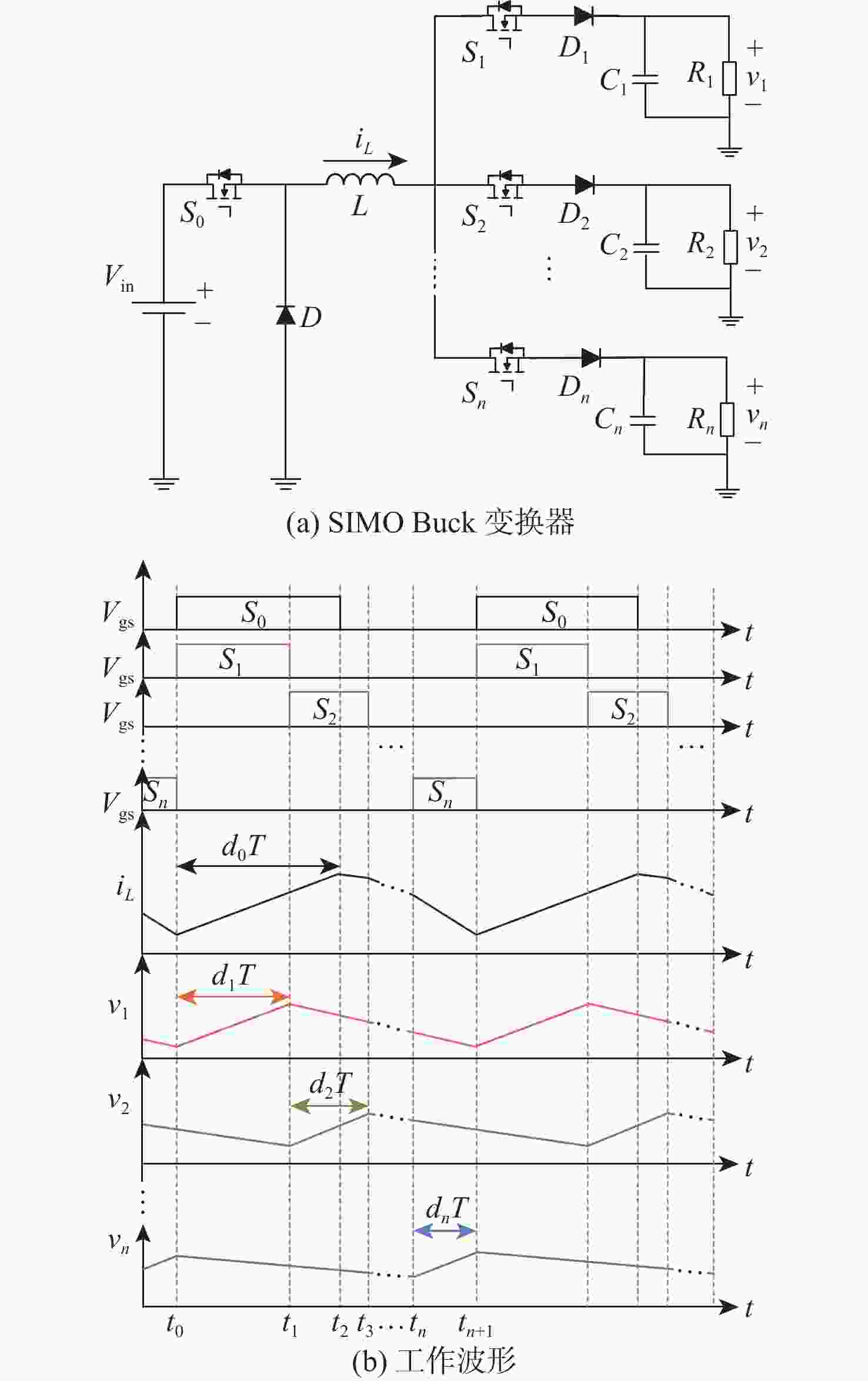
表 1 变换器电路参数
Table 1. Circuit parameters of converter
参数 数值 输入电压Vin/V 25 额定输出电压V1_ref/V 5 额定输出电压V2_ref/V 10 额定输出电压V3_ref/V 15 电感L/μH 500 电容C1,C2,C3/μF 1500 输出负载电阻R1/Ω 1 输出负载电阻R2,R3/Ω 5 表 2 动态响应时间为7个周期时实现最优动态响应的占空比
Table 2. Duty cycles to achieve the optimal dynamic response when dynamic response time is 7 periods
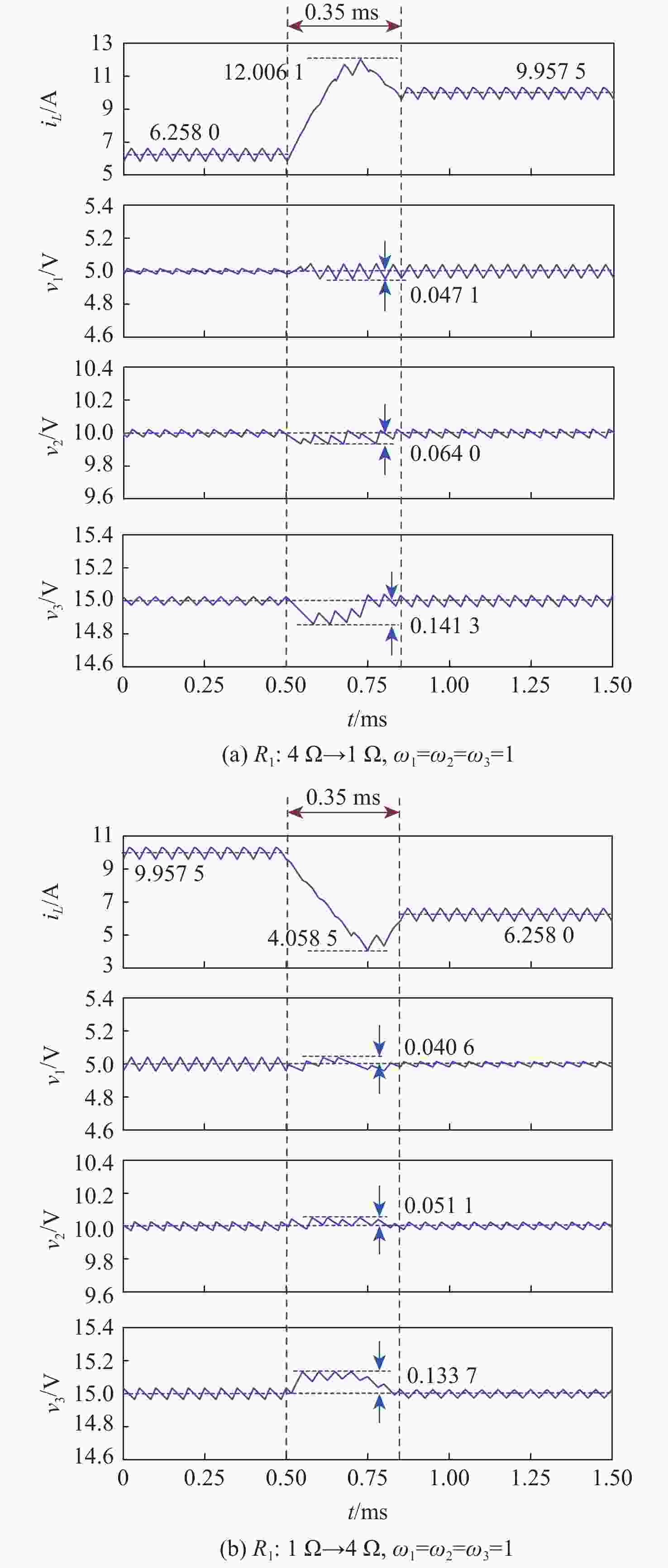
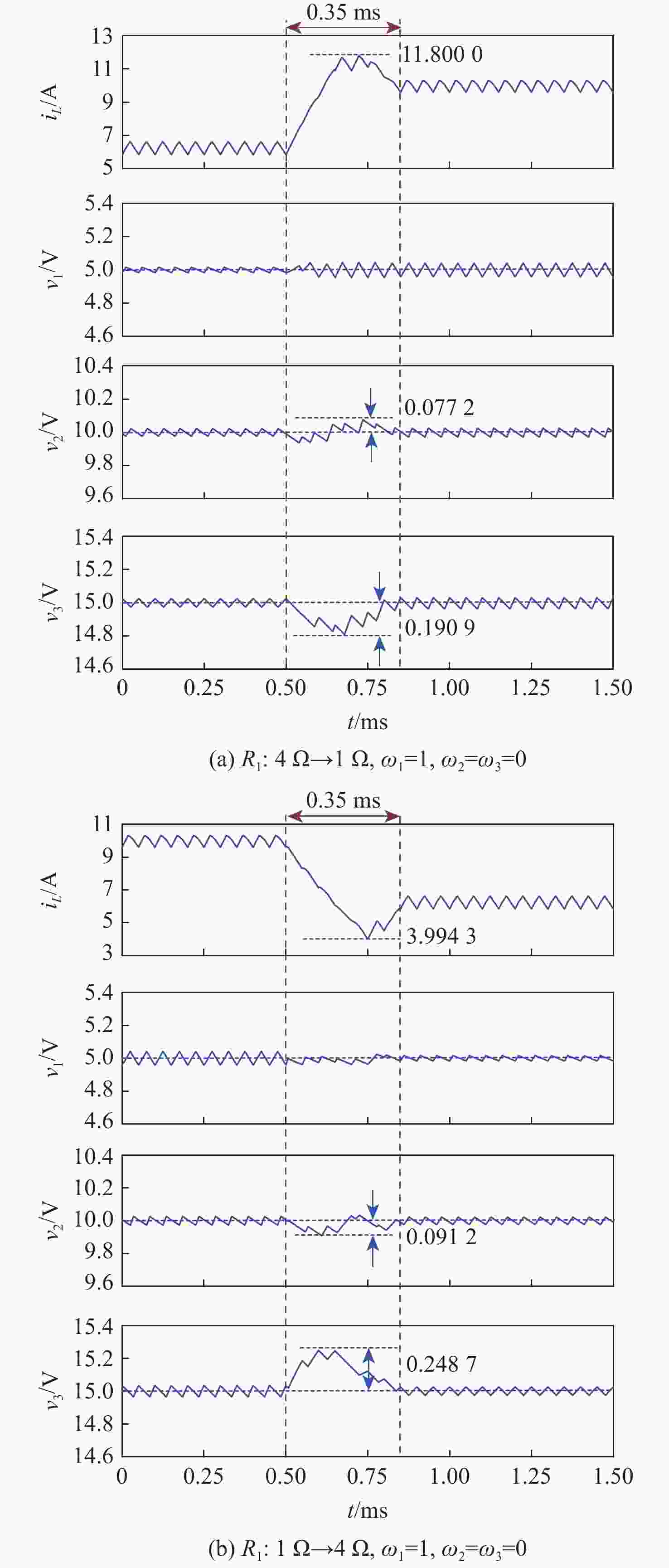
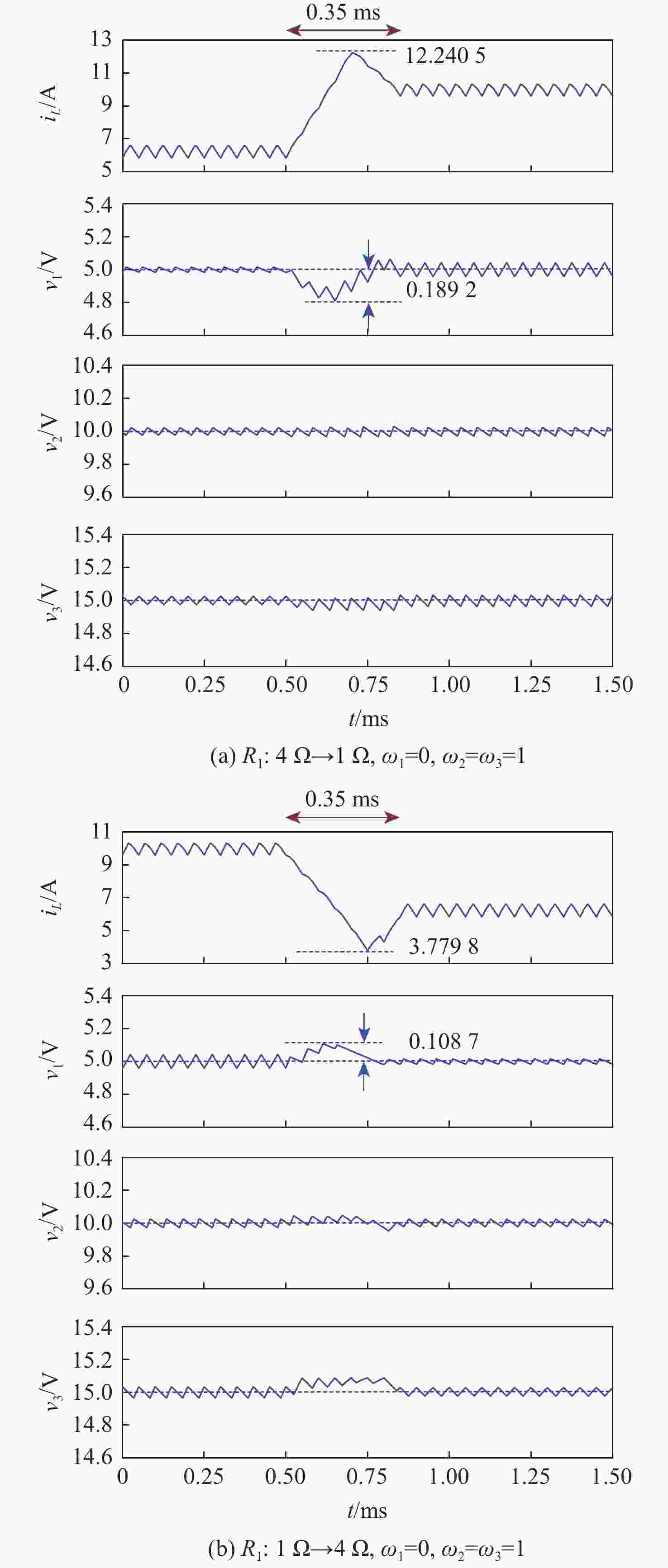
切载 开关管 占空比 T 2T 3T 4T 5T 6T 7T 4 Ω → 1 Ω S0 1.000 0.997 0.924 0.505 0.490 0.060 0.001 S1 0.827 0.438 0.509 0.448 0.435 0.444 0.496 S2 0.173 0.231 0.179 0.254 0.091 0.264 0.218 1 Ω → 4 Ω S0 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.140 0.535 0.992 S1 0.135 0.251 0.265 0.191 0.020 0.237 0.406 S2 0.188 0.348 0.269 0.248 0.504 0.401 0.240 -
[1] HUANG M H, CHEN K H. Single-inductor multi-output (SIMO) DC-DC converters with high light-load efficiency and minimized cross-regulation for portable devices[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(4): 1099-1111. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2014726 [2] XU W W, LI Y, GONG X H, et al. A single-inductor dual-output switching converter with low ripples and improved cross regulation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 303-306. [3] JING X C, MOK P K T, LEE M C. A wide-load-range single-inductor-dual-output boost regulator with minimized cross-regulation by constant-charge-auto-hopping (CCAH) control[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 299-302. [4] MA D S, KI W H, TSUI C Y, et al. Single-inductor multiple-output switching converters with time-multiplexing control in discontinuous conduction mode[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(1): 89-100. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2002.806279 [5] MA D S, KI W H, TSUI C Y. A pseudo-CCM/DCM SIMO switching converter with freewheel switching[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(6): 1007-1014. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.811976 [6] MA D S, KI W H. Fast-transient PCCM switching converter with freewheel switching control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2007, 54(9): 825-829. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2007.900903 [7] TREVISAN D, MATTAVELLI P, TENTI P. Digital control of single-inductor multiple-output step-down DC-DC converters in CCM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2008, 55(9): 3476-3483. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.921234 [8] WANG W, XU J P, WEI X J, et al. Peak inductor current and differential-mode voltage control of single-inductor dual-output buck converters in continuous conduction mode[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 495-499. [9] WANG Y, XU J P, YIN G. Cross-regulation suppression and stability analysis of capacitor current ripple controlled SIDO CCM Buck converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(3): 1770-1780. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2838103 [10] 王瑶. 电容电流-电容电压纹波控制单电感双输出CCM Buck变换器[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(10): 3280-3288.WANG Y. Capacitor current and capacitor voltage ripple controlled single-inductor dual-output CCM Buck converter[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(10): 3280-3288(in Chinese). [11] WANG Y, XU J P, ZHOU G H. A cross regulation analysis for single-inductor dual-output CCM Buck converters[J]. Journal of Power Electronics, 2016, 16(5): 1802-1812. doi: 10.6113/JPE.2016.16.5.1802 [12] PATRA P, GHOSH J, PATRA A. Control scheme for reduced cross-regulation in single-inductor multiple-output DC-DC converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 60(11): 5095-5104. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2012.2227895 [13] DASIKA J D, BAHRANI B, SAEEDIFARD M, et al. Multivariable control of single-inductor dual-output Buck converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(4): 2061-2070. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2013.2266616 [14] LE H P, CHAE C S, LEE K C, et al. A single-inductor switching DC-DC converter with five outputs and ordered power-distributive control[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(12): 2706-2714. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.908767 [15] WOO Y J, LE H P, CHO G H, et al. Load-independent control of switching DC-DC converters with freewheeling current feedback[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(12): 2798-2808. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2005709 [16] 贺素霞, 张具琴. 基于模型预测控制单电感双输出Buck变换器的仿真分析[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40(4): 558-563.HE S X, ZHANG J Q. Simulation analysis of single inductor dual output Buck converter based on model predictive control[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40(4): 558-563(in Chinese). [17] WANG B F, TAN K T, SO P L. Low cross regulation SIMO DC/DC converter with model predictive voltage control[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-5. [18] WANG B F, KANAMARLAPUDI V R K, XIAN L, et al. Model predictive voltage control for single-inductor multiple-output DC-DC converter with reduced cross regulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(7): 4187-4197. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2532846 [19] ZHANG X N, WANG B F, TAN X J, et al. Deadbeat control for single-inductor multiple-output DC-DC converter with effectively reduced cross regulation[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2020, 8(4): 3372-3381. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2019.2950247 [20] TIAN M N, GAO X B, DAI C. Differential evolution with improved individual-based parameter setting and selection strategy[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 56: 286-297. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.03.010 [21] WANG S H, LI Y Z, YANG H Y, et al. Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm with improved mutation strategy[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(10): 3433-3447. doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2588-5 [22] HOU Y, ZHAO L, LU H W. Fuzzy neural network optimization and network traffic forecasting based on improved differential evolution[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 81: 425-432. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.08.041 [23] 李笠, 李广鹏, 常亮, 等. 约束进化算法及其应用研究综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(4): 1-13.LI L, LI G P, CHANG L, et al. Survey of constrained evolutionary algorithms and their applications[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(4): 1-13(in Chinese). [24] NOMAN N, IBA H. constrained differential evolution for economic dispatch with valve-point effect[J]. International Journal of Bio-Inspired Computation, 2011, 3(6): 346. doi: 10.1504/IJBIC.2011.043607 [25] TAKAHAMA T, SAKAI S. Fast and stable constrained optimization by the ε constrained differential evolution[J]. Pacific Journal of Optimizatin, 2009, 5(2): 261-282. -






 下载:
下载: