Energy influence of stages in cruise profile for near space solar powered unmanned aerial vehicles
-
摘要:
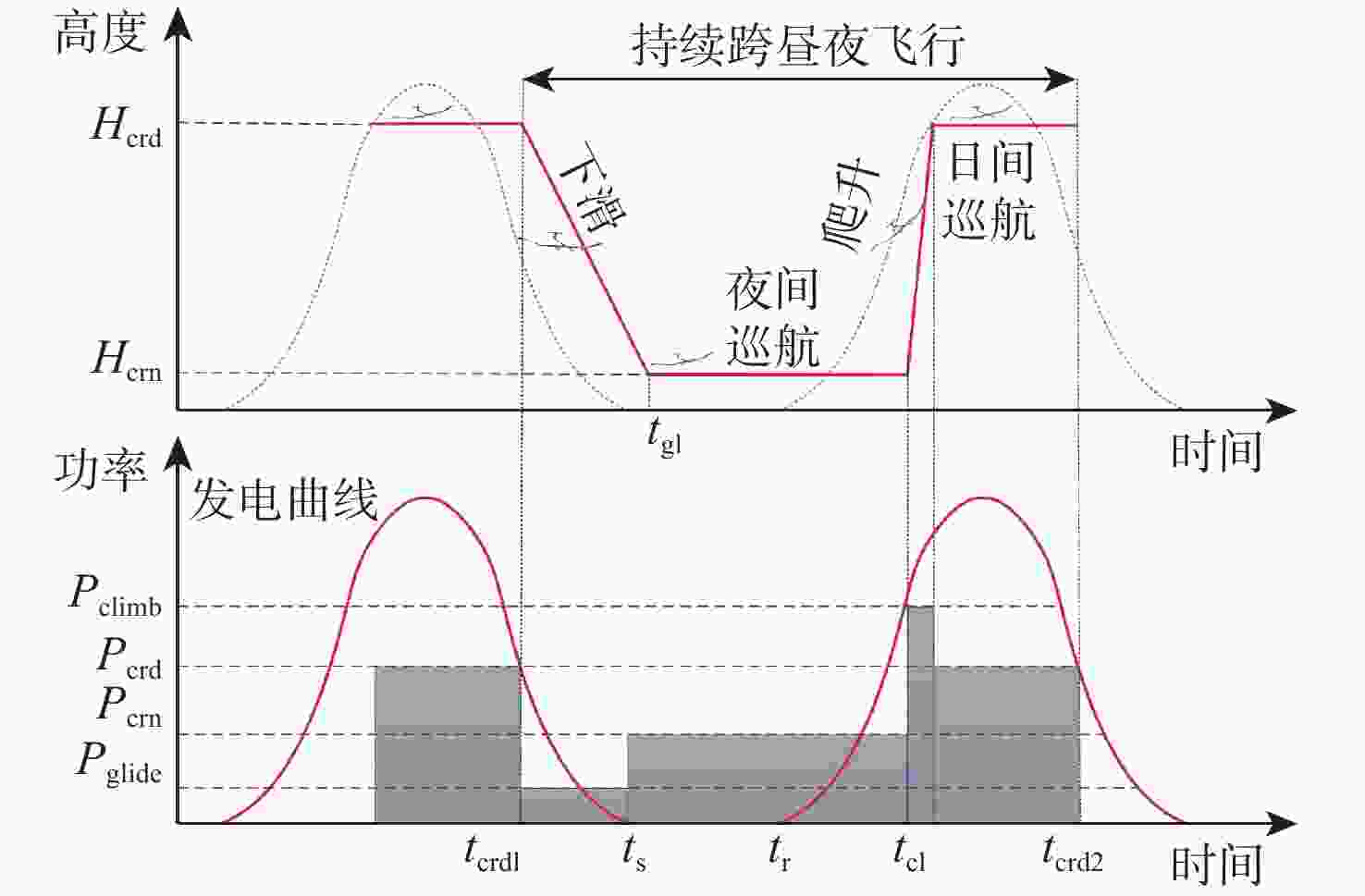
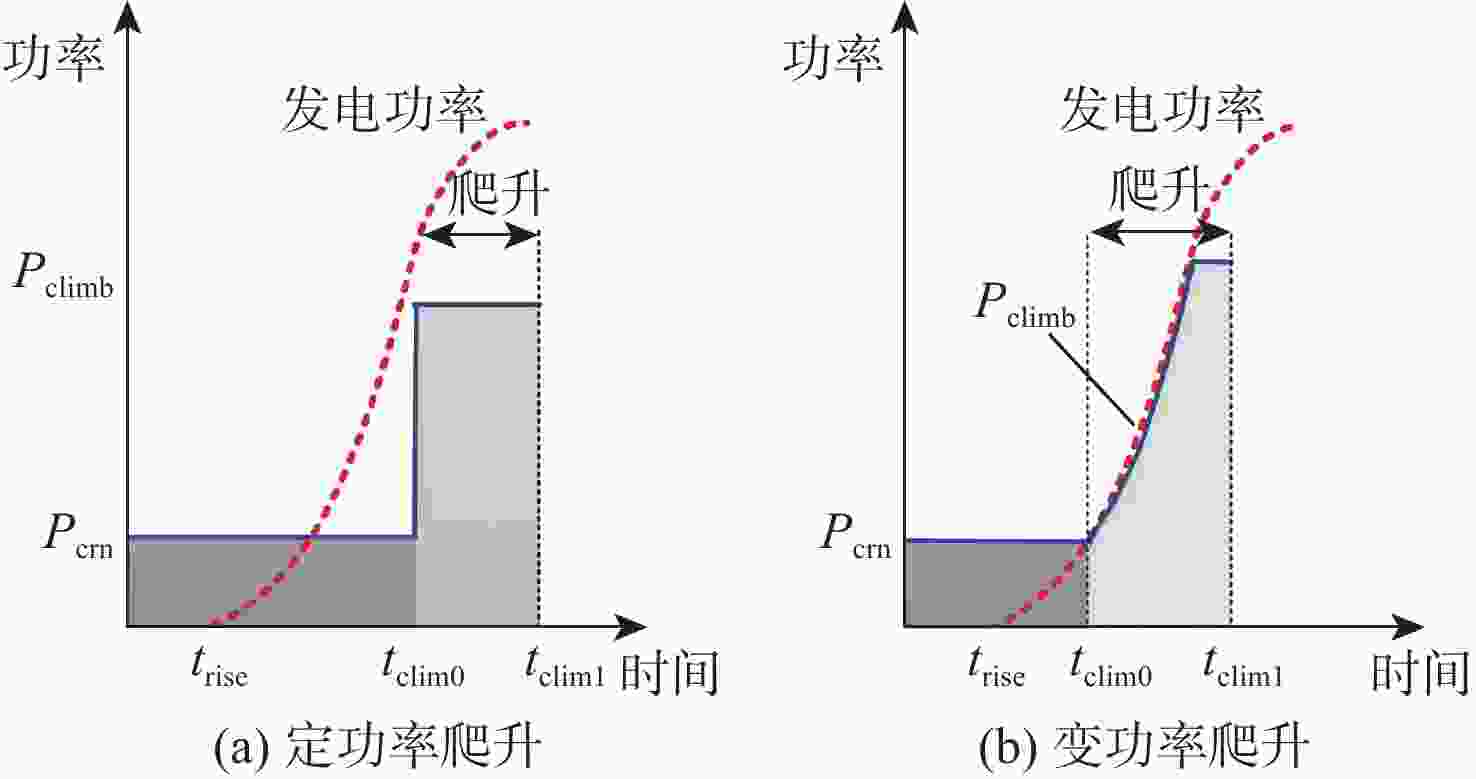
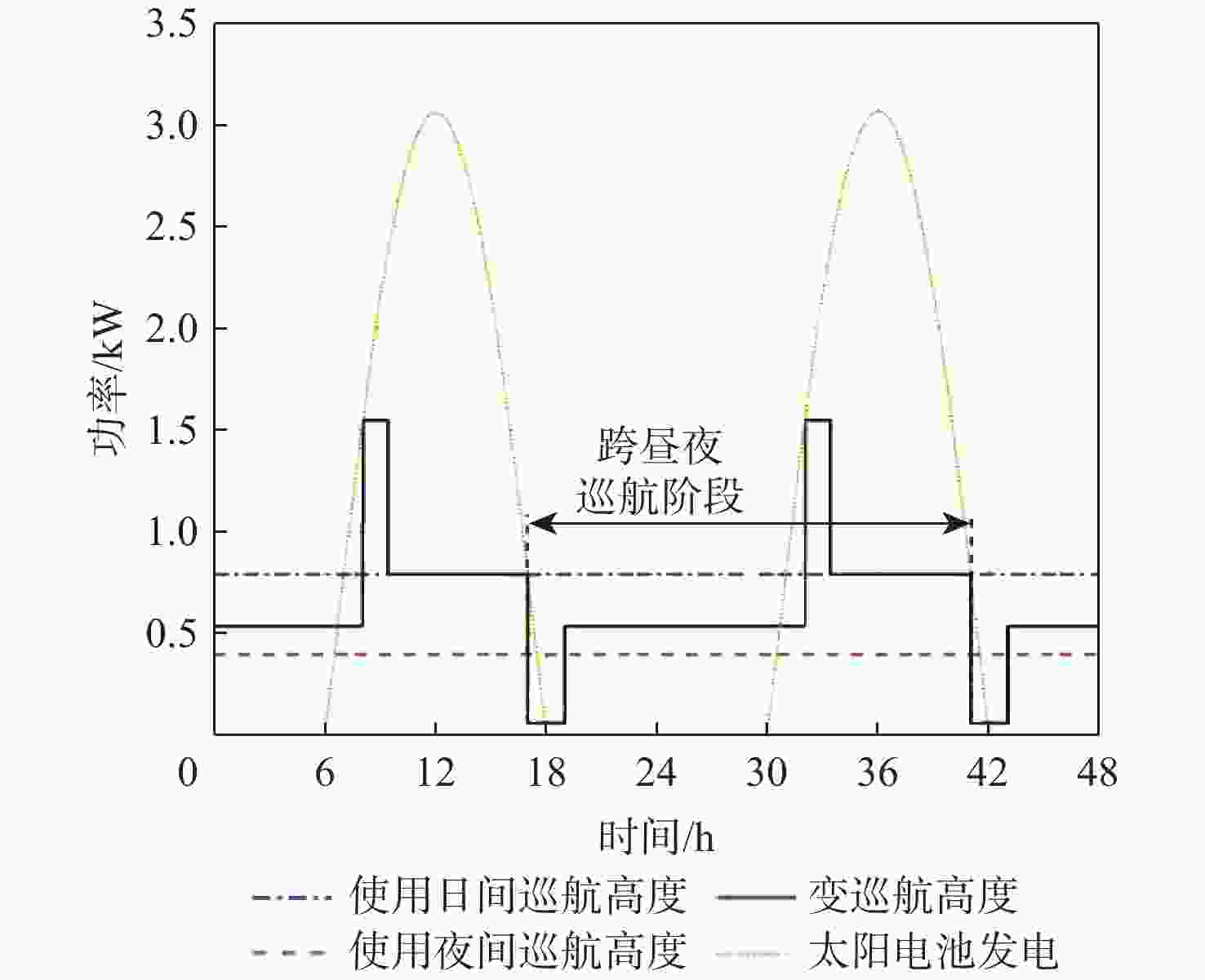
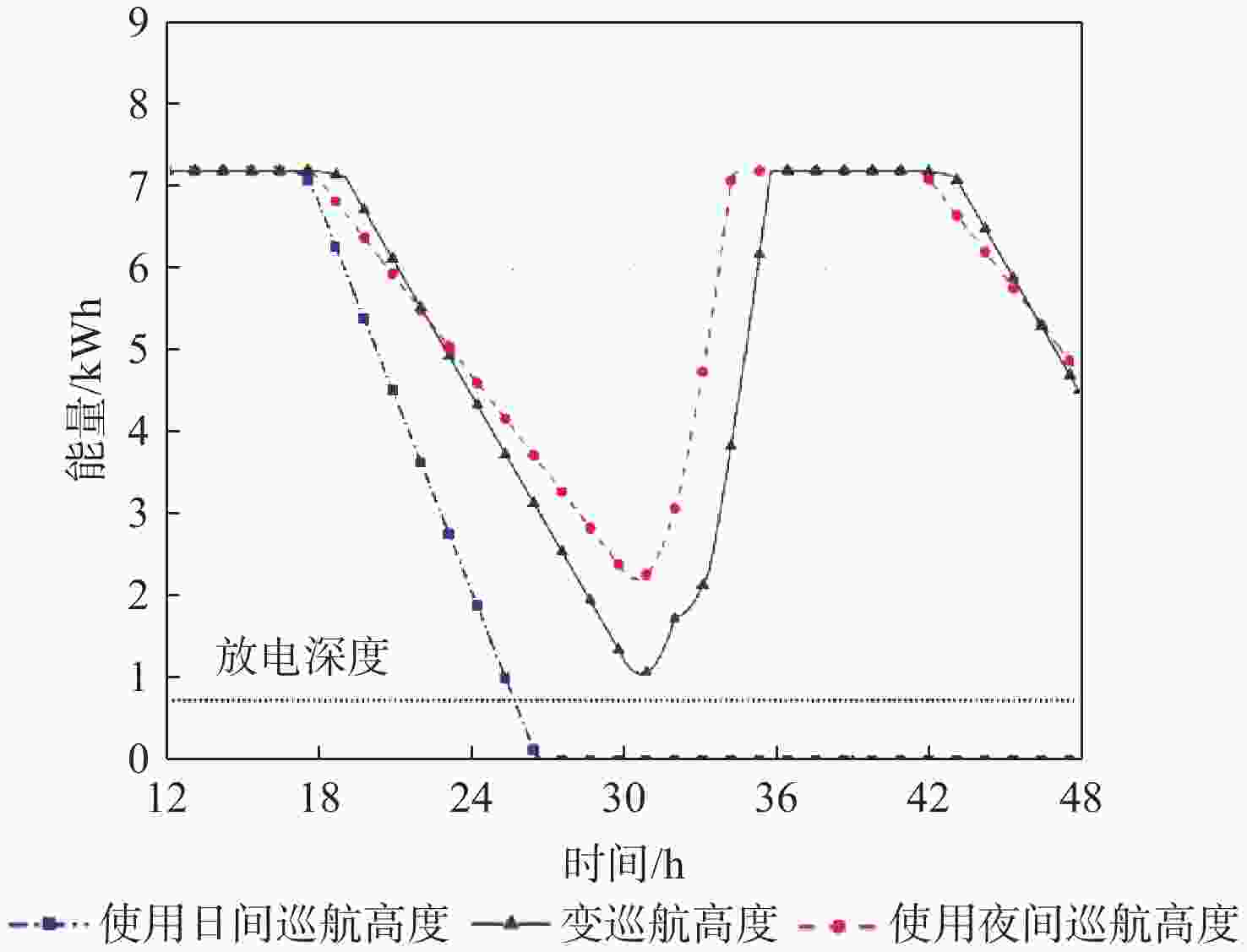
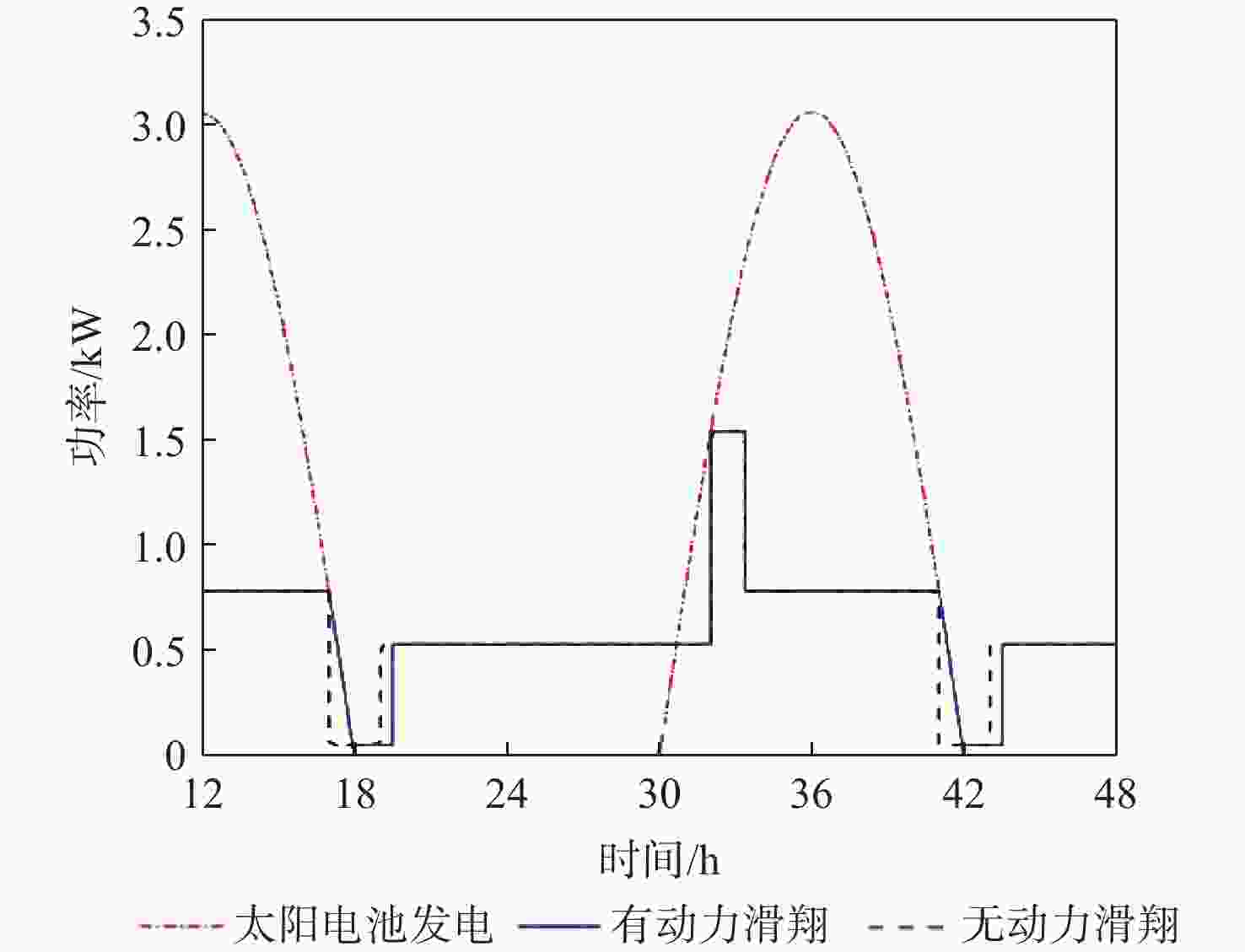
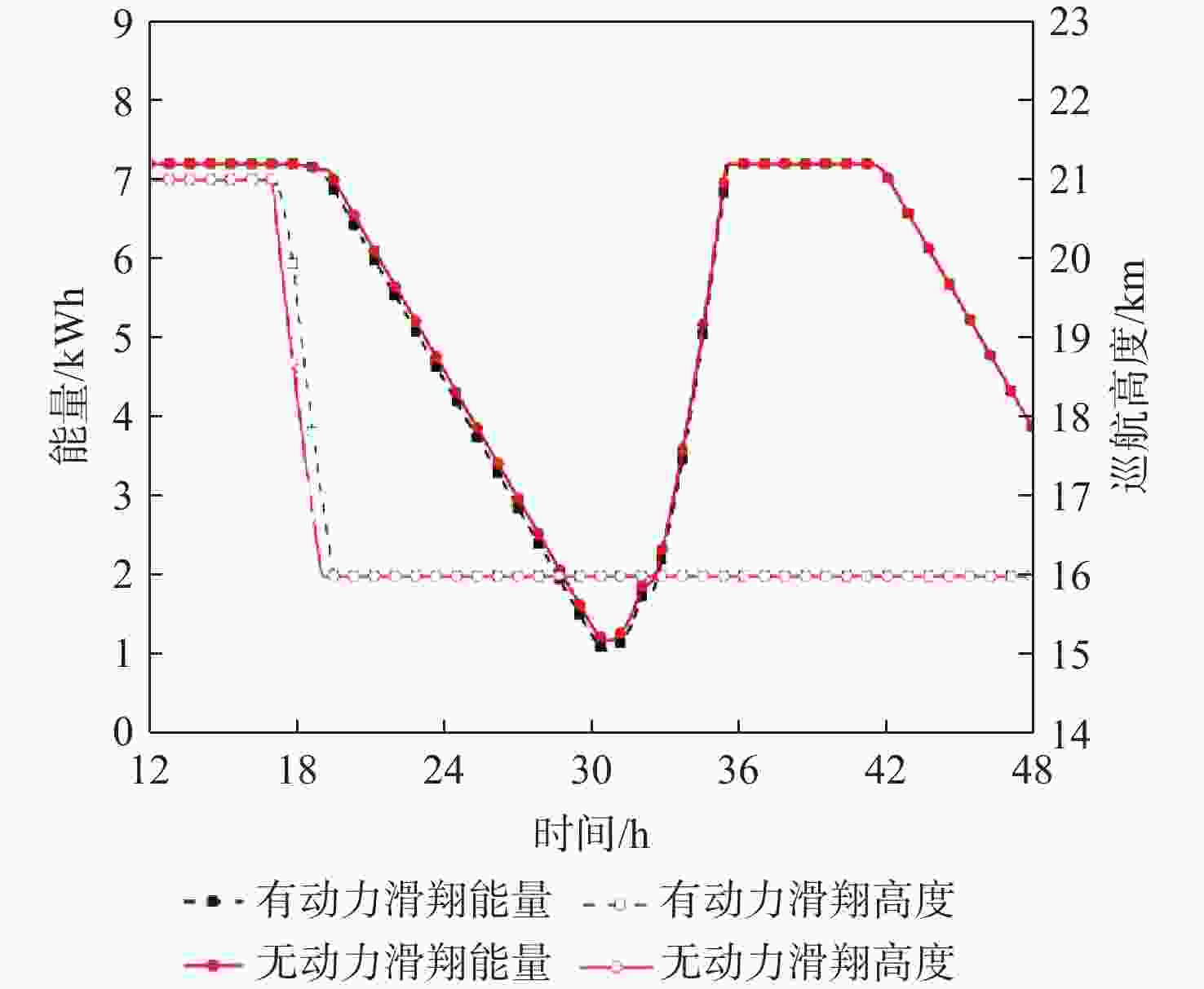
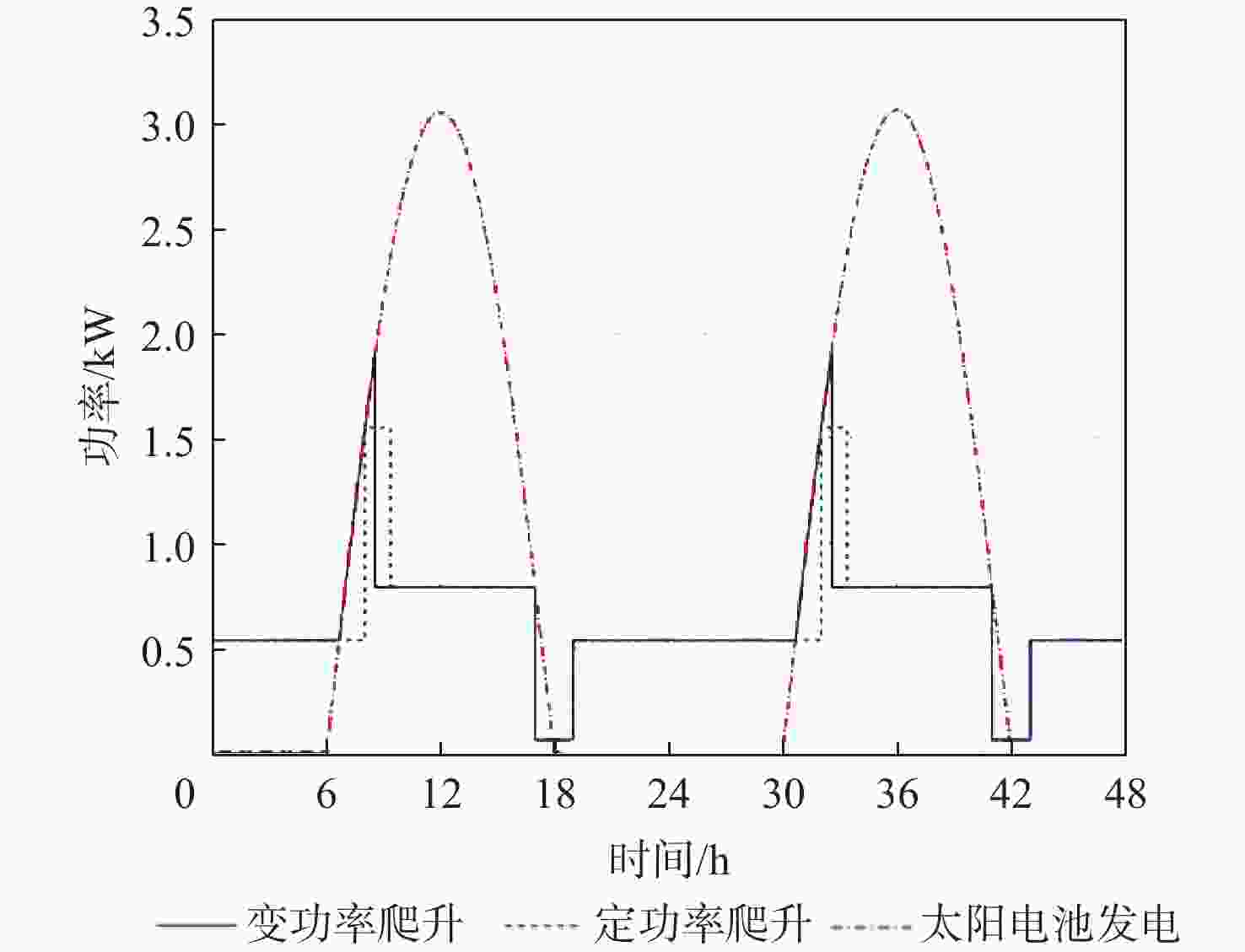
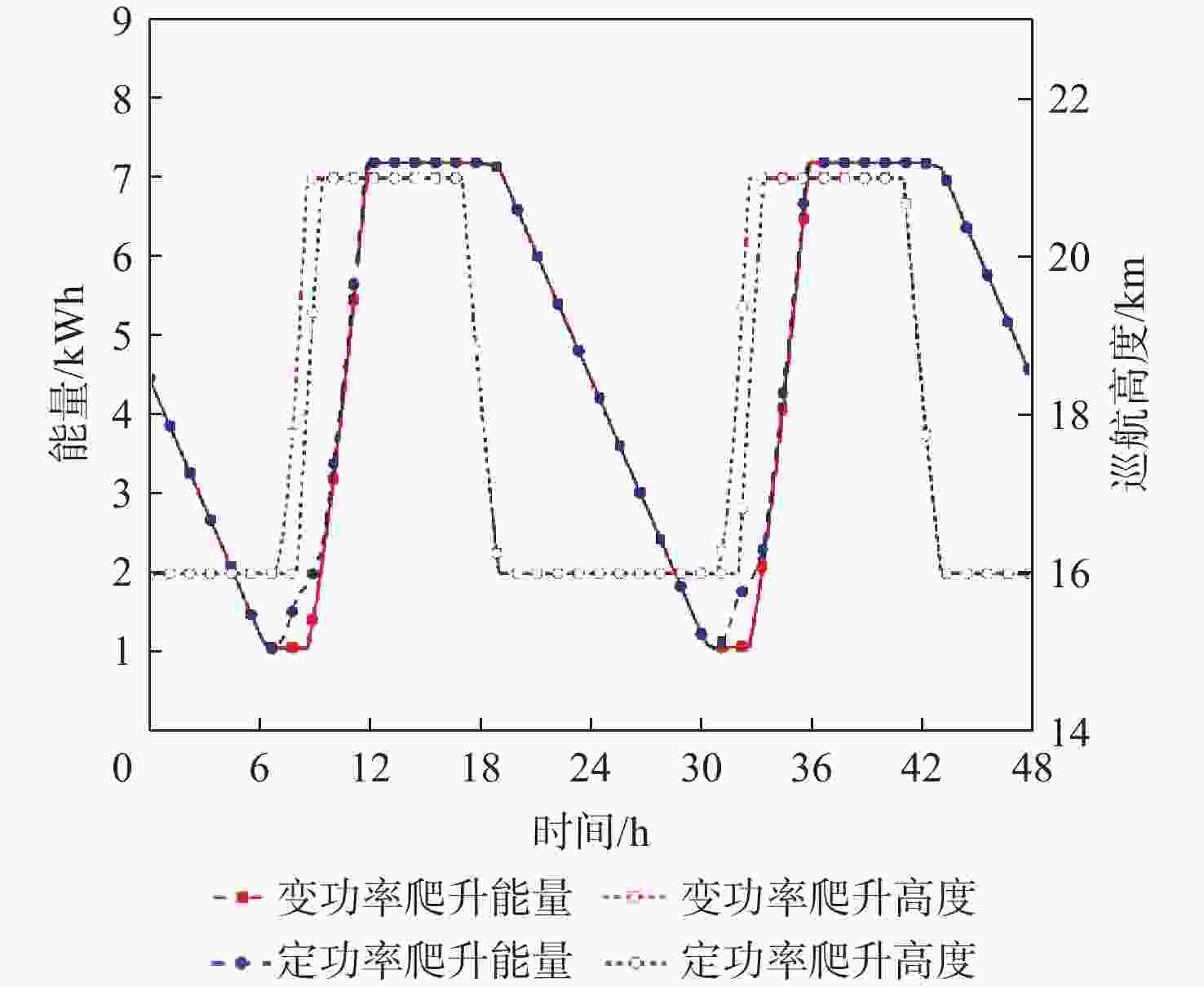
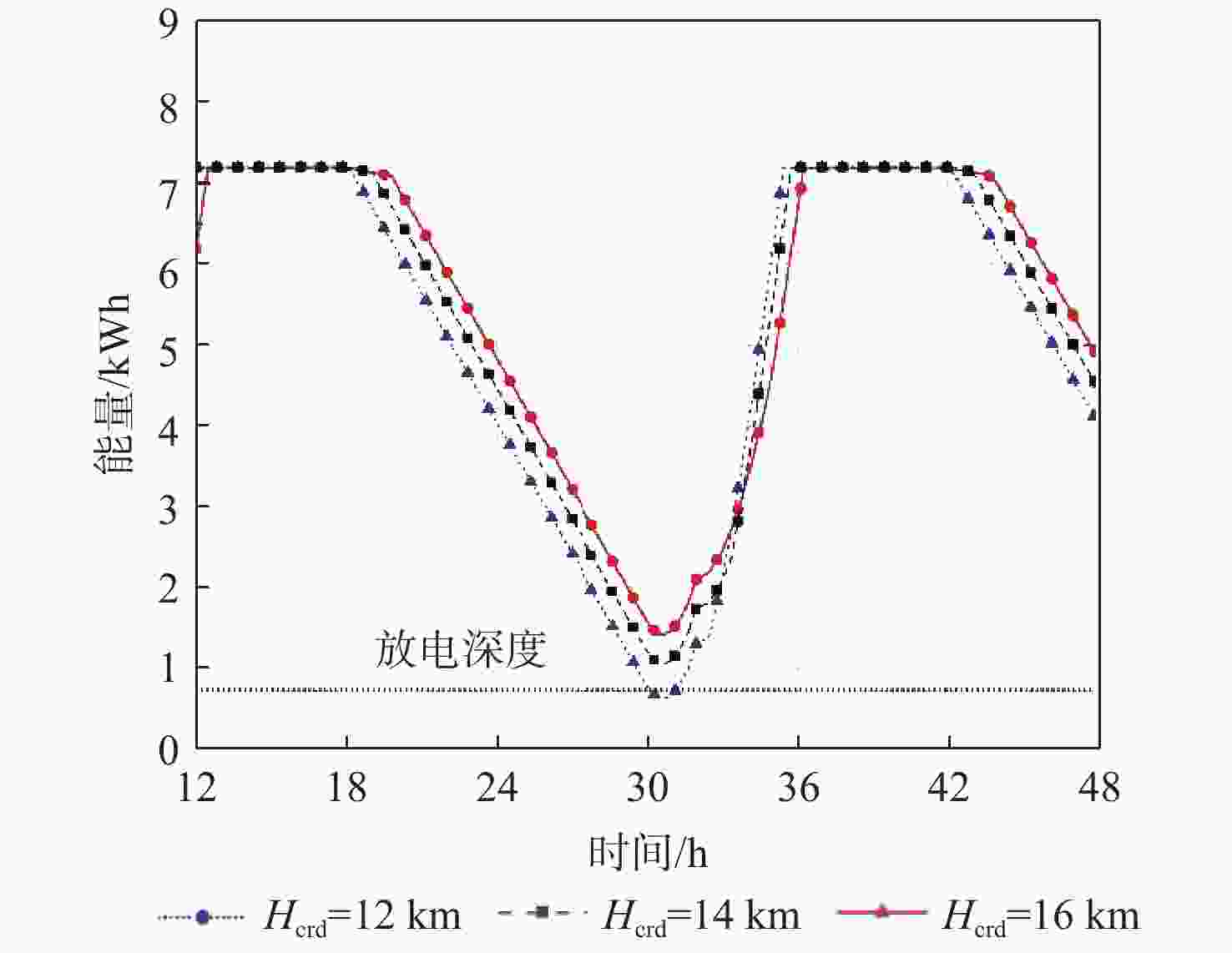
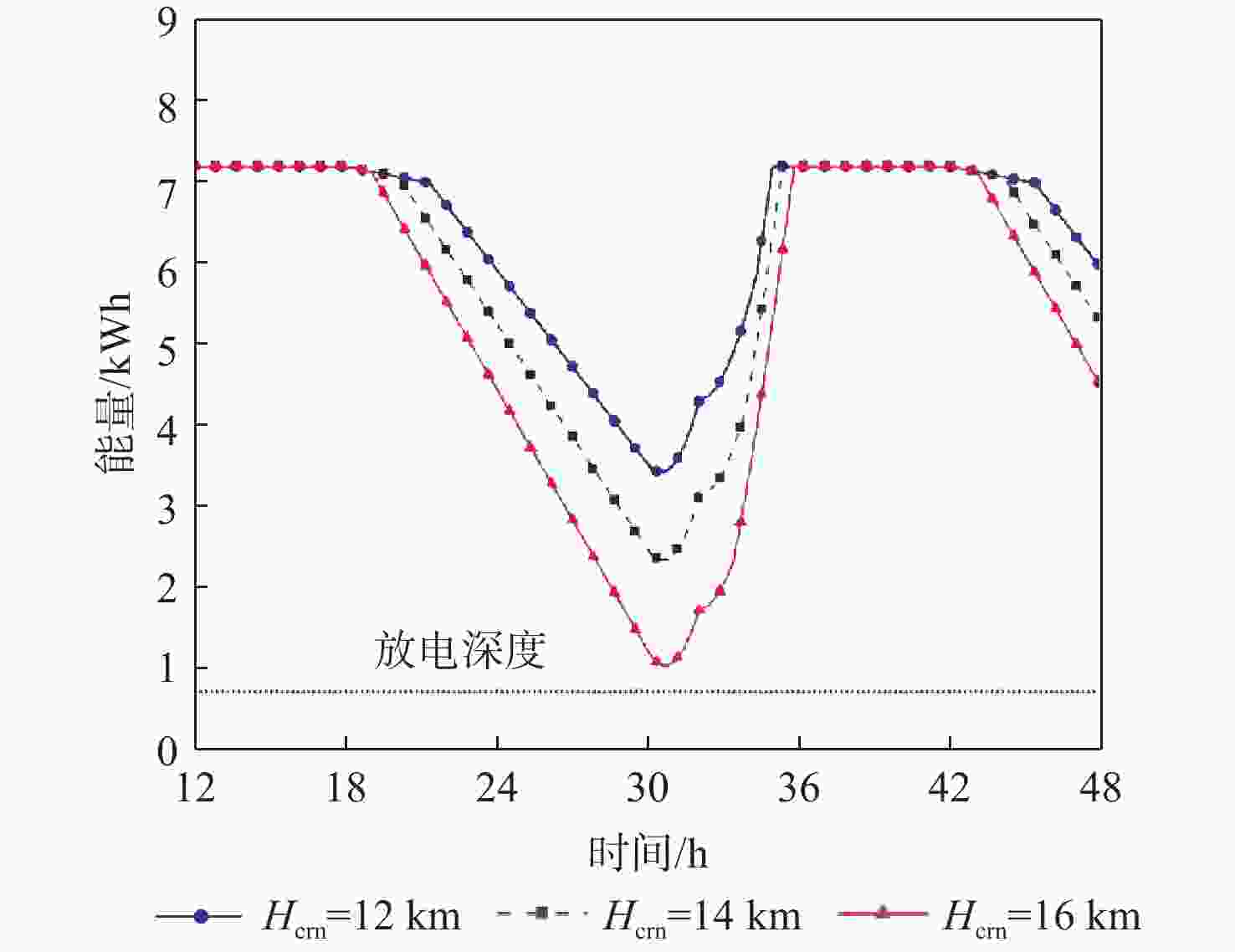
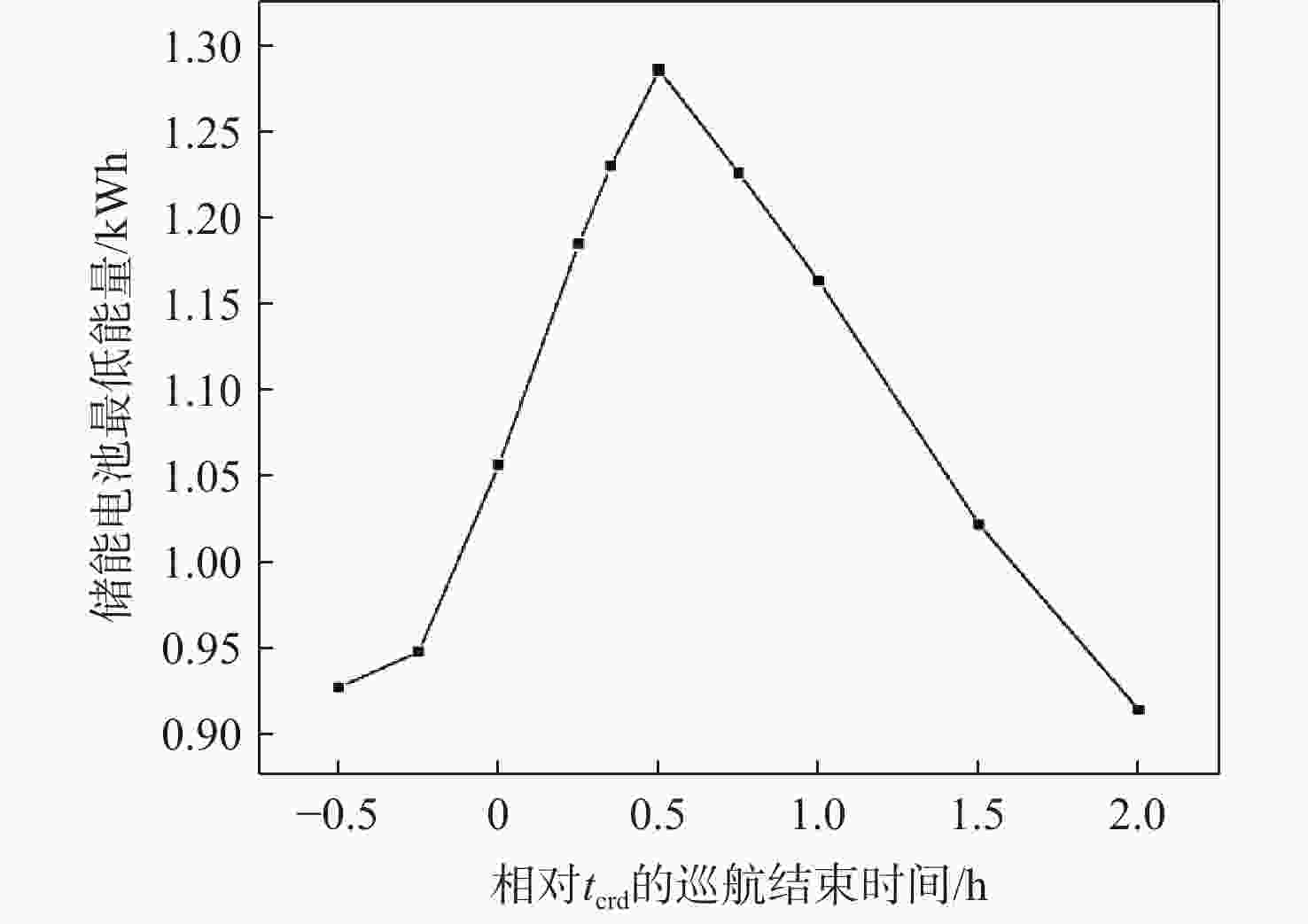
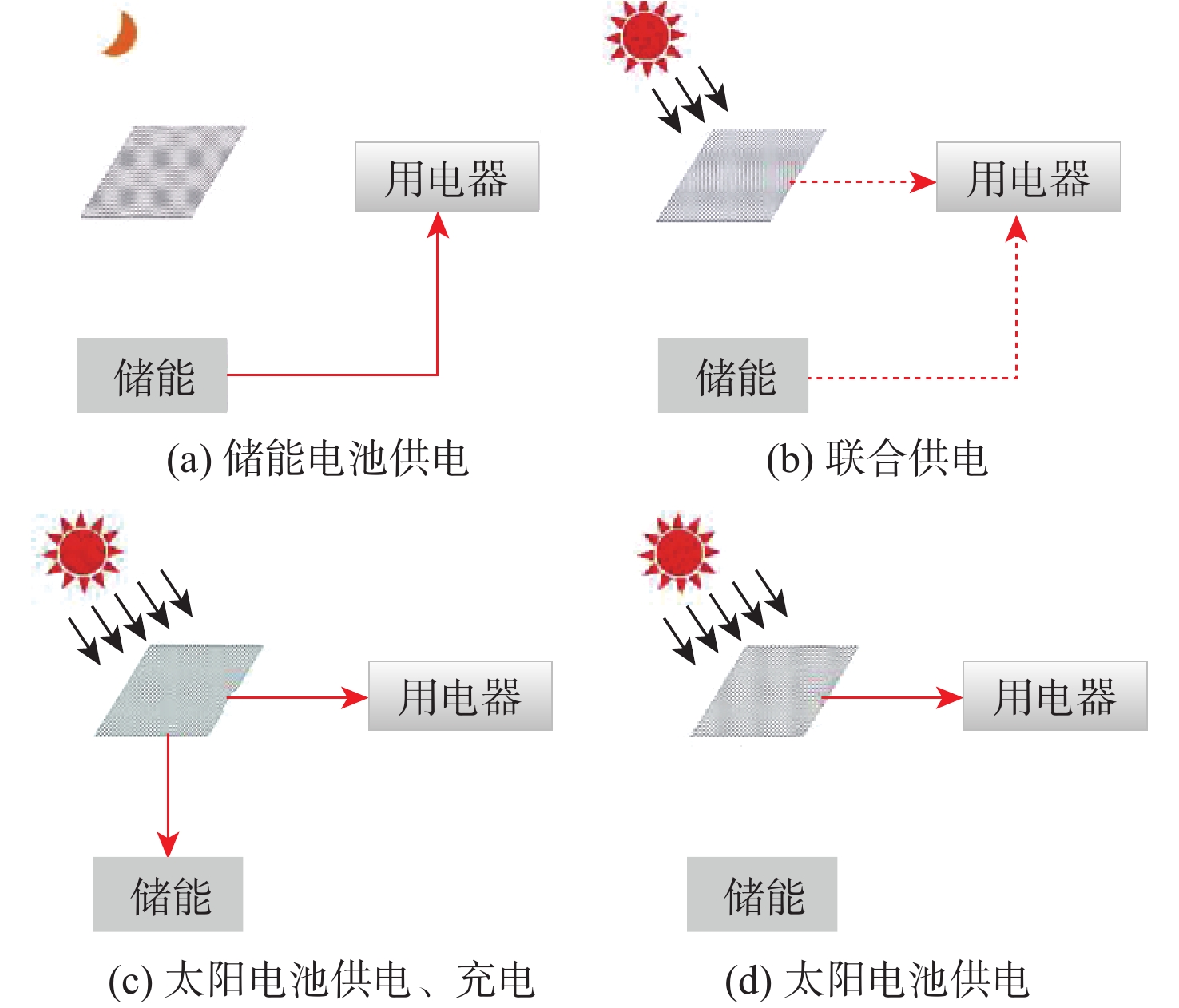
昼夜能量平衡是临近空间太阳能无人机(UAV)具备高空长航时飞行能力的重要前提之一,设计合理的巡航飞行剖面是实现该目标的关键。基于此,通过分析太阳能无人机在巡航飞行剖面中滑翔、爬升、日间平飞和夜间平飞等各阶段的能源供应模式,建立发电、储能、耗能和动力学的模型,重点讨论巡航飞行剖面各阶段工作特性对能源循环的影响。研究结果表明:滑翔和爬升策略对于储能电池的最低电量影响较小;提高日间巡航高度可增加储能电池最低电量,且日间巡航结束时间会影响储能电池最低电量;降低夜间巡航高度可大幅增加储能电池的最低电量。
Abstract:The diurnal energy balance is one of the most important factors for near-space solar-powered unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to perform high-altitude long-duration missions. To achieve this goal, the design of a reasonable cruise flight profile is significant. In this work, the energy supplying modes of stages in cruise flight profile, including gliding, climbing, daytime level flight and night level flight, were analyzed respectively. Then the models of power generation, energy storage, energy consumption and dynamics were established. The effects of each stage’s operational characteristics in the flight profile were then thoroughly examined. The findings demonstrated that the climbing and gliding tactics had no impact on the lowest battery energy. The end time of daytime level flight had an impact on the energy storage battery’s minimum power, and increasing the daytime cruise altitude may, to some extent, raise the battery’s minimum energy. The reducing of the night cruise altitude could greatly increase the minimum battery energy.
-
Key words:
- solar powered unmanned aerial vehicle /
- near space /
- flight profile /
- energy analysis /
- cruise flying
-
表 1 仿真分析使用的参数
Table 1. Parameters used in simulation analysis
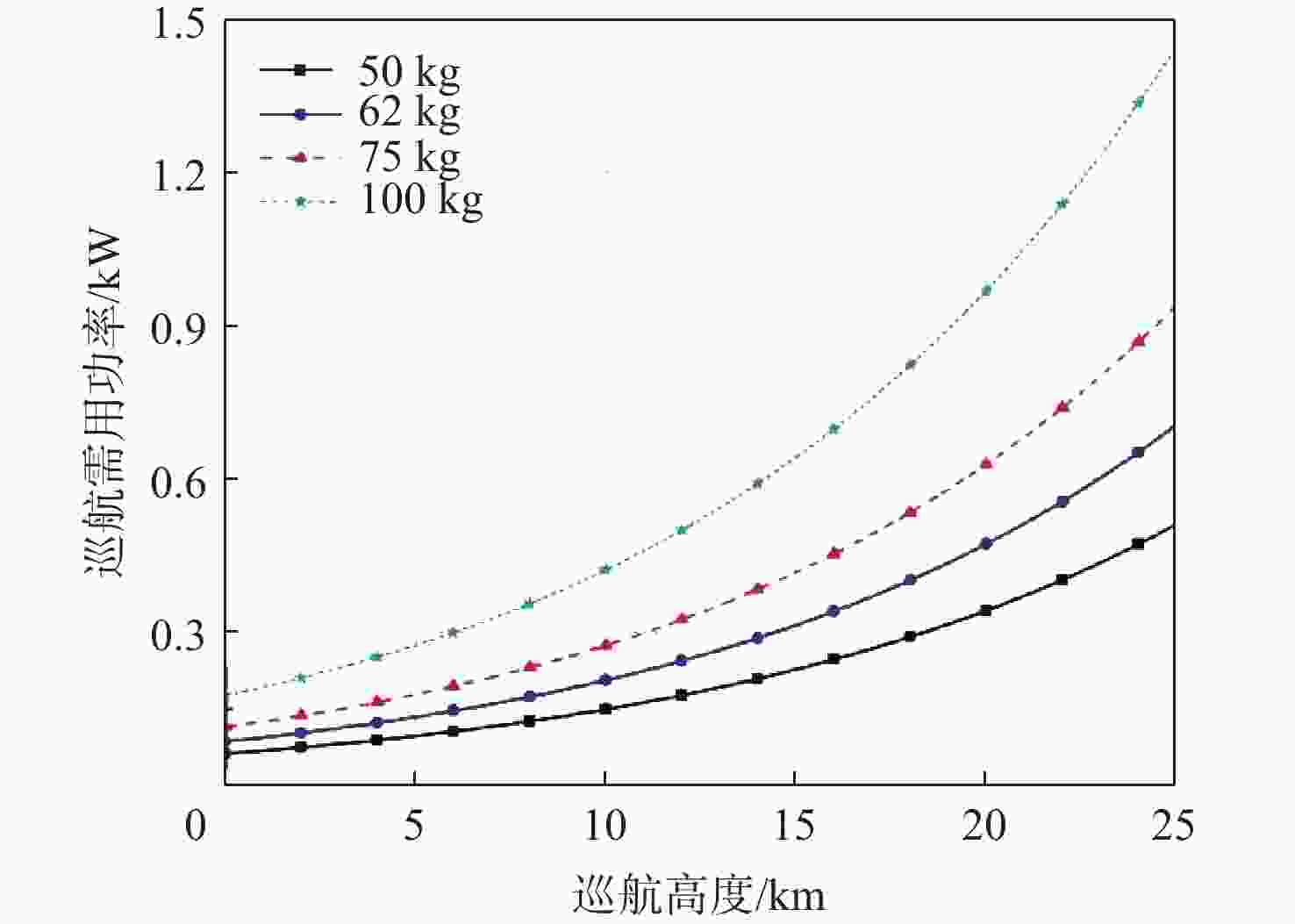
参数 数值 总质量/kg 62 载荷质量/kg 5 储能电池能量密度/(Wh·kg−1) 400 储能电池放电深度/% 90 翼展/m 25 太阳电池面积/m2 15 太阳电池比功率/(W·kg−1) 1000 太阳电池功率密度/(W·m−2) 250 航电与载荷功耗/W 50 日间巡航高度/m 21000 夜间巡航高度/m 16000 -
[1] 侯中喜, 高显忠, 郭正, 等. 太阳能飞机: 高空长航时飞行关键问题[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.HOU Z X, GAO X Z, GUO Z, et al. Solar-powered aircraft[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021(in Chinese). [2] XU Y M, ZHU W Y, LI J, et al. Improvement of endurance performance for high-altitude solar-powered airships: a review[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2020, 167: 245-259. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2019.11.021 [3] 李晨飞, 姜鲁华. 临近空间长航时太阳能无人机研究现状及关键技术[J]. 中国基础科学, 2018, 20(2): 22-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2018.02.004LI C F, JIANG L H. Research status and key technology of near space long endurance high altitude solar-powered unmanned air vehicle[J]. China Basic Science, 2018, 20(2): 22-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2018.02.004 [4] 赵炜, 赵钱, 黄江流, 等. 临近空间太阳能无人机在现代战争中的应用[J]. 空天防御, 2020, 3(2): 85-90.ZHAO W, ZHAO Q, HUANG J L, et al. Application of near space solar powered UAV in modern war[J]. Air & Space Defense, 2020, 3(2): 85-90(in Chinese). [5] 石文, 李广佳, 仪志胜, 等. 临近空间太阳能无人机应用现状与展望[J]. 空天技术, 2022(1): 83-90.SHI W, LI G J, YI Z S, et al. Current status and prospect of solar-powered unmanned aerial vehicle application in near space[J]. Aerospace Technology, 2022(1): 83-90(in Chinese). [6] 高显忠, 邓小龙, 王玉杰, 等. 临近空间太阳能飞机能量最优飞行航迹规划方法展望[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(8): 027265.GAO X Z, DENG X L, WANG Y J, et al. General planning method for energy optimal flight path of solar-powered aircraft in near space[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(8): 027265(in Chinese). [7] 马东立, 张良, 杨穆清, 等. 超长航时太阳能无人机关键技术综述[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(3): 623418. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23418MA D L, ZHANG L, YANG M Q, et al. Review of key technologies of ultra-long-endurance solar powered unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 623418(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23418 [8] GAO X Z, HOU Z X, GUO Z, et al. Reviews of methods to extract and store energy for solar-powered aircraft[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 44: 96-108. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.025 [9] GAO X Z, HOU Z X, GUO Z, et al. Research on characteristics of gravitational gliding for high-altitude solar-powered unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2013, 227(12): 1911-1923. doi: 10.1177/0954410012464838 [10] RONEY J A. Statistical wind analysis for near-space applications[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2007, 69(13): 1485-1501. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2007.05.005 [11] ARNE V, VEGA H, CHRISTIAN W, et al. Results from loads and aeroelastic analyses of a high altitude, long endurance, solar electric aircraft[J]. Journal of Aeroelasticity and Structural Dynamics, 2022, 9(1): 1-22. [12] 吴健发, 王宏伦, 黄宇. 大跨时空任务背景下的太阳能无人机任务规划技术研究进展[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(3): 623414.WU J F, WANG H L, HUANG Y. Research development of solar powered UAV mission planning technology in large-scale time and space spans[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 623414(in Chinese). [13] KLESH A T, KABAMBA P T. Solar-powered aircraft: energy-optimal path planning and perpetual endurance[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2009, 32(4): 1320-1329. doi: 10.2514/1.40139 [14] ZHU W Y, XU Y M, LI J, et al. Performance analysis of rotatable energy system of high-altitude airships in real wind field[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 98: 105689. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105689 [15] CRAIG L N, MARK D G, LISA L K, et al. High altitude long endurance UAV analysis of alternatives and technology requirements development[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 2007. [16] LEE J S, YU K H. Optimal path planning of solar-powered UAV using gravitational potential energy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1442-1451. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2671522 [17] 仲维国, 郭有光, 张凯. 太阳能飞机循环飞行的高度剖面能量策略[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(3): 623429.ZHONG W G, GUO Y G, ZHANG K. Energy strategy on altitude profile for cycle flight of solar powered aircraft[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 623429(in Chinese). [18] 张德虎, 张健, 李军府. 太阳能飞机能量平衡建模[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(增刊1): 16-23.ZHANG D H, ZHANG J, LI J F. Energy balance modeling for solar powered aircrafts[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(Sup 1): 16-23(in Chinese). [19] NI W J, WU D, MA X P. Energy-optimal flight strategy for solar-powered aircraft using reinforcement learning with discrete actions[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 95317-95334. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3095224 [20] 杨炳尉. 标准大气参数的公式表示[J]. 宇航学报, 1983, 4(1): 83-86.YANG B W. Formulization of standard atmospheric parameters[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 1983, 4(1): 83-86(in Chinese). [21] 杨宇丹, 朱炳杰, 郭正, 等. 太阳能无人机能源系统参数的敏度分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2020, 54(10): 1045-1052.YANG Y D, ZHU B J, GUO Z, et al. The sensitivity analysis of energy system parameters of solar powered unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2020, 54(10): 1045-1052(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: