Improved sliding-mode direct power control strategy for MMC-HVDC under asymmetrical grid state
-
摘要:
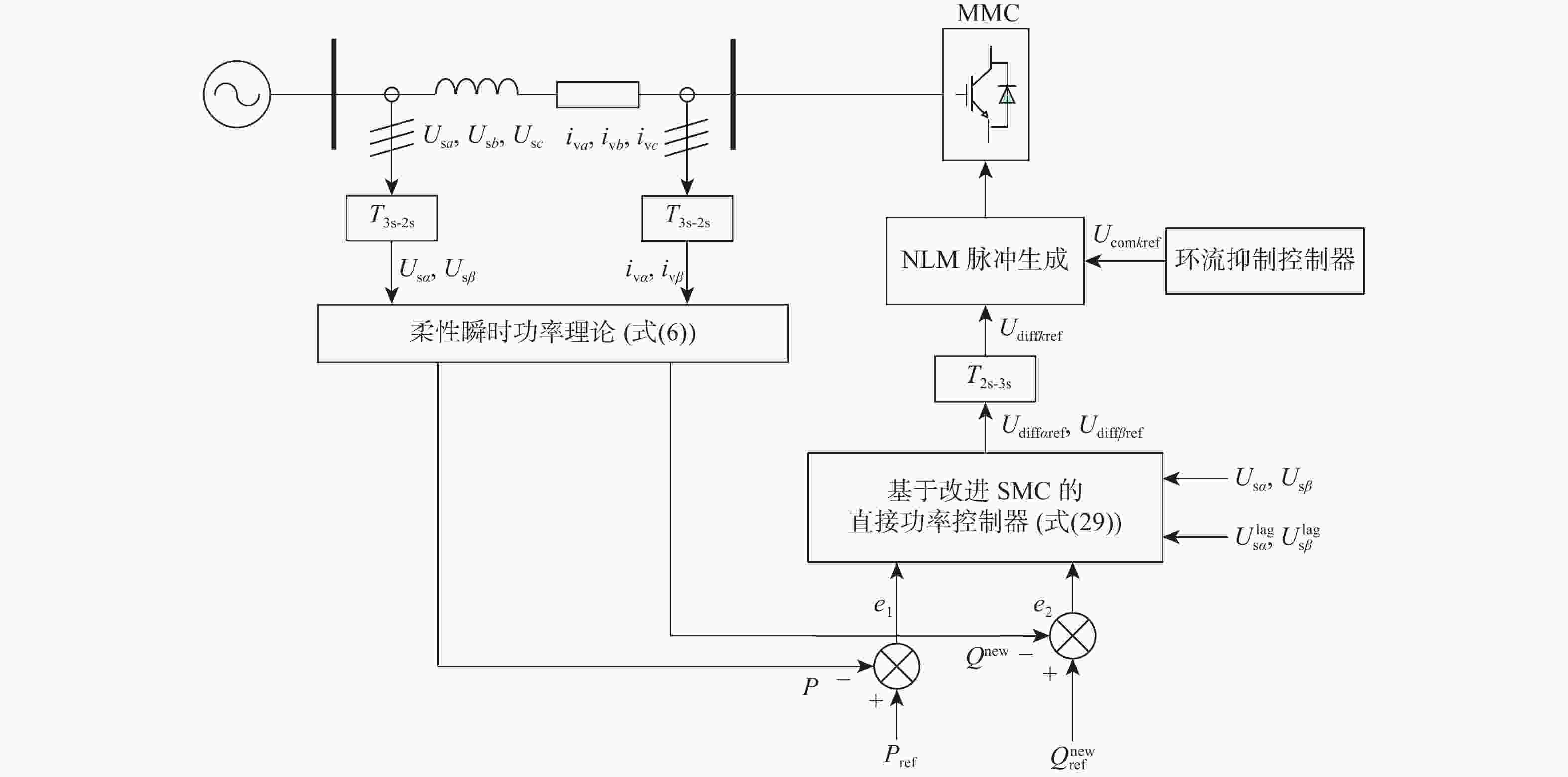
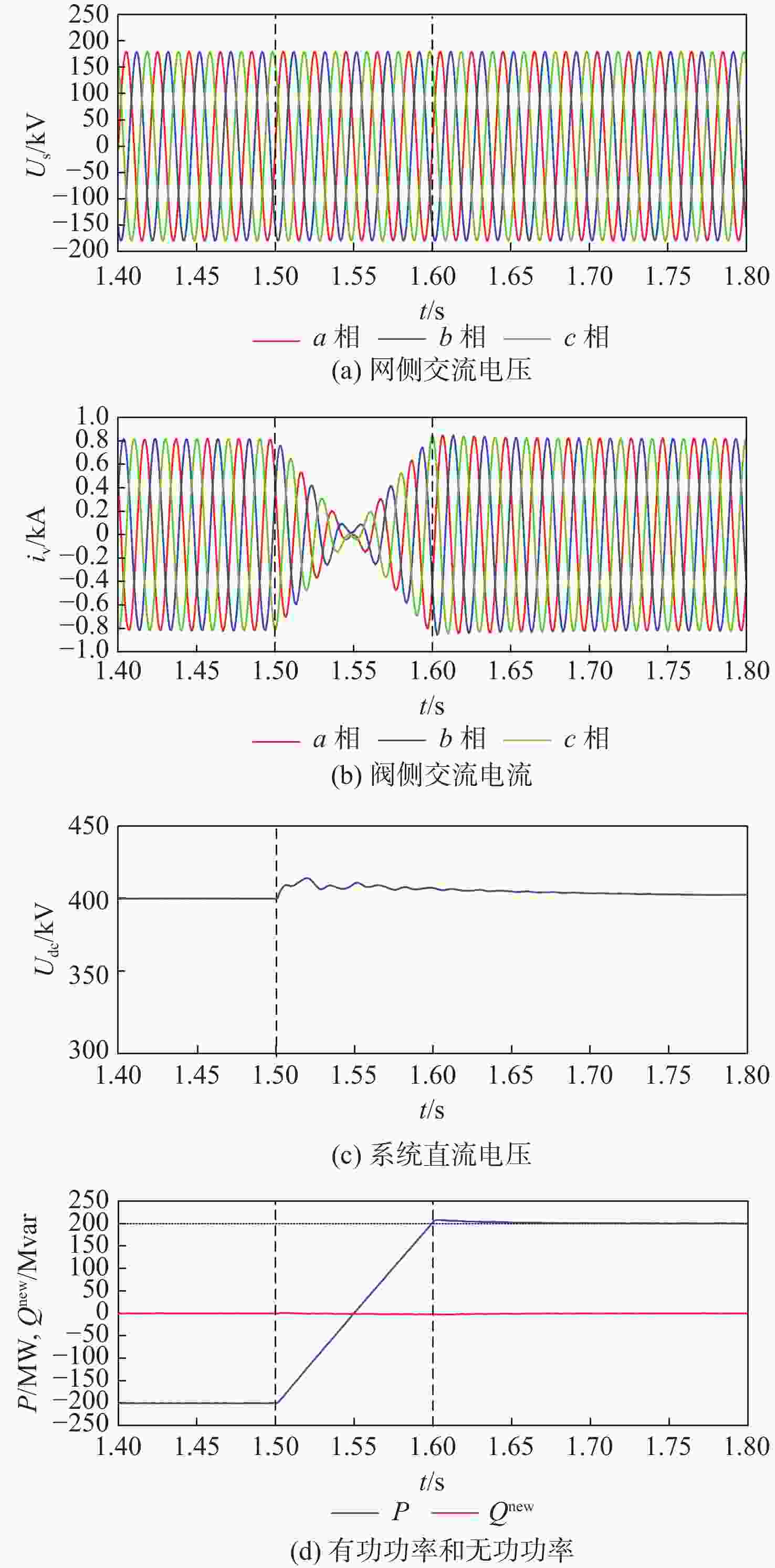
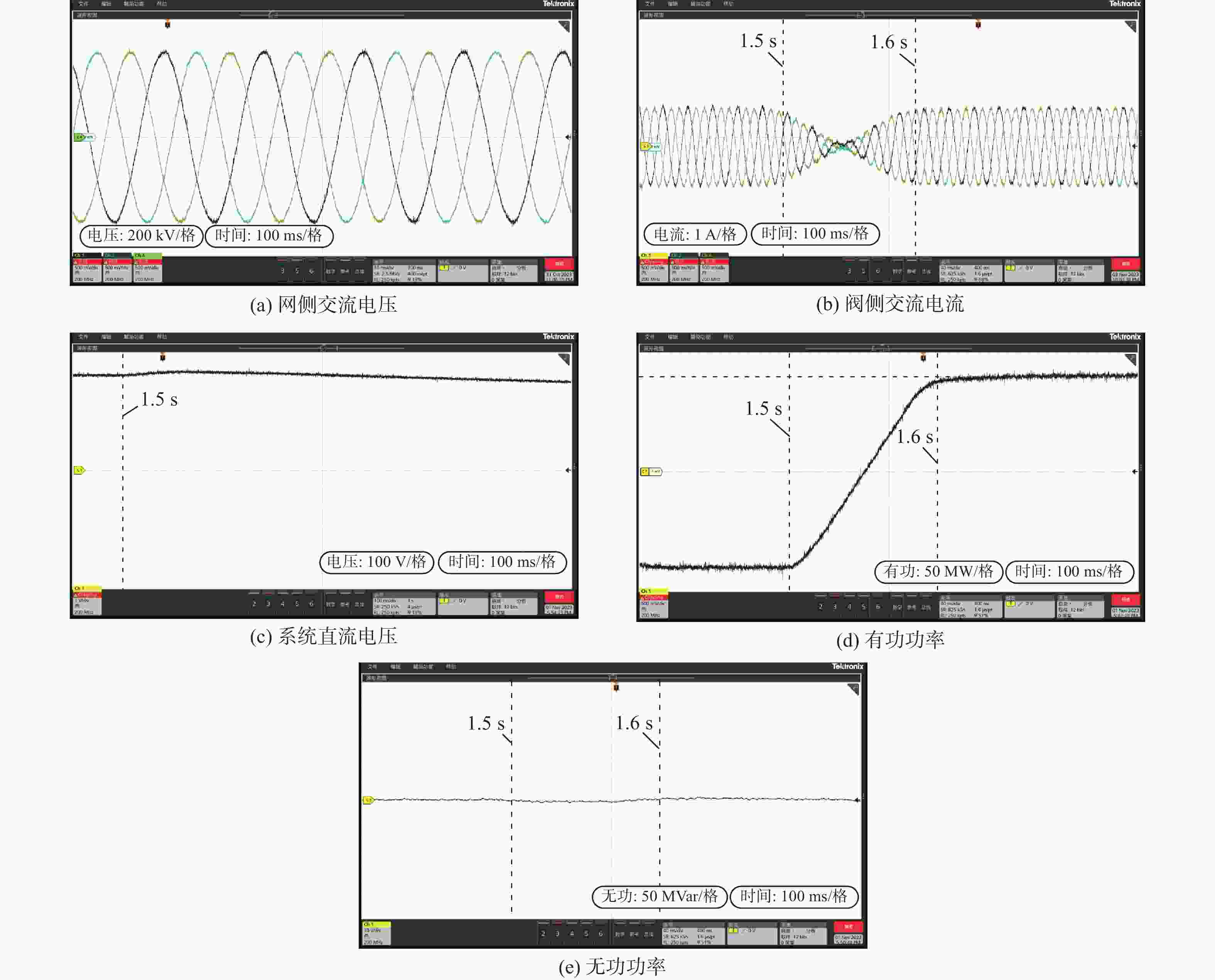
基于模块化多电平换流器的高压直流(MMC-HVDC) 输电系统是动态功率平衡系统,在非对称电网状态下,MMC的功率控制一般采用基于传统瞬时功率模型的双闭环矢量控制策略,存在控制结构复杂、控制精度低等问题。为此,引入柔性瞬时功率模型,以有功功率和柔性无功功率为控制对象建立通用功率方程,提出一种基于柔性瞬时功率模型的MMC-HVDC改进滑模直接功率控制策略。该策略结合柔性瞬时功率模型和改进滑模控制方法,消除非对称电网状态下MMC输出功率的波动分量,省略了电流内环与功率补偿项,优化了控制结构。仿真和实验结果表明:所提控制策略在非对称电网、参数摄动等运行工况下的动态响应能力、控制精度和鲁棒性更强,更能发挥出柔性瞬时功率模型的优势。
-
关键词:
- 基于模块化多电平换流器的高压直流 /
- 非对称电网 /
- 滑模控制 /
- 柔性瞬时功率模型 /
- 鲁棒控制
Abstract:The modular multilevel converter based high voltage direct current (MMC-HVDC) is a dynamic power balancing system. The control system of MMC generally adopts a dual closed-loop vector control strategy based on the traditional instantaneous power model under an asymmetric grid state, which has a complex control structure and low control accuracy. This paper introduces a flexible instantaneous power model and establishes a general power equation with active power and new reactive power as control objects. In order to eliminate the twice grid-frequency ripples in both active and reactive power under asymmetric grid states, an enhanced sliding-mode MMC-HVDC direct power control strategy based on the new instantaneous power model is proposed. This approach combines the improved sliding-mode control method with the flexible instantaneous power model. Furthermore, it omits the inner-loop controller and power compensation terms while optimizing the control structure. According to simulation results, the suggested approach can more effectively take advantage of the benefits of the flexible instantaneous power model because it has superior dynamic responsiveness, control precision, and robustness under operating conditions including asymmetric grid state and parameter perturbation.
-
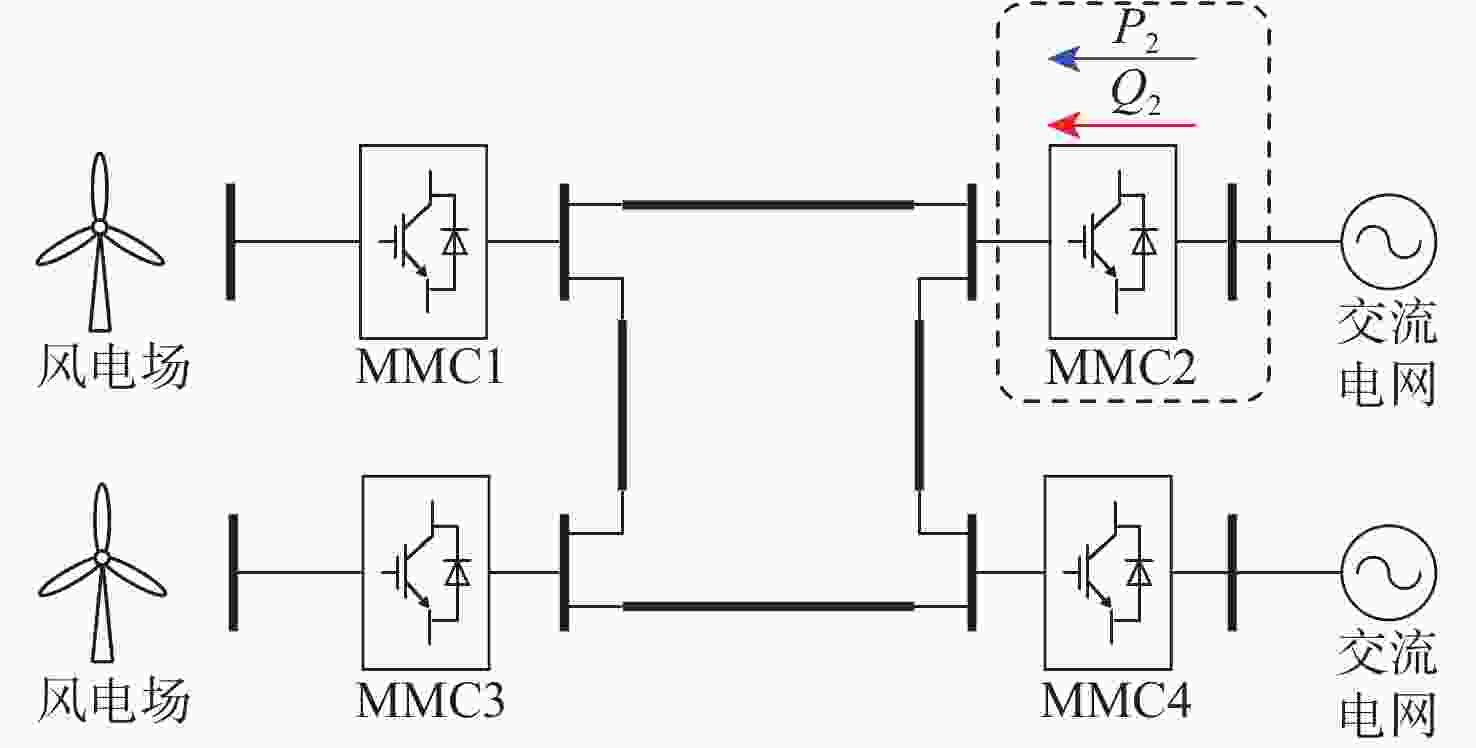
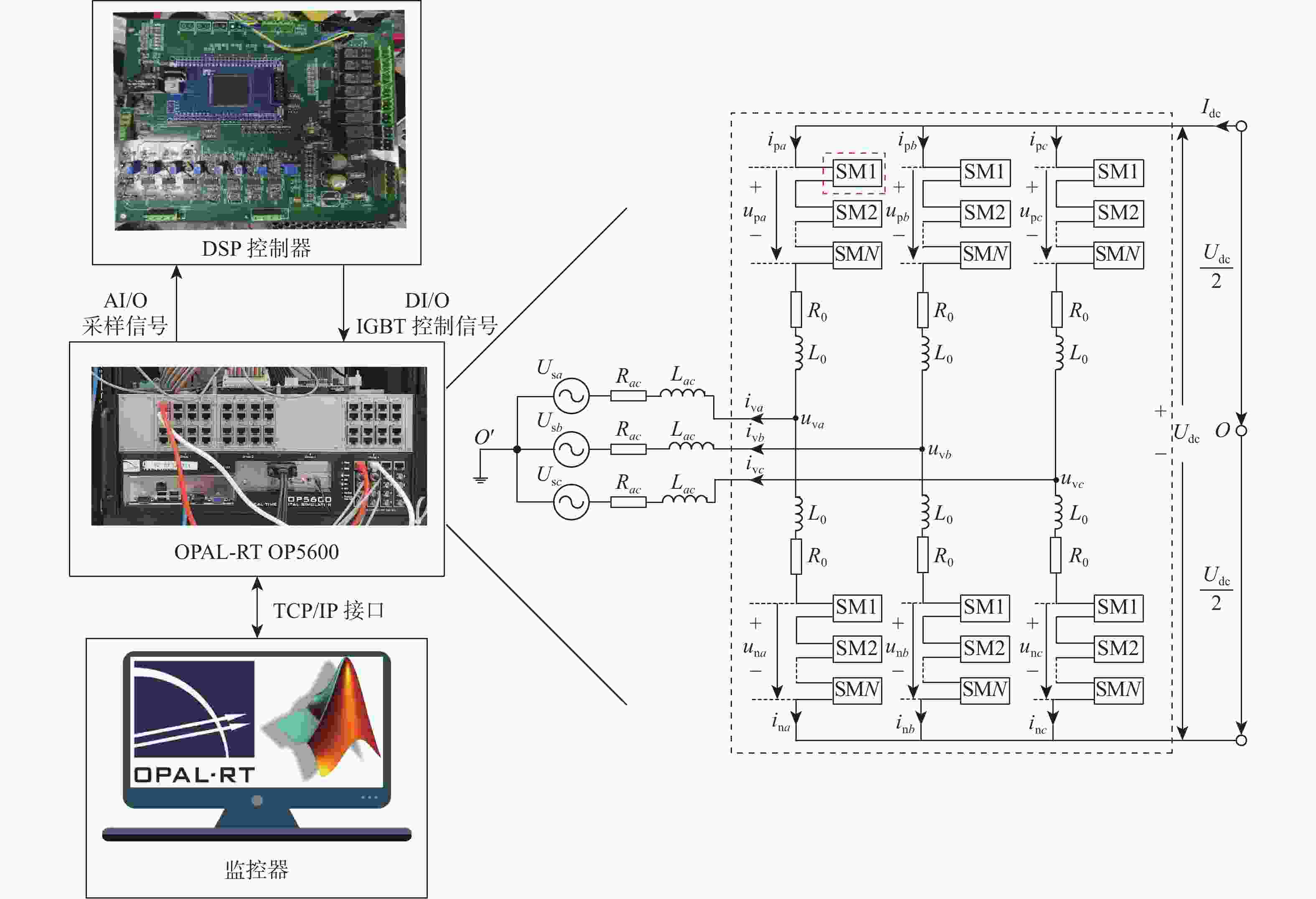
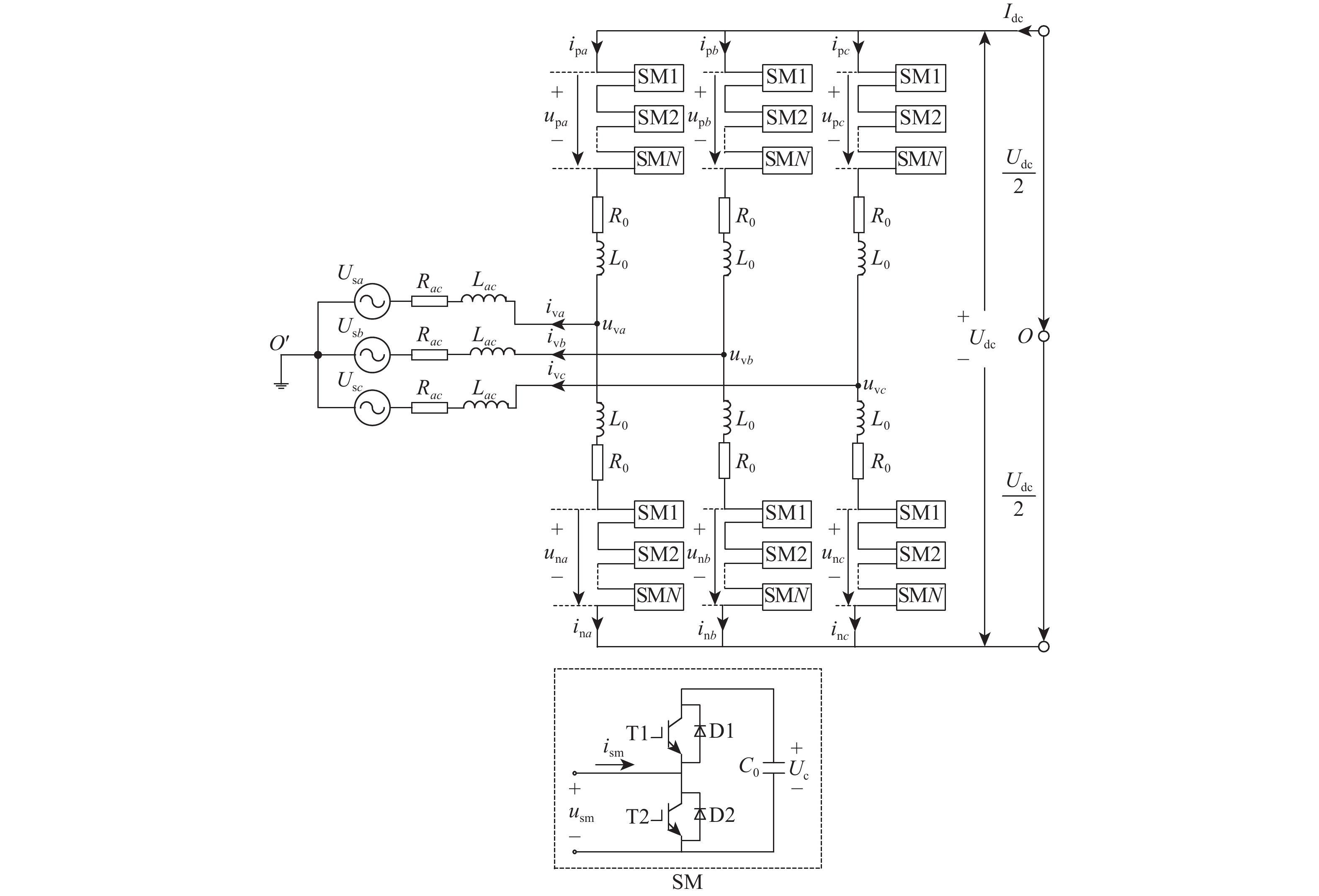
表 1 MMC2换流站参数
Table 1. Parameters of MMC2 converter station
参数 数值 系统直流电压/kV ±200 交流线电压/kV 220 子模块电容/μF 8950 桥臂电感/mH 41.5 子模块数量/个 120 -
[1] MUTHAVARAPU A K, BISWAS J, BARAI M. An efficient sorting algorithm for capacitor voltage balance of modular multilevel converter with space vector pulsewidth modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(8): 9254-9265. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2022.3160665 [2] RAJU M N, SREEDEVI J, MANDI R P, et al. Modular multilevel converters technology: a comprehensive study on its topologies, modelling, control and applications[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2019, 12(2): 149-169. doi: 10.1049/iet-pel.2018.5734 [3] MA K, HE B, XIN X K, et al. Capacitor voltage control for mission profile emulator of submodule in modular multilevel converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(11): 12355-12364. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2021.3082156 [4] NAMI A, LIANG J Q, DIJKHUIZEN F, et al. Modular multilevel converters for HVDC applications: review on converter cells and functionalities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2015, 30(1): 18-36. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2014.2327641 [5] 管敏渊, 徐政. 模块化多电平换流器型直流输电的建模与控制[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2010, 34(19): 64-68.GUAN M Y, XU Z. Modeling and control of modular multilevel converter in HVDC transmission[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2010, 34(19): 64-68(in Chinese). [6] VASILADIOTIS M, CHERIX N, RUFER A. Accurate capacitor voltage ripple estimation and current control considerations for grid-connected modular multilevel converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(9): 4568-4579. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2013.2286293 [7] 李仪, 郭宏, 蔚永强. 永磁同步电动机大惯量负载的滑模变结构控制[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2007, 33(10): 1208-1211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2007.10.019LI Y, GUO H, YU Y Q. Sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor with great inertia load[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2007, 33(10): 1208-1211(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2007.10.019 [8] LI B, XIE Y Z, WEN W J, et al. Improved sliding-mode control for MMC in DC power system[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2020, 14(15): 3035-3042. doi: 10.1049/iet-rpg.2020.0493 [9] WANG S D, DRAGICEVIC T, GAO Y, et al. Machine learning based operating region extension of modular multilevel converters under unbalanced grid faults[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(5): 4554-4560. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2982109 [10] FREYTES J, LI J Q, DE PRÉVILLE G, et al. Grid-forming control with current limitation for MMC under unbalanced fault ride-through[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2021, 36(3): 1914-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2021.3053148 [11] 孔明, 汤广福, 贺之渊, 等. 不对称交流电网下MMC-HVDC输电系统的控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(28): 41-49.KONG M, TANG G F, HE Z Y, et al. A control strategy for modular multilevel converter based HVDC of unbalanced AC systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(28): 41-49(in Chinese). [12] 陈海荣, 徐政. 基于同步坐标变换的VSC-HVDC暂态模型及其控制器[J]. 电工技术学报, 2007, 22(2): 121-126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6753.2007.02.021CHEN H R, XU Z. Transient model and controller design for VSC-HVDC based on synchronous reference frame[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2007, 22(2): 121-126(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6753.2007.02.021 [13] 张建坡, 赵成勇, 敬华兵. 比例谐振控制器在MMC-HVDC控制中的仿真研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(21): 53-62.ZHANG J P, ZHAO C Y, JING H B. Simulating research of proportional resonant controllers in MMC-HVDC[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(21): 53-62(in Chinese). [14] SHANG L, SUN D, HU J. Sliding-mode-based direct power control of grid-connected voltage-sourced inverters under unbalanced network conditions[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2011, 4(5): 570-579. doi: 10.1049/iet-pel.2010.0160 [15] 年珩, 程鹏. 电网电压不平衡时PWM整流器的谐振直接功率控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2013, 28(11): 86-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2013.11.012NIAN H, CHENG P. Resonant based direct power control strategy for PWM rectifier under unbalanced grid voltage condition[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2013, 28(11): 86-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2013.11.012 [16] 张迪, 魏艳君, 马利轩, 等. 不平衡电网电压下基于滑模变结构控制的双馈风电系统网侧变流器控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(10): 266-275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.10.036ZHANG D, WEI Y J, MA L X, et al. Sliding-mode control for grid-side converters of DFIG-based wind-power generation system under unbalanced grid voltage conditions[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(10): 266-275(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.10.036 [17] 梁营玉, 杨奇逊, 刘建政, 等. 电网电压不平衡时MMC-HVDC的无差拍直接功率控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(15): 15-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.15.002LIANG Y Y, YANG Q X, LIU J Z, et al. Deadbeat direct power control for MMC-HVDC under unbalanced grid voltages[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(15): 15-25(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.15.002 [18] 刘子文, 苗世洪, 范志华, 等. 不平衡电网电压下柔性直流输电系统功率滑模补偿策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33(14): 3296-3305.LIU Z W, MIAO S H, FAN Z H, et al. Power sliding mode compensation strategy of VSC-HVDC under unbalanced grid voltage[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(14): 3296-3305(in Chinese). [19] SUH Y, LIPO T A. Modeling and analysis of instantaneous active and reactive power for PWM AC/DC converter under generalized unbalanced network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2006, 21(3): 1530-1540. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2005.860274 [20] ZHANG Y C, QU C Q. Model predictive direct power control of PWM rectifiers under unbalanced network conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(7): 4011-4022. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2387796 [21] 梁营玉. 不对称电网电压下基于降阶矢量谐振器的MMC-HVDC直接功率控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(24): 7294-7303.LIANG Y Y. Direct power control strategy based on reduced order vector resonant controller for MMC-HVDC under unbalanced grid voltages[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(24): 7294-7303(in Chinese). [22] 刘勇智, 鄯成龙, 林博闻, 等. 基于自适应二阶终端滑模的 SRM 直接转矩控制[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2018, 44(10): 2043-2051.LIU Y Z, SHAN C L, LIN B W, et al. Direct torque control of switched reluctance motor based on adaptive second-order terminal sliding mode[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(10): 2043-2051(in Chinese). [23] 李慧洁, 蔡远利. 基于双幂次趋近律的滑模控制方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2016, 31(3): 498-502.LI H J, CAI Y L. Sliding mode control with double power reaching law[J]. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(3): 498-502(in Chinese). [24] 高洁, 王华宇, 徐萌. 开关磁阻电机的分数阶终端滑模控制[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2022, 26(2): 142-150.GAO J, WANG H Y, XU M. Improved terminal sliding mode control strategy of switched reluctance motors based on fractional calculus[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2022, 26(2): 142-150(in Chinese). [25] 李逃昌. 基于新型趋近律的非线性积分滑模控制方法[J]. 控制工程, 2019, 26(11): 2031-2035.LI T C. Nonlinear integral sliding mode control method based on new reaching law[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2019, 26(11): 2031-2035(in Chinese). [26] 刘金琨. 滑模变结构控制MATLAB仿真: 基本理论与设计方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019: 38-39.LIU J K. Sliding mode control design and MATLAB simulation: the basic theory and design method[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2019: 38-39(in Chinese). [27] AKAGI H, KANAZAWA Y, NABAE A. Instantaneous reactive power compensators comprising switching devices without energy storage components[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 1984, 20(3): 625-630. doi: 10.1109/TIA.1984.4504460 [28] 杨锁昌, 张宽桥, 陈鹏. 带攻击角度约束的自适应终端滑模导引律[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2016, 42(8): 1566-1574.YANG S C, ZHANG K Q, CHEN P. Adaptive terminal sliding mode guidance law with impact angle constraint[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(8): 1566-1574(in Chinese). [29] 潘菲, 朱宏玉. 航天器非奇异自适应终端滑模姿轨联合控制[J]. 北京亚洲成人在线一二三四五六区学报, 2020, 46(7): 1354-1362.PAN F, ZHU H Y. Spacecraft non-singular adaptive terminal sliding mode attitude-orbit coupling control[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(7): 1354-1362(in Chinese). [30] LU W X, OOI B T. Optimal acquisition and aggregation of offshore wind power by multiterminal voltage-source HVDC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2003, 18(1): 201-206. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2002.803826 -







 下载:
下载: